* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 5 study guide 15
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
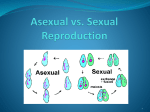
Study Guide Unit 5: Heredity and Genetics Learning Targets Date/Page Needs Got It! More Work! I can differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction I can develop and us a model to display sexual reproduction resulting in genetic variation Vocabulary Additional Questions/Notes Sexual reproduction Asexual reproduction Mitosis Meiosis Genetically (identical and different) Variation Diversity Heredity Budding Binary Fission Pathogenesis Fragmentation Pollination External Reproduction Internal Reproduction Look over the following materials: Asexual vs Sexual Comparison chart Types of asexual reproduction gallery walk notes Reproduction PPT Sexual vs Asexual quiz Punnett Square Heterozygous Homozygous Genotype Phenotype offspring Look over the following materials: Mendel and Me PPT Mendelian Pea activity Monster Genetics Lab Stations Activity (index cards) Finally use the Punnett square practice sheet Example Question: What are the two major differences between sexual and asexual reproduction? Two organisms genetic material is combined and creates a new and genetically different offspring. What type of reproduction allows this genetic diversity? Example Question: What are the possibility for offspring if a heterozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a homozygous short pea plant? The outcome of a cross between two organisms produces 2 heterozygous and 2 homozygous recessive offspring. What were the genotypes of the original parent organisms? I can use a model to show how structural changes to genes may result in harmful, neutral, and beneficial effects. Substitution Insertion Deletion Frameshift Look over the following materials: Monstrous Mutations PPT Monstrous Mutations Notes The analysis Questions from the Monstrous mutations activity **The base pairs are specific. A only binds to T (and T with A), and C only binds to G (and G with C). These are called complementary base pairs. This means that whatever the sequence of bases along one strand, the sequence of bases on the other strand must be complementary to it. (Incidentally, complementary, which means matching, is different from complimentary, which means being nice.) Please correct this in your notes. Example Questions: What affect do mutations have on organisms? During interphase a mistake is made in the copying of the DNA and a few bases are not copied. What type of mutation occurred?