* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grammar Prepositions - Neshaminy School District
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
German grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
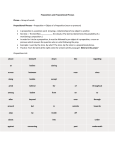
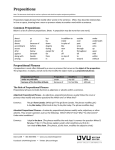
Grammar Prepositions Prepositions begin phrases that modify other words in the sentence. Often, they describe time or space relationships, showing how a noun or pronoun relates to another word within a sentence. COMMON PREPOSITIONS The most frequently used prepositions are at, by, for, from, in, of, on, to, and with. Below is a list of these and other common prepositions. (Note: A preposition may be more than one word.) about aboard above according to across after against along with among as at because of before behind below beneath beside between but by down despite during except for for from in in addition to inside in spite of like near of off on top of out outside over past since through throughout till to toward under underneath until unto up upon with within without PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES A preposition is most often followed by a noun or pronoun that serves as the object of the preposition. The preposition, its object, and all words that modify the object make up a prepositional phrase. Prepositional Phrase under my old table because of his horrible attitude Preposition under because of Modifiers my old his horrible Object table attitude THE ROLE OF PREPOSITIONAL PHRASES Prepositional phrases normally function as adjectives or adverbs within a sentence. _ Adjectival Prepositional Phrases—As adjectives, prepositional phrases usually follow the noun or pronoun they modify and answer questions like Which one? or What kind? EXAMPLES: The girl from Canada. (Which girl? The girl from Canada. The phrase modifies girl.) A day like today. (What kind of day? A day like today. The phrase modifies day.) _ Adverbial Prepositional Phrases—As adverbs, prepositional phrases modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They answer questions such as the following: When? Where? How? Why? To what extent? Under what conditions? EXAMPLES: I slept in the barn. (The phrase modifies the verb slept. It answers the question Where?) For you, I’ll do it! (The phrase explains under what conditions you’ll do it.) I am tired of this show. (The phrase, of this show, modifies the adjective tired.) IDENTIFYING PREPOSITIONS In certain settings, a word that is usually a preposition may actually be a conjunction instead. If the word introduces an object of a preposition (noun + words that modify the noun), then it is a preposition: PREPOSITIONS: Before school (The phrase contains a preposition and a noun, so before is a preposition.) He works as a full-time doctor. (The phrase contains the word as, a noun [doctor], and its modifiers [a full-time], so as must be a preposition. A full-time doctor is its object.) If the word introduces a clause (group of words containing both a noun subject and a verb), then it is not a preposition, but a conjunction. (See Conjunctions handout.) CONJUNCTIONS: Before you went to school (The group of words is a clause because it contains a noun subject [you] and a verb [went]. Therefore, before is a subordinating conjunction.) I will watch as the doctor operates. (The doctor operates is a clause because it has a subject [The doctor] and a verb [operates]. Thus, as must be a subordinating conjunction.) Utah Valley State College Writing Center