* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.2.6. Transmission of Diseases
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Brugia malayi wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Mass drug administration wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
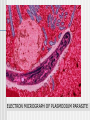
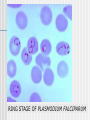
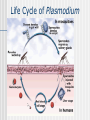
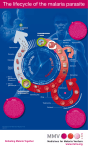
2.2.6. Transmission of Diseases Learning Outcome: Describe the causes and means of transmission of malaria, HIV/AIDS and TB Methods of Disease Transmission Droplets – coughing & sneezing Faecal/Oral – usually from food & drink Direct physical contact – touching, kissing, sexual intercourse Indirect contact – touching a contaminated object Vector transmission – by an insect or other creature Malaria - parasite Caused by a protozoan parasite of the genus Plasmodium Mainly P. falciparum but other species include P. vivax, P. ovale and P. malariae P. knowlesi can cross the species barrier from monkeys to humans The parasite lives in subtropical areas of Africa, Asia and the Americas ELECTRON MICROGRAPH OF PLASMODIUM PARASITE RING STAGE OF PLASMODIUM FALCIPARUM Spread of Malaria Mainly transmitted via the vector method The female Anopheles mosquito feeds nocturnally on blood It transfers the sporozoite phase of the parasite from its salivary glands to the host (mosquito saliva acts as an anticoagulant) If the host already has malaria the mosquito sucks up the gamete stage of the parasite Zygotes develop in the mosquito Life Cycle of Plasmodium Other means of malarial transmission It is also possible to spread the parasite via unhygienic conditions mainly in a hospital environment Unsterilised needles and unscreened blood transfusions also play a part The parasite can also pass across the placenta from mother to foetus HIV/AIDS cause Human Immunodeficiency Virus The virus can sit dormant for many years (HIV Positive stage) Once active it destroys T helper cells rendering the immune system ineffective Then the person has Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome Death usually soon follows due to secondary infections HIV Transmission Rectal, vaginal or oral sex Intravenous drug use – reusing syringes Blood transfusions from unscreened donors In Utero / Perinatal from mother to foetus Breast feeding can also spread the virus Tuberculosis - Cause Causative agent is a rod-shaped bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis or M. bovis are the main species There are many other species that can cause symptoms Over 2 billion people are infected with TB worldwide Mostly the body’s immune system is able to keep the disease at bay Tuberculosis - Transmission Transmitted by the droplet method Needs prolonged contact with a carrier or sufferer to become infected Infected meat or milk of cattle Conditions of deprivation makes infection more likely Overcrowding Poor health or diet Inadequate ventilation