* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 16 Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
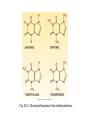
Central Nervous System Stimulants and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder CNS Stimulants Increase the activity of CNS neurons Enhance neuronal excitation; a few suppress neuronal inhibition In sufficient doses, all can cause convulsions Limited clinical applications CNS Stimulants and AttentionDeficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Amphetamines Methylphenidate and dexmethylphenidate Methylxanthines Miscellaneous stimulants Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) Amphetamines Chemistry Dextroamphetamine and levamphetamine Amphetamine Lisdexamfetamine Methamphetamine Mechanism of action Release norepinephrine (NE) Release dopamine (DA) Amphetamines Pharmacologic effects Tolerance With regular use, develops to elevation of mood, suppression of appetite, and stimulation of the heart and blood vessels Physical dependence Central nervous system Cardiovascular system Abstinence syndrome with abrupt withdrawal Abuse High potential for abuse due to euphoria Fig. 36–1. Structural formulas of the amphetamines. Amphetamines Adverse effects CNS stimulation Weight loss Cardiovascular effects Psychosis Amphetamines Toxicity Dysrhythmias Hypertension Dizziness Confusion Hallucinations Convulsions Paranoid delusions Coma Palpitations Cerebral hemorrhage Amphetamines Treatment Chlorpromazine: hallucinations Alpha-adrenergic blocker: hypertension Diazepam: seizures Therapeutic uses ADHD Narcolepsy Amphetamines Preparations, dosage, and administration Dextroamphetamine sulfate Amphetamine/dextroamphetamine mixture Short duration (Dexedrine, Dextrostat) Long duration (Dexedrine Spansules) Short duration (Adderall) Long duration (Adderall-XR) Methamphetamine (Desoxyn) Methylphenidate and Dexmethylphenidate Methylphenidate and dexmethylphenidate are nearly identical in structure and pharmacologic actions The pharmacology of both drugs is nearly identical to that of amphetamines Methylphenidate ADHD and narcolepsy Trade names Ritalin, Metadate, Methylin, Concerta, Daytrana 50:50 mixture of dextro and levo isomers Preparations, dosage, and administration Short duration • Ritalin, Methylin Intermediate duration • Ritalin SR, Metadate ER, Methylin ER Long duration • Concerta, Metadate CD, Ritalin LA Dexmethylphenidate (Focalin) Drug for ADHD Dextro isomer of methylphenidate 50:50 mixture of dextro and levo isomers Schedule II drug Methylxanthines Derivatives of xanthine Caffeine • Few clinical applications • Widespread ingestion for nonmedical purposes Dietary sources • Chocolate • Desserts • Soft drinks • Cola nut Methylxanthines Mechanism of action Low doses Decrease drowsiness and fatigue and increase capacity for prolonged intellectual exertion Increasing doses Reversible blockade of adenosine receptors Calcium permeability Accumulation of cyclic AMP Nervousness, insomnia, tremors Seizures with very large amounts AMP = adenosine monophosphate. Fig. 36–2. Structural formulas of the methylxanthines. Methylxanthines Pharmacologic effects Central nervous system Heart Blood vessels Bronchi Kidney Reproduction Pharmacokinetics Readily absorbed from the GI tract Achieve peak plasma levels within 1 hour Eliminated by hepatic metabolism Methylxanthines Therapeutic uses Neonatal apnea Promoting wakefulness Other applications Acute toxicity Stimulation of the CNS Tachycardia Respiratory stimulation Sensory phenomena Methylxanthines Preparations, dosage, and administration For promoting wakefulness For neonatal apnea Theophylline Theobromine Miscellaneous CNS Stimulants Pemoline Actions, uses, and adverse effects • Causes less cardiac stimulation and vasoconstriction • Can cause liver failure Preparations, dosage, and administration Miscellaneous CNS Stimulants Modafinil (Provigil, Alertec) Therapeutic use • Promotes wakefulness Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics • Rapidly absorbed in the GI tract • Elimination by hepatic metabolism • Half-life: about 15 hours Miscellaneous CNS Stimulants Modafinil (Provigil, Alertec) (cont’d) Adverse effects • Headache • Nausea • Nervousness • Diarrhea • Rhinitis Drug interactions • Oral contraceptives • Cyclosporine Miscellaneous CNS Stimulants Modafinil (Provigil, Alertec) (cont’d) Preparations, dosage, and administration Blockade Strychnine: not used as a medicine Poisoning • Causes: accidental ingestion, street drugs • Symptoms: convulsions, depression • Treatment: intravenous diazepam, general anesthesia, or neuromuscular blocker Armodafinil Doxapram Cocaine Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Children Signs and symptoms Inattention Hyperactivity Impulsivity Fidgety Unable to concentrate ADHD in Children Signs and symptoms (cont’d) Unable to wait his or her turn Switches excessively from one activity to another Calls out excessively in class Present before age 7 years Present for at least 6 months ADHD in Children Etiology Management overview Cognitive therapy Stimulant drugs Drug therapy I: CNS stimulants Methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta, others) Dexmethylphenidate (Focalin) Dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine, others) Amphetamine mixture (Adderall) Pemoline (Cylert) ADHD in Children Drug therapy II: atomoxetine Description and therapeutic effects • Nonstimulant • No potential for abuse • Administered once a day ADHD in Children Drug therapy II: atomoxetine (cont’d) Mechanism of action • Selective inhibitor of NE reuptake Pharmacokinetics • Plasma levels peak in 1–3 hours • Metabolized in the liver ADHD in Children Drug therapy II: atomoxetine (cont’d) Adverse effects • GI reactions • Reduced appetite • Dizziness • Somnolence • Mood swings • Trouble sleeping ADHD in Children Drug therapy II: atomoxetine (cont’d) Drug interactions • MAO inhibitors (isocarboxazid, phenelzine) • CYP2D6 (paroxetine, fluoxetine, quinidine) Role in ADHD therapy Preparations, dosage, and administration • Children who weigh less than 70 kg • Children who weigh 70 kg or more ADHD in Children Drug therapy III: antidepressants Tricyclic antidepressants • Decrease hyperactivity • Little effect on impulsivity and inattention • Second-line drugs Bupropion (Wellbutrin) • Can reduce behavioral symptoms • Less effective than stimulants • Poses risk of seizure • Second-line drug ADHD in Adults Drug therapy III: antidepressants 60% of ADHD cases persist into adulthood Symptoms • Poor concentration • Stress intolerance • Antisocial behavior • Outbursts of anger • Inability to maintain a routine Drug therapy • Methylphenidate Drugs Used for ADHD Drug therapy Methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) Dexmethylphenidate (Focalin) Dextroamphetamine (DextroStat) Amphetamine mixture (Adderall) Nonstimulants Atomoxetine (Strattera) Guanfacine (Intuniv) Clonidine (Kapvay)