* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download introduction
Artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Operations research wikipedia , lookup
Computational fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Knapsack problem wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Predictive analytics wikipedia , lookup
Financial economics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical physics wikipedia , lookup
History of numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Generalized linear model wikipedia , lookup
Computer simulation wikipedia , lookup
Natural computing wikipedia , lookup
Lateral computing wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Computational complexity theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical computer science wikipedia , lookup
Multiple-criteria decision analysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical economics wikipedia , lookup
Inverse problem wikipedia , lookup
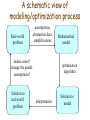
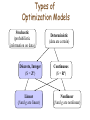
Math443/543 Mathematical Modeling and Optimization A schematic view of modeling/optimization process Real-world problem assumptions, abstraction,data, simplifications makes sense? change the model, assumptions? Solution to real-world problem Mathematical model optimization algorithm interpretation Solution to model What is a model? • Model: A schematic description of a system, theory, or phenomenon that accounts for its known or inferred properties and maybe used for further study of its characteristics. • Mathematical models – are abstract models – describe the mathematical relationships among elements in a system • In this class, mathematical models dealing with discrete optimization Mathematical models in Optimization • The general form of an optimization model: min or max f(x1,…,xn) (objective function) subject to gi(x1,…,xn) ≥ 0 (functional constraints) x1,…,xn S (set constraints) • x1,…,xn are called decision variables • In words, the goal is to find x1,…,xn that – satisfy the constraints; – achieve min (max) objective function value. Types of Optimization Models Stochastic (probabilistic information on data) Discrete, Integer (S = Zn) Linear (f and g are linear) Deterministic (data are certain) Continuous (S = Rn) Nonlinear (f and g are nonlinear) What is Discrete Optimization? Discrete Optimization is a field of applied mathematics, combining techniques from • combinatorics and graph theory, • linear programming, • theory of algorithms, to solve optimization problems over discrete structures. Examples of Discrete Optimization Models: Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) There are n cities. The salesman starts his tour from City 1, visits each of the cities exactly once, and returns to City 1. For each pair of cities i,j there is a cost cij associated with traveling from City i to City j . Goal: Find a minimum-cost tour. Examples of Discrete Optimization Models: Job Scheduling There are 4 jobs that should be processed on the same machine. (Can’t be processed simultaneously). Job k has processing time pk . Here is an example of a possible schedule: Job 3 0 Job 1 2 Job 4 6 Job 2 9 Goal: Find a schedule which minimizes the average completion time of the jobs. 14 time Examples of Discrete Optimization Models: Shortest Path Problem In a network, we have distances on arcs ; source node s and sink node t . 3 a 1 1 1 2 s d 4 7 c 2 t 2 1 b 4 5 2 e Goal: Find a shortest path from the source to the sink. Problems that can be modeled and solved by discrete optimization techniques • • • • • Scheduling Problems (production, airline, etc.) Network Design Problems Facility Location Problems Inventory management Transportation Problems Problems that can be modeled and solved by discrete optimization techniques • • • • • Minimum spanning tree problem Shortest path problem Maximum flow problem Min-cost flow problem Assignment Problem Solution Methods for Discrete Optimization Problems • • • • Integer Programming Network Algorithms Dynamic Programming Approximation Algorithms