* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
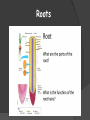
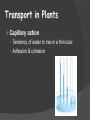
Plants Structure, Growth, & Development Plant Structure Introduction https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DGpPHrLF-5M Parts of a Seed Seed Each seed contains a plant embryo Each seed also contains food for the embryo A tough outer case protects the embryo, known as a seed coat Parts of a Seed External seed coat Developing plant embryo Stored food called endosperm Seed Dispersal The main function of the fruit is to disperse the seeds Four Types: • Self dispersal • Wind dispersal • Water dispersal • Animal dispersal Seed Dormancy Ensures that the seed will germinate only when there are optimal conditions Plants stay dormant until the right environmental conditions Seed Germination Seeds do not always germinate right away; can wait for long periods of time to grow Seed need water, nutrients and the right temperature to grow Order of Growth embryonic root, embryonic shoot, leaves Seed Labeling You have 5 minutes to complete the diagram Lima Bean Dissection https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pQYJ2PSDu3A Plant Growth & Tissue Meristems Plant cells that contain stem cells Apical meristems • Elongate shoots and roots through primary growth • Located at the tips of roots and in the buds of shoots Lateral meristems • Add thickness of stems and roots through secondary growth Tissue Systems Dermal tissue system Consists of the epidermis Ground tissue Various cells specialized for: Storage Photosynthesis Support Three Tissue Systems: Dermal, Vascular, & Ground Each plant organ has… Dermal, vascular, and ground tissues Dermal tissue Ground tissue Vascular tissue Vascular Tissue Vascular tissue system Transport of materials between roots and shoots Xylem Transports water upward from roots into the shoots Phloem Transports nutrients from where they are made to where they are needed Vascular Tissue Roots Roots Root Structure Apical meristem New cells along roots & stem; differentiate into other tissue Root Cap Protects root as it grows Key role in water & mineral transport Roots Anchor plants firmly in the ground Absorb water and minerals from the soil Some roots can be used to grow a new plant Types Roots Fibrous roots • Multiple smaller roots Tap roots • Large main central root Roots Absorption of water & minerals near root tips • Large numbers of tiny root hairs increase the surface area of the root Minerals use active transport Roots Labeling You have 5 minutes to complete your roots diagram Stems Stems Structure Produce leaves, branches, and flowers Hold leaves up Transport substance between roots and leaves Transport system Stems Xylem and phloem Major tubule systems Transport water & nutrients Nodes Attachment for leaves Internodes = stem between nodes Petiole “Stem” of the leaf Types of Stems Woody Thick cell walls Trees, shrubs, and vines Herbaceous Supported by hydrostatic pressure (turgor) Dandelions, zinnias, petunias Underground Stems Tubors Used to store food for the plant Bulbs Allows the plant to be dormant with cold temperature Rhizome Horizontal underground stem = produces shoot and root systems of a new plant Stems Lenticles • Pore in the stem providing direct gas exchange Buds • Undeveloped shoot from which embryonic leaves or flower parts arise Transport in Plants Capillary action • Tendency of water to rise in a thin tube • Adhesion & cohesion Leaves Leaves Sight of photosynthesis Anatomy Cuticle – covers and protects leaf Blade – thin flattened section Petiole – stalk that attaches stem to blade Covered by epidermis and cuticle Create water proof barrier Mesophyll & Stomata Mesophyll – site of photosynthesis Palisade mesophyll – absorb light Spongy mesophyll – air space for gas diffusion Stomata – pores on the underside of the leaf CO2 enters O2 + H2O exit Most active during the day Guard Cells – open and close stomata Leaf Adaptations Excess of Sunlight • Thick cuticle • Small/narrow leaves Limited Sunlight • Thin cuticle • Large/broad leaves Transport & Tropisms Transport in Plants Transpiration Osmotic pressure moves water out of vascular tissue This pulls water up from the stem to the leaves Affected by heat, humidity, wind Gravity Response to gravity is gravitropism Roots show positive gravitropism Stems show negative gravitropism Hydrotropism Roots grow toward water (positive) Thigmotropism Growth in response to touch Plant grows toward (+) or away from (-) pressure • Vines and other climbing plants Thermotropism Plant response to temperature Phototropism Plants grow toward a source of light Tropisms https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pCFstSMvAMI Plant Hormones Plant Hormones & Tropisms Hormones • Chemical signals that coordinate growth, development, and responses to stimuli • Tropisms are often caused by hormones Auxin Any chemical substance that promotes cell elongation (growth) in different target tissues Formation & branching of roots Gibberellins Stem elongation (growth) Fruit growth Seed germination Cytokinins Stimulate cell division Found in actively growing tissues Ethylene “Aging” hormone Causes fruits to ripen