Large–Scale Tikhonov Regularization for Total Least
... a linear model is error free, and all errors are confined to the right hand side b. However, in engineering applications this assumption is often unrealistic. Many problems in data estimation are obtained by linear systems where both, the matrix A and the right-hand side b, are contaminated by noise ...
... a linear model is error free, and all errors are confined to the right hand side b. However, in engineering applications this assumption is often unrealistic. Many problems in data estimation are obtained by linear systems where both, the matrix A and the right-hand side b, are contaminated by noise ...
Bridge Mathematics SPI`s
... were less important. Although we must teach them all we realize that some do not require the time and effort that the others do. I will indicate the less important ones by putting them at the end of the section and will mark them “not as important”. Number Sense and Operation 3181.1.5.1 Understand ...
... were less important. Although we must teach them all we realize that some do not require the time and effort that the others do. I will indicate the less important ones by putting them at the end of the section and will mark them “not as important”. Number Sense and Operation 3181.1.5.1 Understand ...
Enforcement in Abstract Argumentation via Boolean Optimization
... are used as practical NP-oracles by calling them several times, refining the solution each time [32, 33, 56]. The computational problems where we perform acceptance queries on a given AF are in this work regarded as static, or non-dynamic, since we assume that the AF does not change in time. However ...
... are used as practical NP-oracles by calling them several times, refining the solution each time [32, 33, 56]. The computational problems where we perform acceptance queries on a given AF are in this work regarded as static, or non-dynamic, since we assume that the AF does not change in time. However ...
Regularization Tools
... problems in details, for displaying these properties, and for easy generation of simple test problems. By means of the routines in Regularization Tools, the user can— at least for small to medium-size problems—experiment with different regularization strategies, compare them, and draw conclusions fr ...
... problems in details, for displaying these properties, and for easy generation of simple test problems. By means of the routines in Regularization Tools, the user can— at least for small to medium-size problems—experiment with different regularization strategies, compare them, and draw conclusions fr ...
Appendix - UBC Math
... where S ≥ 0 is the rate of studying and f ≥ 0 is the rate of forgetting. We will assume that S and f are constants that are different for each person. [Your answers to the following questions will contain constants such as S or f .] (a) Mary never forgets anything. What does this imply about the con ...
... where S ≥ 0 is the rate of studying and f ≥ 0 is the rate of forgetting. We will assume that S and f are constants that are different for each person. [Your answers to the following questions will contain constants such as S or f .] (a) Mary never forgets anything. What does this imply about the con ...
Optimizing Network Resource Sharing in Grids
... scaling, that b = 1. We claim that the solution of the linear program (3) can be computed in polynomial time. Indeed, the constraints (1) and (1) now write AX 6 C, where: • A is a matrix of size (N + M ) × K. There are N rows for the ingress points, followed by M rows for the egress points. There is ...
... scaling, that b = 1. We claim that the solution of the linear program (3) can be computed in polynomial time. Indeed, the constraints (1) and (1) now write AX 6 C, where: • A is a matrix of size (N + M ) × K. There are N rows for the ingress points, followed by M rows for the egress points. There is ...
Informed RRT*: Optimal Sampling-based Path Planning Focused via
... the current solution path. This assumes that the current solution is either homotopic to the optimum or separated only by small obstacles. As this assumption is not generally true, path-biasing algorithms must also continue to sample globally to avoid local optima. The ratio of these two sampling me ...
... the current solution path. This assumes that the current solution is either homotopic to the optimum or separated only by small obstacles. As this assumption is not generally true, path-biasing algorithms must also continue to sample globally to avoid local optima. The ratio of these two sampling me ...
Vydatná motivace jako predkrm, porádná porce Gödelových vet a
... I Natural language and natural reasoning scenarios cognitive science, psychology, linguistics, and philosophy Aim: to understand valid reasoning in natural reasoning scenarios and their transformations into formal one II Formal interpreted languages and artificial reasoning scenarios mathematics and ...
... I Natural language and natural reasoning scenarios cognitive science, psychology, linguistics, and philosophy Aim: to understand valid reasoning in natural reasoning scenarios and their transformations into formal one II Formal interpreted languages and artificial reasoning scenarios mathematics and ...
Assigning agents to a line
... must be allocated to positions with limited capacities, and propose an algorithm for it based on market-clearing prices, which also guarantees that assignments are envy-free, i.e., no agent would prefer the assignment of some other agent. Their algorithm, however, is not strategyproof, i.e., it does ...
... must be allocated to positions with limited capacities, and propose an algorithm for it based on market-clearing prices, which also guarantees that assignments are envy-free, i.e., no agent would prefer the assignment of some other agent. Their algorithm, however, is not strategyproof, i.e., it does ...
Computing the Greatest Common Divisor of - CECM
... in the size of coefficients when using naive methods to solve linear equations over F[x1 , . . . , xn ]. Using homomorphisms to map the GCD problem to a simpler domain can improve arithmetic calculation and lead to better approaches to avoid the problems with coefficient growth. In [1], Brown develo ...
