* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy - Earth Systems A
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
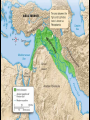
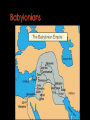
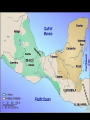
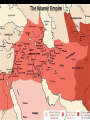
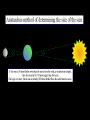
The study of celestial objects that originate outside of the Earth’s atmosphere Astronomy is the oldest of the sciences The belief that the position of the Sun and the Stars affect your life Studied the skies for: Navigation Telling time Planting and harvesting crops Making Calendars Worshiping their gods Built observatories called ziggurats Named brighter stars and planets Tracked the movement of planets Kept records of star and planet movement Aligned their pyramids with the Sun and stars Kept records of eclipses, comets, meteor showers and supernova explosions Mayans and Aztecs Made calendars that included the Moon, the Sun, the stars and Venus First astronomical instrument: Astrolabe http://theflatearthsociety.org/cms/ Earth is a cylinder floating in space and the Sun, Moon, stars and planets are wheels filled with fire Earth is a sphere: NOT FLAT Earth is the center of the solar system Tried to prove that the Earth is a sphere Earth is the center and is too big to move Calculated the size of the Sun and the Moon The Sun is the center of the solar system; NOT EARTH Used geometry to calculate the circumference of the Earth Made maps: north, south, east and west Also Latitude and longitude Made the first Sun-centered model of the solar system The laws of planetary motion Planet’s orbits are elliptical, not circular Invented the first telescope Discovered moons around Jupiter and the Saturn's rings Mapped the moon Law of universal gravity and laws of motion explained how planets orbit Discovered Uranus Spent his life improving telescopes Theory of relativity E = mc² Space and time curve in the presence of matter Discovered evidence to help prove that the universe is expanding Red shift data Catholic priest and physics professor Proposed the Big Bang Theory





































![Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007097773_1-15996a23762c2249db404131f50612f3-150x150.png)