* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AUGUSTUS and His Successors
Survey
Document related concepts
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
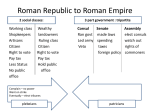
AUGUSTUS and His Successors Augustus, the first emperor of Rome, was a capable leader who did much to benefit Rome. However all of his immediate successors were not the greatest leaders. They included some of the most infamous and notorious leaders of all time. Tiberius 14 AD - 37 AD Caligula 37 AD - 41 AD Caudius 41 AD - 54 AD Nero 54- 68 AD After Nero’s death Rome would eventually come under the rule of some great emperors. Known as the “Good emperors” They included : Nerva Trajan Hadrian Antoninus Pius Marcus Aurelius All these rulers though would be part of Rome’s greatest period of peace and prosperity. THE PAX ROMANA (31 B.C - 180 A.D.) The roughly two hundred year period that began with Augustus’ rule and ended with Marcus Aurelius’ death in 180 ad. came to be known as the Pax Romana or Roman Peace. During this Period Rome: - Had great economic growth - Expanded their borders - Became more united as an empire - contributed some of its greatest cultural achievements The Pax Romana would impact Rome in four major ways. Economic Impact Rome’s economy was greatly strengthened during the Pax Romana. Rome was able to greatly increase its ability to trade. to do this first they established a uniform system of currency. This way all parts of the provinces had one form of money that they knew the value of. To further increase trade throughout its large empire it had to improve its roads and the safety of those who ventured into the provinces. Rome excelled in road building and constructed many roads to connect to its most famous road The Appian Way. During the Pax Romana, Rome built over 50,000 miles of roads that connected its large empire. Political Impact During the Pax Romana, Rome would see a great change in its government. Rome’s territory was now considered to be part of a large empire, under the rule of an emperor with absolute authority. The emperor would still need a great deal of assistance to have his policies carried out. To meet this need Rome created a civil service system, where jobs would go to the most capable people rather than be given out as favors to others. However, there would be some other key changes in government. More rights for those in the provinces Augustus wanted to make sure that the people in the provinces had a role in the government so that the empire would be more united. To do this Rome: -allowed foreigners to serve in the Roman Army for the first time -created a universal law code for the empire Social Impact Rome’s economy prospered during the Pax Romana. In general standards of living went up. A true middle class started to develop in Rome as more Plebeians started to acquire wealth. This led to much more stability among the social classes. With fewer Plebeians living in poverty, and more available opportunities the Plebeians had less to be upset about. In addition, the government took great steps to try to make the lives of the poor a little less miserable. Rome began to have public shows ad free entertainment at places like the colosseum and circus maximus. The circus maximus: A large chariot track that could seat 150,000 spectators Artistic/Scientific Impact During the Pax Romana the Romans made a number of key contributions in the areas of learning. Science/Technology/Architecture The Romans used a key architectural design, The Roman Arch, to create public buildings and projects. They built structures used to move water over large areas of land called Aqueducts. The Segovia Aqueduct In addition they built better roads that lasted longer and were easier to travel on than older roads. Some key examples of Roman Architecture The Colosseum (below): Host to Gladiator Battles and other public entertainment Now Then The Pantheon (below): A temple dedicated to all the roman gods and built from a breakthrough construction material: Concrete. The Forum: Rome’s center for Trade and Politics The Arch of Titus: A large arch remembering a Roman military victory over the Hebrews More Scientific Achievements Astronomy Ptolemy: Famous Egyptian Astronomer, his work on planetary motion would be of great use to later astronomers . Health and Medicine Rome focused heavily on public health as well. The Romans constructed: -public baths -a public water system -Medical Schools Language/Literature Latin: the official language of the Romans - influenced many languages that developed in Europe. - the Romance or Romantic Languages include : Romanian, Italian, French, Spanish, and Portuguese. Perhaps the greatest piece of Roman Literature Virgil’s The Aeneid was written during the Pax Romana. It is very similar to the Oddysey as it tells of one soldier, Aeneas, and his return from the Trojan War. He eventually becomes the foundation for Latin civilization and Rome. Click Here for a Link to a summary of the Aeneid