* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solving Multi-Step Equations - peacock
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
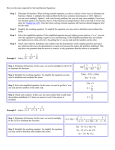
Solving Multi-Step Equations Section 2-3 Part 2 Goals Goal • To solve multi-step equations in one variable. Rubric Level 1 – Know the goals. Level 2 – Fully understand the goals. Level 3 – Use the goals to solve simple problems. Level 4 – Use the goals to solve more advanced problems. Level 5 – Adapts and applies the goals to different and more complex problems. Vocabulary • None Two Special Techniques Two Special Techniques for Solving Multi-Step Equations. 1. Clear the equation of fractions by multiplying both sides of the equation by the LCD of all denominators in the equation. 2. Simplify equations with decimal coefficients by multiplying both sides of the equation by a factor 10 (usually 10 or 100) to make all the coefficients whole numbers. Example: Clear Fractions Using the LCD Solve . Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions. Multiply both sides by 24, the LCD of the fractions. Distribute 24 on the left side. 3y – 18 = 14 +18 +18 3y = 32 Simplify. Since 18 is subtracted from 3y, add 18 to both sides to undo the subtraction. Example: Continued 3y = 32 3y = 32 3 3 Since y is multiplied by 3, divide both sides by 3 to undo the multiplication. Example: Clear Fractions Using the LCD Solve: 1 1 3 m 5 2 4 10 1 1 20 m 20 5 2 4 M (20) Simplify A(10) D(4) 5 3 20 4 4m 10 15 4m 25 m 25 4 Your Turn: Solve . Multiply by the LCD to clear the fractions. Multiply both sides by 12, the LCD of the fractions. Distribute 12 on the left side. 8r + 9 = 7 –9 –9 8r = –2 Simplify. Since 9 is added to 8r, subtract 9 from both sides to undo the addition. Your Turn: Continued 8r = –2 8r = –2 8 8 Since r is multiplied by 8, divide both sides by 8 to undo the multiplication. Your Turn: 1. 1 1 1 x 2 3 5 21 x 10 2. 2 5 5 x 3 6 4 5 x 8 Your Turn: 3. 3x x 5 4 8 x 8 4. n 3n 1 5 10 5 n 2 Example: Simplifying Decimal Coefficients Solve 1.5 = 1.2y – 5.7. Multiply by a factor of 10 to clear the decimals. (10)1.5 = (10)1.2y – (10)5.7 Multiply both sides by 10, to make the decimals whole numbers. 15 = 12y – 57 + 57 72 = 12y 72 = 12y 12 12 6=y + 57 First y is multiplied by 12. Then 57 is subtracted. Work backward: Add 57 to both sides. Since y is multiplied by 12, divide both sides by 12 to undo the multiplication. Example: Simplifying Decimal Coefficients Solve: M (100) A(20) D(40) 0.4x 0.2 0.16 40x 20 16 40x 4 x 0.1 01 40 4 0 40 . Your Turn: Solve: M (1000) A(20) D(2) 0.002k 0.02 4.02 2k 20 4020 2k 4000 k 2000 Your Turn: 1. 2.5n 0.1n 9.8 n 28 2. 0.25 d 12 4 d 28 Joke Time • What is a forum? • Two-um plus two-um! • Why did Mickey Mouse go to space? • To visit Pluto. • • • • Knock Knock? Who’s There? Armageddon! Armageddon who? Armageddon out of this place! Assignment • 2.3 Pt 2 Exercises Pg. 107 – 108: #8 – 36 even