* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.6, Sec.3 * Causes of Volcanic Eruptions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
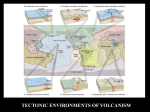
Learning Objectives I can describe the formation and movement of magma. I can explain the relationship between volcanoes and plate tectonics. I can summarize the methods scientists use to predict volcanic eruptions. Ch.6, Sec.3 – Causes of Volcanic Eruptions The Formation of Magma - changes in the pressure & temperature of the mantle cause magma to form - soft, igneous rock remains a solid in the Earth because of the intense pressure caused by the weight of the rock above it - magma is usually created in a liquid form at a plate boundary where the pressure is less and the magma can become less dense and rise to the surface Ch.6, Sec.3 – Causes of Volcanic Eruptions Where Volcanoes Form - the majority (95%) of volcanoes form on the boundary between tectonic plates, like along the Ring of Fire Ch.6, Sec.3 – Causes of Volcanic Eruptions When Tectonic Plates Separate - deep cracks, or rift zones, often will form at divergent plate boundaries - most of the volcanic activity on Earth occurs at the mid-ocean ridges along a divergent plate boundary Ch.6, Sec.3 – Causes of Volcanic Eruptions When Tectonic Plates Collide - as oceanic crust is subducted under a continental plate, the pressure and temperature increases - the increase in pressure & temperature allows the water in the oceanic crust to be released - once released, the water mixes with mantle rock, lowering the rock’s melting point, causing it to melt into magma Ch.6, Sec.3 – Causes of Volcanic Eruptions Hot Spots - some volcanoes can occur in spots very far away from tectonic plate boundaries in areas called hot spots - scientists are not sure if they form from cracks in the crust or from mantle plumes rising to the surface - the Hawaiian Islands & Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming are underneath hot spots Ch.6, Sec.3 – Causes of Volcanic Eruptions Predicting Volcanic Eruptions - the three classes of volcanoes are extinct, dormant, and active (scientists study dormant & active volcanoes) - small earthquakes are a good sign a volcano will erupt soon - changes in the gasses found in the magma (sulfur dioxide & carbon dioxide) also can signal a possible eruption - we can also use GPS to monitor any changes in a volcano’s slope angle Ch.6, Sec.3 – Causes of Volcanic Eruptions Ch.6, Sec.3 – Causes of Volcanic Eruptions