* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The pelvis is also called the innominate bone—comprised of 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
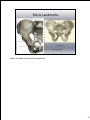
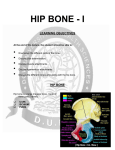
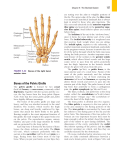
The pelvis is also called the innominate bone—comprised of 3 bones fused together: ilium, pubis, and ischium. What kind of joint is this?? There are 2 pelvic bones to make up the pelvic girdle. Each pelvic bone is also called an os coxae (right and left). The sacrum forms the back of the pelvis. The pubic bones from the 2 innominate bones articulate with each other at the pubic symphysis (which will be addressed in a few slides). 1 *Remember the Ilium is the top part of the pelvic bone and articulates the pelvis with the spinal column through the sacrum.* Iliac crest—rounded top edge Anterior superior iliac spine—rounded anterior point Anterior inferior iliac spine—rounded pt below ASIS Posterior superior iliac spine—rounded posterior point Posterior inferior iliac spine—rounded pt below PSIS Greater sciatic notch—large groove below PIIS Gluteal lines—slash markings that are attachments for the gluteal muscles 2 The ilium is where you put your hands on your hips. 3 *Remember the Ischium is the posterior part of the pelvis bone. The ischial tuberosity is what you sit on. For those of you that have been told that you have a “bony butt” it is because the people you have sat on can feel your ischial tuberosities very well.* Ischial spine—pointy process below greater sciatic notch Lesser sciatic notch—below ischial spine Ischial tuberosity—rounded edge Ramus—before the fissure to the pubis; helps form the bridge 4 Notice the ramus helping form the bridge to the pubic bone. 5 *The pubic bone is the most anterior part of the innominate bone. Superior ramus—top part of the bridge towards the ilium Inferior ramus—bottom part of the bridge towards the ischium Pubic symphysis—located anteriorly and is where the 2 pelvic bones come together; it becomes more flexible during pregnancy and childbirth. Pubic arch—the “V” underneath where the 2 pubic symphyses come together 6 7 Notice the pubic arch and pubic symphyses. 8 The inguinal ligament can be located more easily when you do hip flexion—the crease by your groin is where the inguinal ligament is. It goes from the ASIS to the pubis and it helps with flexibility and provides the lower border for your abdomen. It also serves as a major source of muscular attachments. The sacrailiac joint is the roughed up part of the ilium where the sacrum is inserted. The obturator foramen is the big hole below the acetabulum and is made up of the pubis and ischium. The acetabulum is the deep socket for the femur to go and it is made up of all 3 of the bones: ilium, ischium, & pubis 9 Which pelvis is female and which one is male??? A female pelvis is wider, flared out more, flatter, shallower, has a wider pubic arch, and is lighter to allow for childbearing. Also, the ischial tuberosities are shorter and are turned outward, as well as the sacrum/coccyx curve in less sharply for females too. 10 It is through the hip joint that the entire weight of the trunk and upper extremities is transferred to the lower extremities. Fractures of the femur are typically due to severe impact or compressive forces. Fractures of the femoral neck are more common in the elderly and may require hip replacement surgery. 11 The femoral artery, vein, and nerve are crucial to function of the lower extremity. If the femoral artery and/or vein is cut during an injury a person can bleed out in minutes, and so a blood transfusion is usually necessary for survival. The femoral artery, vein, and nerve can be located using the “femoral triangle” which is formed by the inguinal ligament (superior border), the sartorius muscle (lateral border), and the adductor longus muscle (medial border). 12 Head—fits in acetabulum of the pelvis Greater trochanter—big projection on lateral side of head Lesser trochanter—smaller bump on posterior side, below the greater trochanter Intertrochanteric line—line between the 2 trochanters Pectineal line—short posterior line below lesser trochanter Linea aspera—long posterior line used for muscle attach. Intercondylar fossa (notch)—big divot between condyles on posterior Adductor tubercle—bump right above medial epicondyle Popliteal groove—groove in between epicondyles on posterior 13 Now remember the 3 bones of the pelvis and where they are located. Ilium is the top part; ischium is the posterior section; pubis is the anterior part. So the iliofemoral ligament goes from the ilium to the femur on the anterior side. The pubofemoral ligament connects the pubis to the femur and is also on the anterior side. The ischialfemoral ligament connects the ischium to the femur and is located on the posterior side since the ischium is posterior. What type of joint is the hip?? It can do flex/ext, abd/adduction, int./ext. rotation, horizontal abd/add, and circumduction 14 The patella is an example of what type of bone?? It is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. What is the definition of a sesamoid bone?? 15 The patella also helps protect the structures underneath it, but its main function is to create a greater rotary force of the knee joint. 16 17 Fibula is the smaller, lateral lower leg bone. It is thinner than the tibia. The fibula is a non-weight bearing bone! The head of the fibula articulates with the lateral condyle of the tibia. The head and neck are located proximal and the lateral malleolus is the projection on the lateral side of your ankle. 18 The tibia is the larger, medial lower leg bone. It is the major weight-bearing bone. The femur rests solely on the tibia! The tibia is much bigger because of this to handle all of the weight coming down upon it. 19 Medial & Lateral condyles—located on top, proximally Intercondylar emminence—ridge in between condyles Tibial tuberosity—bump on anterior side Anterior crest (Tibial crest)—ridge, shin bone Popliteal line—curved line on posterior side Medial malleolus—projection on medial side by the ankle 20 The proximal tibiofibular joint helps dissipate torsional loads applied at the ankle and it is a gliding joint. The distal tibiofibular joint is an amphiarthrosis joint. The 4 ligaments of the knee help to stabilize it. The MCL and LCL help stabilize sideways motion by preventing abduction and adduction of the joint. The cruciate ligaments cross each other through the middle of the knee joint. So the ACL and PCL help limit rotation of the knee as well as forward movement of the femur over the tibia. 21 Click on the hyperlink to see a Terrible Triad Injury, which is a tear to all 3 of those major areas: medial meniscus, ACL, and MCL. The Terrible Triad can occur due to a sudden stop and twisting. 22