* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Golden Age of Athens
Survey
Document related concepts
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek architecture wikipedia , lookup
Thebes, Greece wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Acropolis of Athens wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
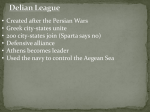
Ancient Greece: Democracy and Greece’s Golden Age World History Core Cultural Interaction Democratic principles and classical culture flourished during Greece’s golden age. Why is it important today?!?!? At its height, Greece set lasting standards in art, politics, literature, and philosophy that are still influential today. Setting the Stage……. For 50 years (477-431 BC) Athens grew intellectually and artistically = Golden Age of Athens Achievements in: Drama Sculpture & Architecture Poetry Philosophy Science Math Pericles’ Plan for Athens leader of Athens through Golden Age 461-429 BC, aka “Age of Pericles” 3 GOALS (1) strengthen democracy (2) hold and strengthen empire (3) glorify Athens GOAL 1: Strengthen Democracy Increased # of paid public officials Having paid officials meant even poor could serve if elected or chosen by lot Direct Democracy: form of government in which citizens rule directly and not through representatives Important Question?????? How accurate do you think Pericles’ statement that Athenian democracy was in the hands of the “whole people”? Goal 2: Hold and Strengthen Empire Delian League– Athens dominated all city-states in it Used $$$ from League to build up Athenian Navy Athens needed trade (waterways) to obtain grain and raw materials to support the city-state Athens military strength= Pericles treated members of league as part of an empire Peloponnesus city-states resisted (Ex. Sparta) Goal 3: Glorify Athens Used $$$ from League to undergo massive building projects to make Athens beautiful Convinced Assembly to buy gold, ivory, and marble with funds More $$$ was also needed to contract artists, architects, and workers Glorious Art and Architecture Goal: Greatest Greek artists/architects to glorify Athens PARTHENON = center of his plans Architecture and Sculpture: Parthenon Parthenon (temple) 23,000 sq foot building in traditional Greek design Built to honor Athena (Goddess of wisdom and protector of Athens) Statue of Athena inside 32 ft tall Drama and History Greeks invented drama as an art form and built the 1st theaters Civic Pride and Honor to Gods Wealthy put on productions Plays showed leadership, justice, and duties owed to Gods http://www.thehistoryhub.com/theatre-of-dionysus-facts-pictures.htm Tragedy Serious drama about love, hate, war, and/or betrayal Tragic hero: important figure and gifted with extraordinary ability Tragic flaw: hero’s downfall (often pride) Sophocles: wrote over 100 plays, Oedipus the King, 18 first prizes, 7 survived Aeschylus- won 13 first prizes, 7 plays have survived Comedy Scenes with slapstick comedy and crude humor Made fun of politics and respected people Satire: The use of humor, irony, exageration, or ridicule to expose and criticize peoples stupidity Aristophanes: Lysistrata in which women of Athens try to force their husbands to end the Peloponnesian War History Recap: Dorian Age, no written records…had works of Homer, but not considered accurate Herodotus: a Greek, living in Athens, pioneered accurate reporting Book on Persian War = 1st history book Thucydides: believed certain events and political situations recur over time = important to write events down Important Question????? Do you think that Thucydides was right in his assertion that history sometimes repeats itself??? YES OR NO….. Athenians and Spartans Go to WAR!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Athens = power, prestige, and power = other city-states hostility SPARTA!!! Sparta declared war in 431 BC Important Question????? What might have been Pericles’ goals in the Peloponnesian War? Peloponnesian War Athens = Navy Sparta = Army Pericles’ Strategy: avoid land battles and wait for a sea opportunity Sparta marched into Athens territory Pericles had no other choice but to bring people into city walls City safe from hunger as long as ships could come into ports 2nd year of war PLAGUE outbreak in Athens, killing 1/3rd of population and PERICLES!!! Athens still continued to fight for several years 421 BC signed a truce (worn out by war) Sparta Gains VICTORY! Peace did not last, 415 BC Athens sent fleet to Syracuse (Sicily) to destroy them, one of the greatest allies of Sparta Ended in crushing defeat in 413 BC Athens, weak and few, continued to fight for nine more years 404 BC Athenians surrendered Lost empire, power, and wealth Philosophers Search for TRUTH! After war = time of doubt and uncertainty = rise of great thinkers Determined to seek truth… Complete the reading for the Persian and Peloponnesian Wars and then answer the questions that follow. Philosophers = “lovers of wisdom” Based philosophy on 2 assumptions: (1) The universe is put together in an orderly way, subject to absolute and unchanging laws (2) Understand laws through logic and wisdom Socrates Absolute standards did exist for truth and justice Question yourself and moral character “The unexamined life is not worth living” 399 BC, age 60, trial for “corrupting youth of Athens” and “neglecting the city’s Gods” His defense: teachings good for Athens, because forced people to think about their actions and values Condemned to death, drinking hemlock Socratic Method Form of cooperative argumentative dialogue between individuals, based on asking and answering questions to stimulate critical thinking and to draw out ideas and underlying presumptions. Plato Student of Socrates 370 BC wrote The Republic, set forth vision of a perfectly governed society Not democracy All citizens fall naturally into 3 groups (1) farmers and artisans (2) warriors (3) ruling class Person with greatest insight and intellect from ruling class would be chosen as philosopher-king Aristotle Student of Plato Questioned nature of world and of human belief, thought, and knowledge Invented method of arguing according to rules of logic Invented basis of scientific method used today Famous pupil Alexander the Great (more information to follow….) Alexander the Great Socrates Raphael Plato Aristotle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0F5qlu3n SDY Science Archimedes Archimedes screw War Machines (mainly used to defend his home city-state Syracuse) Science Hippocrates Father of medicine Did not condone use of leeching (encouraged exercise) Doctors and nurses have to take Hippocratic oath (will not purposefully hurt patients, will do their best to help) Math Euclid Father of Geometry Pythagoras Pythagorean Theorem- states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.