* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download energy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
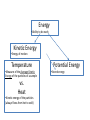
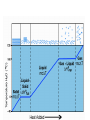
ENERGY Energy •Ability to do work Kinetic Energy •Energy of motion Temperature •Measure of the Average Kinetic Energy of the particles of a sample vs. Heat •Kinetic energy of the particles (always flows from hot to cold) Potential Energy •Stored energy Temperature Scales in Science • Celsius : – The lowest point on the scale is -273.15 °C • Absolute Zero • Kelvin: – The lowest point on the scale is 0K • Absolute Zero NEVER, EVER USE FAHRENHEIT IN SCIENCE!!!!! IT IS THE “F” WORD!!! What is Absolute Zero? • The point at which no more heat can be removed from a system • Almost no movement of molecules • Theoretical temperature Temperature Conversions Table T K= °C + 273 °C = K-273 (this is not on the table) Energy Changes In a chemical or physical change there may be a transfer of energy (heat) Exothermic process: there is a release of energy (heat) Endothermic process: there is absorption of energy (heat) Energy changes Exothermic Reactions will feel “hot” Endothermic Reactions will feel “cold” What is heat? • Bill Nye The Science Guy on Heat Heating and Cooling Curves • Shows the heating or the cooling of a specific substance • Heat is added at a constant rate • When a substance is undergoing a phase change THE TEMPERATURE DOES NOT CHANGE until the phase change is complete Phase changes (Vocabulary) • • • • • • Melting (Fusion) Vaporization (l-g) Sublimation (solidgas) Deposition (gas solid) Freezing (fusion) Condensation (g-l) GAS T e m p er at ur e (◦ C ) Endothermic Boiling Point LIQUID Melting Point SOLID Time (minutes) GAS T e m p e r a t u re Exothermic LIQUID Freezing Point (◦C) SOLID Time (minutes) Condensation Point T e m p er at ur e (◦ C ) Δ Kinetic Energy Kinetic Energy is constant Δ Kinetic Energy Kinetic Energy is constant Δ Kinetic Energy Time (minutes) Potential Energy is constant T e m p er at ur e (◦ C ) Potential Energy is constant Δ Potential Energy Potential Energy is constant Time (minutes) Δ Potential Energy T e m p er at ur e (◦ C ) q = mCΔT q = mHv q = mCΔT q = mHf q = mCΔT Time (minutes) Law of Conservation of Energy In any chemical or physical process, energy is neither created nor destroyed, it is merely transferred. How is heat measured? • Calorimetry – The precise measurement of heat flow into or out of a system. – The heat released by a system is equal to the heat absorbed by its surroundings – The heat absorbed by a system is equal to the heat released by the surroundings – A calorimeter is an insulated device used to measure the absorption or release of heat Constant Pressure Calorimeter • Most changes in the lab occur at constant pressure • The heat of a system is it’s enthalpy (H) • The heat released or absorbed by a system at constant pressure is equal to the system’s change in enthalpy (ΔH ) • ΔH = q • q= mC ΔT Heat mass Change in temperature (Final Temperature – Initial Temperature) Specific heat ΔH Process Heat Positive (Final Temperature is higher than the initial temperature) Endothermic Absorbed Negative(Final Temperature is lower than the initial temperature) Exothermic Released • Calorimetry