... in the size of coefficients when using naive methods to solve linear equations over F[x1 , . . . , xn ]. Using homomorphisms to map the GCD problem to a simpler domain can improve arithmetic calculation and lead to better approaches to avoid the problems with coefficient growth. In [1], Brown develo ...
q ~r
... By the end of this unit, you should be able to: – Explore the consequences of a set of propositional logic statements by application of equivalence and inference rules, especially in order to massage statements into a desired form. – Critique a propositional logic proof; that is, determine whether o ...
... By the end of this unit, you should be able to: – Explore the consequences of a set of propositional logic statements by application of equivalence and inference rules, especially in order to massage statements into a desired form. – Critique a propositional logic proof; that is, determine whether o ...
q ~r
... By the end of this unit, you should be able to: – Explore the consequences of a set of propositional logic statements by application of equivalence and inference rules, especially in order to massage statements into a desired form. – Critique a propositional logic proof; that is, determine whether o ...
... By the end of this unit, you should be able to: – Explore the consequences of a set of propositional logic statements by application of equivalence and inference rules, especially in order to massage statements into a desired form. – Critique a propositional logic proof; that is, determine whether o ...
Martingale problem approach to Markov processes
... Markov chains and Markov processes have played a very important role in applications of probability theory to real world problems. The early development of probability theory focused on experiments that could be repeated large number of times leading to the law of large numbers and central limit the ...
... Markov chains and Markov processes have played a very important role in applications of probability theory to real world problems. The early development of probability theory focused on experiments that could be repeated large number of times leading to the law of large numbers and central limit the ...
The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A
... WWW.C E M C .U WAT E R LO O.C A | T h e C E N T R E fo r E D U C AT I O N i n M AT H E M AT I C S a n d CO M P U T I N G ...
... WWW.C E M C .U WAT E R LO O.C A | T h e C E N T R E fo r E D U C AT I O N i n M AT H E M AT I C S a n d CO M P U T I N G ...
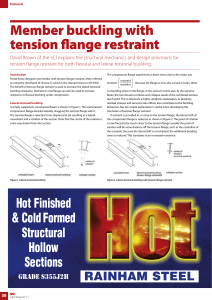
Member buckling with tension flange restraint
... fibres, the two stresses combine and collapse results if the combined stresses reach yield. This is obviously a highly simplistic explanation, as plasticity, residual stresses and second-order effects also contribute to the buckling behaviour, but the simple explanation is useful when developing the ...
... fibres, the two stresses combine and collapse results if the combined stresses reach yield. This is obviously a highly simplistic explanation, as plasticity, residual stresses and second-order effects also contribute to the buckling behaviour, but the simple explanation is useful when developing the ...
SOME FEATURES OF α-T0 SPACES IN SUPRA FUZZY TOPOLOGY
... Definition: Let (X, t) and (X, s) be two topological spaces. Let t* and s* are associated supra topologies with t and s. respectively and f : (X, t*) (Y, s*) be a function. Then the function f is a supra fuzzy continuous if the inverse image of each i.e., if for any v s*, f-1 (v) t*. The funct ...
... Definition: Let (X, t) and (X, s) be two topological spaces. Let t* and s* are associated supra topologies with t and s. respectively and f : (X, t*) (Y, s*) be a function. Then the function f is a supra fuzzy continuous if the inverse image of each i.e., if for any v s*, f-1 (v) t*. The funct ...
- Wiley Online Library
... interpolation [12, 21, 22] or piecewise linear basis functions [14, 23]. In the context of solution of differential equations with random inputs, in addition to approximating the unknown stochastic solution, we are also interested in computing its moments, e.g. mean and variance. These moments are d ...
... interpolation [12, 21, 22] or piecewise linear basis functions [14, 23]. In the context of solution of differential equations with random inputs, in addition to approximating the unknown stochastic solution, we are also interested in computing its moments, e.g. mean and variance. These moments are d ...
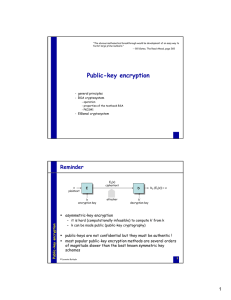
Public-key encryption
... Implementing RSA – Fermat-test Fermat theorem: if p prime and gcd(b, p) = 1, then bp-1 ≡ 1 (mod p) a composite number n is pseudo-prime for a base b if bn-1 ≡ 1 (mod n) where 1 < b < n and gcd(b, n) = 1 Public-key encryption / RSA ...
... Implementing RSA – Fermat-test Fermat theorem: if p prime and gcd(b, p) = 1, then bp-1 ≡ 1 (mod p) a composite number n is pseudo-prime for a base b if bn-1 ≡ 1 (mod n) where 1 < b < n and gcd(b, n) = 1 Public-key encryption / RSA ...
Coping with friction for non-penetrating rigid body simulation
... the units of mass times acceleration and cannot produce velocity discontinuities.) The first result of this paper is a proof that computing friction forces according to the principle of constraints is likely to require exponential time (section 5). Under the Coulomb friction model, even in the absen ...
... the units of mass times acceleration and cannot produce velocity discontinuities.) The first result of this paper is a proof that computing friction forces according to the principle of constraints is likely to require exponential time (section 5). Under the Coulomb friction model, even in the absen ...