* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biodiversity
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
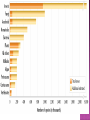
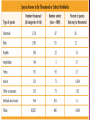
Section 1 Biodiversity short for “biological diversity” Refers to the number of different species in an area A lot of biodiversity means a lot of ecosystem stability! Why – should we study biodiversity The complex relationships are hard to study, but humans need to understand and preserve biodiversity for our own survival. Unknown Diversity – how many species are there on Earth? Known species = 1.7 million (mostly insects) Total species = 10 million (just an estimate) Unknown species exist in remote wilderness, deep in oceans, and even in cities. Levels of Biodiversity Species Diversity Ecosystem Diversity Number of different species in an area Most attention at this level Variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes Genetic Diversity All the different genes contained within all members of a population Biodiversity affects the stability of ecosystems and the sustainability of populations. Species are connected to ecosystems Every species is depended on or depends on at least one other species, in ways that are not always obvious. Keystone Species – species that are critical to the functioning of an ecosystem Species and Population Survival Genetic diversity increases the chance that some members of a population will survive environmental changes. Medical, Industrial, and Agricultural Uses People use a variety of organisms for food, clothing, shelter and medicine. ¼ of drugs are derived from plants Almost all antibiotics come from chemicals found in fungi. Ethics, Aesthetics, and Recreation Some people believe that we should preserve biodiversity for ethical reasons. Species and ecosystems have a right to exist whether or not they have any other value. Each organisms is a gift with a higher purpose. Ecotourism A form of tourism that supports the conservation and sustainable development ecologically unique areas. Region of Earth which is 1) extremely biologically diverse 2) under severe threat due to habitat loss, climate change, or extensive species loss. Section 2 Between 1800 and 2100, up to 25% of all species on Earth may have become extinct. Mass Extinction – the extinction of many species in a relatively short period of time. Species Prone to Extinction Species with small populations in small areas. Species that migrate, those that need large or special habitats, and those that are exploited by humans. Endangered Species – a species that is likely to become extinct if protective measures are not taken immediately. Threatened Species – a species with a declining population and that is likely to become endangered Habitat As populations grow, we use more land to build homes and harvest resources. Habitat loss causes almost 75% of the extinctions now occurring. Invasive Destruction and Fragmentation Exotic Species Exotic Species – not native to a particular region Exotic species can threaten native species that have no natural defenses against them Harvesting, Hunting, and Poaching Thousands of rare species worldwide are harvested and sold for use as pets, houseplants, wood, food, or herbal medicine. Many countries have laws to regulate hunting, fishing, harvesting and trade of wildlife. When these crimes continue illegally it is called poaching. Pollution Pesticides, cleaning agents, drugs, and other chemicals make their way into the food webs around the world. The long term effects of chemicals may not be clear until many years have passed. Endemic Species – species that are native to and found only within a limited area. Tropical Rain Forests Coral Reefs and Coastal Ecosystems Islands Section 3 Captive Breeding Programs Breeding species in captivity Preserving Genetic Material Store genetic material for future use in research or species-recovery efforts. Material may be stored as seeds, sperm, eggs, or DNA. Zoos, Aquariums, Parks and Gardens Conservation Strategies Priority to protecting entire ecosystems instead of individual species Identify areas of native habitats that can be preserved, restored, and linked into large networks. More Study Needed US laws 1973 – Endangered Species Act Recovery and Habitat Conservation Plans A plan that attempts to protect one or more species across large areas of land through tradeoffs or cooperative agreements. International Cooperation International Trade and Poaching The Biodiversity Treaty Preserve biodiversity and ensure the sustainable and fair use of genetic resources in all countries. Private Conservation Efforts World Wildlife Fund The Nature Conservancy Conservation Internation