* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Innocent Heart Murmurs - sha
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
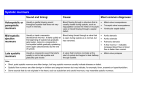
Innocent Heart Murmurs Mansour Al-Mutairi MD Consultant Pediatric cardiologist King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center Assistant Professor, Cardiac Sciences KSAU-HS, NGHA Riyadh , Saudi Arabia Misconceptions Innocent Heart Murmurs Patient with Heart Murmur Innocent Heart Murmur Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Characteristic’s of Innocent Murmur: Innocent Heart Murmurs Characteristic’s of Pathological Murmur: Innocent Heart Murmurs Classification of innocent murmur: • Four systolic innocent murmurs: o Still’s murmur or vibratory systolic murmur o Physiological or functional pulmonary flow murmur. o Peripheral Pulmonary arterial stenosis murmur of the newborn. o Aortic systolic murmur. • One continuous innocent murmurs: o Venous hum. Innocent Heart Murmurs Still’s Vibratory Systolic Murmur: • Most common , described by George F. Stills in 1909 as “A twanging sound” • Peak incidence in children 3 to 7 years, disappears at puberty • Musical, vibratory, low to medium in pitch, early systolic ejection murmur. • Maximum at LLSB and extending to apex, loudest in supine position and change in character with upright position but seldom disappear. • Turbulence produced by the physiological narrowing of the LV outflow tract. • Highly associated with false tendons (16.8%). Innocent Heart Murmurs Physiological or functional pulmonary flow Murmur: • Early systolic, crescendo-decrescendo, grade II-III at LUSB. • Best heard in supine position (↑ by pectus excavatum). • Decreases during upright position and held inspiration. • Turbulent flow at the origin of the RT & LT pulmonary arteries • DDx the murmur of ASD-II. Innocent Heart Murmurs Peripheral Pulmonary Stenosis of the Newborn: • Short early to mid-systolic ejection murmur of medium pitch & intensity at the axillae and back. • Heard in newborns and infants less than 1 year. • Result from the turbulence in the PA’s. • It increase with ↓ heart rate. • DDx is PPS, ASD-II. Innocent Heart Murmurs Aortic Systolic Murmur: • Short, low to medium pitch. • Arise from the outflow tract in older children and adults. • Audible maximally in the aortic area. • DDx from the systolic murmur of the HCM especially with history of sudden death or +ve FH or if increase with Valsalva maneuver. Innocent Heart Murmurs Venous Hum: • • • • • • • • The most common type of continuous innocent murmurs. The diastolic component is louder. Whining, intensity varies. Increased when child sitting / standing ,neck extended and looking away from the examiner. Disappear with lying down and occluding neck veins with fingers. Louder at high right sternal border and infraclavicular area however sometimes maximum on the left or equal in intensity bilaterally. Result form turbulent blood flow at the junction between JV and the SVC. DDx PDA. Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Neonatal screening exam: Innocent Heart Murmurs Neonate and young infant Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Older child Innocent Heart Murmurs Variable murmur ( Yes & no !) Innocent Heart Murmurs FH: Hereditary disease, CHD, RF, sudden death. Pregnancy : Infections, medications, smoking or alcohol intake. Postnatal: Birth weight, weight gain, feeding pattern, cyanosis, squatting, S.O.B, tachypnea, chest infections, exercise intolerance, chest pain, joint pain and neurologic symptoms. Innocent Heart Murmurs Clinical examination: Inspection: General appearance, nutritional status, dysmorphism, syndromes, clubbing and signs of RD. Palpation: (rate, regularity, volume, delay), (proper cuff), apical impulse and PMI , hyperactive precordium and thrills. Auscultation: Heart sound and Others: Abdominal examination. . Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Complete heart block Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs The Role of the Pediatrician Today The Role of the Pediatric Cardiologist Innocent Heart Murmurs Innocent Heart Murmurs