* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulation flashcards - mvhs
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
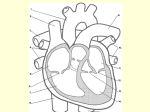
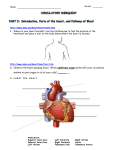
TRACE THE PATH OF BLOOD FROM THE VENA CAVA TO THE AORTA PURKINJE FIBERS Distinguish between the: PULMONARY ARTERY and PULMONARY VEIN Distinguish between: SYSTOLIC and DIASTOLIC Blood Pressures Distinguish between: CLOSED And OPEN Circulatory Systems Distinguish between: SINGLE And DOUBLE Circulatory Systems Distinguish between: SYSTEMIC and PULMONARY Circuits ERYTHROCYTE FIBRIN PLATELETS THROMBIN ATHEROSCLEROSIS Distinguish between: SINOATRIAL and ATRIOVENTRICULAR NODES Distinguish between: AMPHIBIAN and REPTILE Circulation Distinguish between: ARTERIES and VEINS Pulmonary Artery – Takes deoxygenated blood from _______ to lungs (from right ventricle to lungs) Purkinje Fibers – Conducting fibers in the ventricles that takes action potential and distributes it through ventricular muscle mass for contraction. Vena Cava -> RIGHT ATRIUM -> Atrioventricular Valve -> RIGHT VENTRICLE -> Pulmonary Valve -> PULMONARY ARTERY -> Lungs -> PULMONARY VEIN -> Left Atrium -> Atrioventricular Valve -> LEFT VENTRICLE -> Aortic Valve -> AORTA Single Circulation – Blood is pumped to _________ and then to ________ and then returns to heart in one circuit. Ex. __________ Double Circulation – Blood is pumped to gills/lungs, back to ________, and then to body (two circuits – pulmonary and systemic). Ex. __________ Open Circulatory System – Fluid leaves vessels and is squeezed through intercellular spaces. A heart may help distribute the fluid, but the fluid leaves the vessel. Ex.: Arthropods and Mollusks. Systolic Blood Pressure – Pressure of blood during ____________ of the ventricles. Fibrin – Active form of _____________, an enzyme important in clot formation. In clot formation, exposed collagen from the wound binds _____________ that signal more platelets to bind and begin a cascade of events that involve clotting factors and activation of enzymes. Erythrocyte – Red Blood Cell (contains _____________ which carries oxygen). Atherosclerosis – Clogging of the _____________ with a tough substance called __________. _____ - ______________ lipoproteins promote this disease, while _______ ______________ lipoproteins deter it. Thrombin – Active form of prothrombin. Clotting factors cause prothrombin to activate into thrombin. Thrombin then causes ____________ to polymerize and form threads of fibrin to clot blood. Platelets – Cell fragment formed in bone marrow with membrane (no nucleus) that is important in ___________. They release clotting factors. Arteries – Muscular blood vessel that carries blood ____________ the heart. Amphibian Circulation – _________ chambered heart with partially separated ventricle. Reptile Circulation- Ventricles are partially divided by a septum. Reptiles also have two _________ and can redirect blood to bypass pulmonary circuit. Crocodilians and alligators have completely separated ventricles. Sinoatrial Node – Pacemaker cells of Pulmonary Vein – Takes oxygenated blood from __________ to heart (to left atrium) Veins – Blood vessels that return blood to heart. They contain _________ to prevent backflow of blood. Diastolic Blood Pressure – Pressure of the blood during __________ of the ventricles. Closed Circulatory System – Blood stays in vessels separate from tissue fluid. Ex: Vertebrates and Annelids Systemic Circuit – Part of circulation that serves body (everything except for gills or lungs). Pulmonary Circuit – Part of circulation that serves _______ or gills. mammalian heart. These cardiac cells initiate an action potential that stimulates _______ contraction. Acetylcholine causes slower heart beat while norephinephrine causes increased heart beat. Atrioventricular Node – Cardiac muscle cells in junction between atria and ventricles that generates action potential after receiving from _________________.