* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the syntactic category of
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive semantics wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Antisymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Distributed morphology wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Dependency grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Classifier (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Agglutination wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Danish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
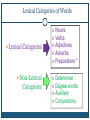
LEXICAL CATEGORIES LI 2013 N AT H A L I E F. M A R T I N Syntactic Categories • C AT E G O R I E S O F W O R D S • D I S T I N G U I S H I N G C AT E G O R I E S : 1. MEANING 2. INFLECTION 3. DISTRIBUTION Contemporary Linguistics Analysis: p. 146-150. Making Sense of It All! What is the syntactic category of: g) Mimsy a) Brillig h) Borogroves b) Slithy i) Mome c) Toves* j) Raths d) Gyre* k) Outgrabe e) Gimble* f) Wabe* Which are English words? Why is it important that those words remain there? Syntactic Categories = Word Classes = Parts of Speech All languages have syntactic categories. The syntactic category of a word determines the role it can play in a sentence. Only a noun can complete the sentence “Give a __________ to me.” Syntactic Categories (1) Lexical categories Noun (N) Verb (V) Adjective (A) Preposition (P) Adverb (Adv) Clearly identifiable meanings! Examples moisture, policy melt, remain good, intelligent to, near slowly, now Syntactic Categories (2) Non-lexical categories Determiner (Det) Degree word (Deg) Auxiliary (Aux) Conjunction (Con) Functional words! Examples the, this very, more will, can and, or Lexical Categories of Words Lexical Categories Non-Lexical Categories Nouns Verbs Adjectives Adverbs Prepositions * Determiner Degree words Auxiliary Conjunctions TRICKS! Distinguishing Categories By meaning: Nouns = entities (people, things), including individuals (Harry, Sue), objects (book, desk), Verbs = actions (run, jump), sensations (feel, hurt), and states (be, remain) Adjectives: Properties and attributes of a noun. Adverbs: Properties and attributes of the actions, sensations, and states (verbs) Manner and time What about words like: likelihood, give a push, near, etc. Distinguishing Categories Native speakers may have a good intuition about the syntactic category of a word. But linguists require more objective ways of determining syntactic categories. There are two tests one can use: 1. 2. Inflection Distribution Test 1: Inflection Certain inflectional paradigms apply only to one syntactic category. For example, if a word can take the inflectional suffix -ed in English, it must belong to the verb category. Lets try in out: The cute cat dances. You think the end is near. What about these words: sing (-ed*), intelligent (-er*), knowledge(-s*), etc. Test 2: Distribution The words with which a word may co-occur can be used to determine its syntactic category. Example: only nouns can come after a or the in English. All languages have such distributional restrictions on syntactic categories. Lets try in out: Great joy is to come in the morning. Joy comes later today. Holidays are the best! Distribution tests – Rules of other languages Distribution tests for syntactic categories are different in all languages. Chinese has no articles like a, the. So you can’t test for nouns with them. But in Chinese, only nouns co-occur with “classifiers”. If a word can come after a classifier, it must be a noun. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences. a. The glass suddenly broke. Det / N / Adv / V b. A jogger ran towards the end of the lane. Det / N / V / P / Det / N / P / Det / N c. The peaches never appear quite ripe. Det / N / Adv / V / Deg / A d. Gillian will play the trumpet and the drums in the N/ Aux / orchestra. /N V / Det / N / Conj / Det / N/ P / Det Translation and Lexical Categories W H AT G O T L O S T I N T R A N S L AT I O N ? F O U N D O N M Y H E AT E R :