* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Ecology
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Assisted colonization wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Decline in amphibian populations wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
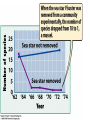
What is Ecology? • Defined: Studying how life interacts within the biosphere is called Ecology • All life interacts within the biosphere – Area within the deepest ocean trenches to the highest mountains Populations Click on information box • Defined: Group of one species living in the same area • Population changes based on: – Births, Deaths, Immigration, Emigration, Available resources Population Patterns • Populations go through 3 stages: 1) Slow growth • Population is slowly adapting to particular environment 2) Exponential growth • High birth rates due to abundant resources 3) Carry capacity • Defined: greatest number of individuals that the environment can sustain • Birth & death rates eventually balance • What stage is the human population in? What happens once we reach Carrying Capacity? Some populations stabilize for the long term Some populations experience a sharp decline called a “crash” Which will humans experience? Communities • Defined: Populations of many species living in the same area at the same time • Each organism has it own HABITAT – Habitat: Place where an organism lives • Each species has its own NICHE – Niche: The role/needs of a species – Ex: Termites return nutrients to the soil Ecosystems • Defined: Communities of species interacting with the living & non-living • Biotic (living) Factors: o Animals: Mice, Reptiles, Insects o Plants: Cactus, Flowers, Shrubs • Abiotic (non-living) Factors: o Sand, rocks, sunlight, climate, soil, water, etc… • Ecosystem changes affect biodiversity o Keystone species greatly alter ecosystems What is a Biome? • Defined: Large area with distinct climate, plant, and animal life • Climate factors: sun, rain, topography • Climate determines life • Defined: All organisms and the part of the Earth where life exists • Biosphere changes can affect life • Ex: More CO2 in the atmosphere… causes warmer temps The Biosphere Review 1) What is ecology? 2) What are two reasons that populations will increase? 3) What are two reasons that populations will decrease? 4) What are factors that control population growth called? 5) How does a population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere differ? 6) What is a keystone species? 7) Place the levels of ecology in order from smallest to largest. – Ecosystem, Population, Biosphere, Community, Biome