* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download III. Conduct of the War: Battles and Strategy
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Aleutian Islands Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
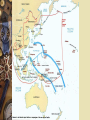
III. Conduct of the War: Battles and Strategy A. Germany and Britain 1. Following the invasion of Poland, Hitler launched a blitzkrieg, or lightning attack against France 2. By 1941 most of Europe and North Africa was under Nazi control 3. Hitler send his air force, the Luftwaffe, to Britain prior to an invasion 4. In the Battle of Britain, the Royal Air Force defeated the Luftwaffe and the invasion was postponed 5. Next, Hitler began bombing British cities but it too failed 6. Germany stopped bombing in May 1941 B. War at Sea 1. New technology determined how battles would be fought a. German submarines came close to controlling the Atlantic b. The Allies convoy system protected the ships c. In the Pacific, battleships and mainly the aircraft carrier was responsible for allied victory 2. Tanks played an increasingly important role in Russia and North Africa 3. Germany was first to use missiles (against Britain in 1945) 4. Allies perfected saturation bombing of German cities C. Germany and Russia 1. The Nazis invaded Russia in 1941 2. Millions of soldiers died on both sides in huge battles 3. Germany lost so many men in the advance came to a halt after Stalingrad 4. It was the turning point for the Nazi on the Eastern Front D. Normandy Landings (D-Day) D-Day Memorial -Why Bedford? Lost 19 men that day - the largest per capita loss of any town in America on that day 29th Infantry Division 116th Infantry Regiment Co A Bedford Co B Lynchburg Co C Harrisonburg Co D Roanoke HQ Co 2nd Battalion Alta Vista Co E Chase City Co F South Boston Co G Farmville Co H Martinsville 1. American and Allied troops under General Eisenhower landed in German-occupied France on June 6, 1944 2. Despite intense German opposition and heavy American casualties, the landing succeeded and liberation of western Europe began E. War in the Pacific War Comes to America 1. Japanese war planes from aircraft carriers attacked the US Fleet in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii on December 7, 1941 2. The attack destroyed much of the American fleet and killed several thousand Americans 3. FDR immediately asked for a declaration of war calling December 7 "a date that will live in infamy." 4. US strategy called for an "island hopping" campaign, seizing islands closer and closer to Japan and using them as bases for further attacks 5. US used submarine warfare against Japanese shipping to cut off her supplies F. Significant Battles in the Pacific 1. Midway Island a. American forces defeated a much larger Japanese force as it attempted to seize Midway Island b. A Japanese victory would have allowed Japan to invade Hawaii c. American victory ended the Japanese threat of invasion d. Midway was the turning point of the war in the Pacific 2. Iwo Jima and Okinawa a. American invasion brought American forces closer to Japan b. Bloody battles in which many on both sides died c. Many Japanese soldiers and civilians committed suicide rather than surrender 3. Hiroshima and Nagasaki a. President Truman ordered the use of the Atomic bomb on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki b. Done in order to save thousands of American lives in a full-scale invasion of Japan's main islands c. Tens of thousands were killed in the cities d. Japanese leaders soon surrenders and accepted an unconditional surrender IV. Domestic Effects of the War War’s Affect on America A. World War II ushered in social changes and established reform agendas that would effect the country through the 20th century 1. Women a. Women entered into previously male job roles b. Worked in industry as well as traditional roles: clerks, etc. c. Jobs in the military were noncombat jobs 2. African Americans a. Struggled to obtain desegregation of the armed forces and end discriminatory hiring practices b. In the military, they generally served in segregated units and assigned to non-combat roles c. Demanded the right to served in combat rather than support roles (Tuskegee Airmen served in Europe with distinction) Native Americans – Code Talkers V. The Holocaust A. Called by the Nazis the "Final Solution" 1. Specific groups were often the object of hatred and prejudices 2. Faced increased risk of discrimination during wartime Germany B. The Affected Groups 1. Jews 2. Poles (from Poland) 3. Slavs 4. Gypsies 5. "Undesirables" (homosexuals, mentally ill, political dissidents) C. Significance of the Holocaust 1. Nazi leaders were convicted of war crimes in the Nuremberg trials 2. the Nuremberg trials emphasized individual responsibility 3. the trials led to increased demand for a Jewish homeland VI. Geneva Convention and POWs The Geneva Convention attempted to ensure the humane treatment of prisoners of war by establishing rules to be followed by all nations. The treatment of prisoners of war in the Pacific Theater often reflected the savagery of the fighting there. In the Bataan Death March, American POWs suffered brutal treatment by the Japanese after surrender of the Philippines. The treatment of prisoners of war in Europe more closely followed the ideas of the Geneva Convention