* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grasslands and Tundra
Canada lynx wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Geography of Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Polar ecology wikipedia , lookup
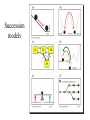
Grasslands and Tundra Temperate grasslands Found in areas of moderate rainfall, typically between 25 and 75 cm per year. Dry seasons sufficient to exclude most trees. Frequent fires. North American grasslands are dominated by “bunch grasses.” The North American Great Plains can be divided into several prairie types. They differ primarily on the basis of the amount of rain and the time of the dry season. Tall-grass prairie Mixed-grass prairie Short-grass prairie Tundra ecosystems are found where cold, hard winds and/or permafrost prevent the growth of large woody plants. We recognize two types of tundra: Arctic tundra Alpine tundra Arctic tundra have long winters of extreme cold. Permafrost is common. Arctic tundra is dominated by lichens, mosses, sedges, and small woody plants. Alpine tundra is found high in mountains at all latitudes. Conditions are variable. Permafrost is rare. Are grassland ecosystems equilibrium systems? This is significant in determining whether they will return if stresses are removed. Some have suggested that they may have “multiple stable states.” Succession models Population cycles are commonly seen in tundra habitats. They can be classified into three types: 1. 3-4 year cycles common in microtine rodents. 2. 9-10 year cycles as shown by snowshoe hares. 3. Longer cycles as seen in some larger tundra animals. Lemming population cycle Cycle of snowshoe hare and lynx. Suggested Causes of Population Cycles • Herbivory hypothesis • Food supply-predation hypothesis • Predation hypothesis Human impact on grassland and tundra ecosystems has been severe. Grazing impact of livestock is often due to selective herbivory. Decreasers versus increasers Invading species like cheatgrass (Bromius tectorum) has replaced native grasses over large areas. Arctic National Wildlife Refuge Oil in the ANWR