* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab 2
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
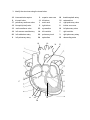
Lab 2 Pre-Lab Questions 1. Define the following terms: Macrocytic: abnormally large cell Normochromic: being normal in color Etiology: the cause or origin. (like in the cause of a disease or condition) Anemia a pathological condition in which blood oxygen level is reduced, due to too few RBCs, reduction in hemoglobin concentration or defective hemoglobin Leukemia uncontrolled, abnormal proliferation of one or more of the leukocyte precursor cells Eosinophilia increase in the number of circulating eosinophils beyond normal Hematology study of blood and blood producing organs Hemoglobin S abnormal hemoglobin type produced in relation to sickle cell trait Smudge a ruptured leukocyte in a blood smear. Intrinsic factor a small protein produced by the parietal cells of the stomach and required for absorption of vitamin B 12 2. Match the term with the appropriate description: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. mediastinum fibrous pericardium parietal pericardium superior vena cava trabeculae carneae pulmonary veins papillary muscle h. pulmonary trunk i. interventricular septum j. coronary sinus k. ventricles l. inferior vena cava m. visceral pericardium n. fossa ovalis o. chordae tendineae p. pectinate muscle q. aorta r. apex s. intercalated disc t. myocardium u. atria v. endocardium w. auricles Q largest artery in the body I internal partition that divides the ventricles internally D three veins that deliver blood to the right artrium L receives blood from the lower limbs and abdominal organs and drains into the right atrium. J a venous sinus that opens into the right atrium C lines the internal surface of the fibrous pericardium G muscle that plays a role in valve function R lies in the left fifth intercostal space; points inferiorly towards the left hip U superior heart chambers F vessels that deliver blood to the left atrium A the medial cavity of the thorax E irregular ridges of muscle found in the internal walls of the ventricles W small protruding ear like flaps that increase atrial volume to a small degree V maintains a smooth surface for blood flow; lines heart chambers and covers heart valves T middle heart layer N remnant of fetal circulation located in the interatrial septum M also known as the epicardium P ridged bundles of muscle tissue in the anterior atrial walls K inferior chambers of the heart B outer, tough dense connective tissue layer of the pericardium O collagen cords connected to the AV valves; anchor the valves to papillary muscle 3. Identify the structures using the terms below: 16 interventricular septum 2 superior vena cava 18 brachiocephalic artery 6 tricuspid valve 11 left atrium 21 endocardium 17 pulmonary semilunar valve 1 aortic arch 4 right pulmonary veins 12 bicuspid (mitral) valve 5 right atrium 8 inferior vena cava 13 aortic semilunar valve 23 myocardium 10 left pulmonary veins 19 left common carotid artery 14 left ventricle 7 right ventricle 20 left subclavian artery 22 pulmonary trunk 3 right pulmonary artery 9 left pulmonary artery 24 epicardium 15 descending aorta 18 19 17 21 23 16 24 20 22 4. Match the terms below with the descriptions: a. b. c. d. e. right coronary artery marginal artery left coronary artery great cardiac vein pulmonary semilunar valve f. tricuspid valve g. aortic semilunar valve h. anterior interventricular artery i. middle cardiac vein j. posterior interventricular artery k. bicuspid valve These two structures prevent the backflow of blood into the atria f, k These two structures prevent the backflow of blood into the ventricles e,g These two structures arise from the base of the aorta and supply blood to coronary circulation a,c These two vessels supply blood to the interventricular septum h,j These two structures are tributaries of the coronary sinus d,i This vessel supplies blood to the right ventricular wall b 5. Describe the location and position of the heart in the human body: The heart lies within the mediastinum extending obliquely from the second rib to the fifth intercostals space. It lies anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum and medial to the lungs. 6. Compare the function of the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit Pulmonary circuit consists of blood vessels that transport blood to and from the lungs. These blood vessels carry oxygen poor blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and carry oxygen rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium. Systemic circuit consists of blood vessels that carry blood to and from the various body systems. These blood vessels carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the tissues of the body and bring back deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.