* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download European Maritime Empires
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
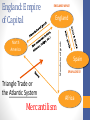
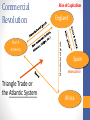
European Maritime Empires Mr. Millhouse AP World History Hebron High School Winners: Spain & Portugal? Winners: Spain & Portugal? Spanish Empire: An Empire of Silver • Mostly in the Americas • Mine gold & silver • Used natives as labor • Encomiendas • Repartimiento • Mita • Sociedad de Castas • Mestizos • Catholic Church • Jesuits Portuguese Empire: A Trading-Post Empire • Indian Ocean Trading-Posts • Trades spices & sugar • Used slaves as labor • El Mina • Brazil 1st plantation colony • Imports 20% of all slaves • Sociedad de Castas • Mulattos • Catholic Church • Jesuits Losers: Spain & Portugal? Decline of Spanish Empire: Too rich, too fast? • External Pressure • English, French, & Dutch competition in Caribbean • Costly wars with other European nations • England (Spanish Armada) • Internal Weakness • Inflation • Never develops native industries • Financial systems not sophisticated enough Decline of Portuguese Empire: Too big, too small? • External Pressure • Dutch takeover Indian Ocean • Costly wars with other European nations • Netherlands • Internal Weakness • Too small • Never develops native industries • Not enough resources Winner: Netherlands (Dutch) An Empire of Spices? An Empire of Sugar? Empire of Commerce Dutch settlers in South Africa were called Boers Dutch East India Co. • Dutch East India Co. (V.O.C.) was a joint-stock company founded in 1602 • Second oldest multinational corporation • British East India Co. founded in 1600 • First trade company to exchange stock • Amsterdam Stock Exchange founded in 1602 • Granted a 21 year monopoly of the spice trade • “Powers” of the V.O.C. • Wage war • Negotiate treaties • Establish colonies • Established Batavia (Jakarta) in 1619 • Mint its own coins Mercantilism Mercantilism is an economic theory based on the following ideas: 1. There is a limited amount of wealth (gold & silver) in the world 2. The country with the most wealth wins 3. Winning takes maintaining a favorable balance of trade by maximizing exports, minimizing imports, and extracting resources from your colonies 4. Control trade by granting charters to joint-stock companies (V.O.C.) to monopolize trade Battle for Last: England v. France France: Empire of Fur? England: Empire of Cotton? England: Empire of Capital ENGLAND WINS! England Manufactured goods North America Triangle Trade or the Atlantic System Mercantilism Spain SPAIN LOSES! Africa Meanwhile back in Europe… Protestant Reformation Europe after Reformation… WAR!!! Scientific Revolution North America Triangle Trade or the Atlantic System England Manufactured goods Commercial Revolution Rise of Capitalism Spain SPAIN LOSES! Africa Meanwhile back in Europe… Post-Classical Europe: A Review Roman Empire Germanic Kingdoms (31 BCE – 476 CE) Clovis, Charlemagne, etc. Byzantine Empire Feudal Kingdoms (conquered 1453) Feudal Monarchy France, England, etc. Magna Carta, 1215 Political Trends 1450-1750 • Three new developments • Rise of nation-states • A political unit consisting of an autonomous state inhabited predominantly by a people sharing a common culture, history, and language. • Rise of absolute monarchy • Monarch serves as the source of power in the state and is not legally bound by any constitution (Spain, France, Russia, etc.) • Rise of limited monarchy • Parliamentary monarchy or constitutional monarchy (England & Netherlands) • Monarch acts as head of state with powers limited by a parliament or a constitution Europe in 1700 C.E. Absolute Monarchy: France • Louis XIV (1638-1715) • Named king at age 4 • Advised by Cardinal Mazarin until 1661 • Divine Right of Kings • Secularized France • Promoted France as a nation-state • Believed the monarch personified the state • Nicknamed the Sun King • “L’État c’est moi” or “I am the state” Louis XIV ruled France for over 72 years. Reign of Louis XIV • Limited power of nobility & Catholic church • Increased size of French bureaucracy • Mercantilism was used to increase the wealth of France • With mercantilism the monarch controls trade • Jean Baptiste Colbert • Fought several wars • War of Spanish Succession • Put France in major debt • Colonization • North America and India • Revoked the Edict of Nantes • Built the Palace of Versailles Palace of Versailles Palace of Versailles • Palace used as a symbol of French wealth and power • Daily routines at Versailles were exploited by Louis XIV • Nobility competed against each other to perform menial tasks for the king Hall of Mirrors Versailles – Some Statistics • Modern cost: over $2,000,000,000 • Annual upkeep took 25% of France’s income • Main wing 500 yards long • Two wings: 150 yards long • 2,000 rooms • 15,000 acres of gardens with 1,400 fountains