* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Separations - RIT
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
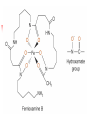
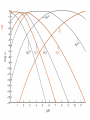
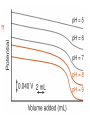
Chapter 13 “EDTA” Titrations It’s a Complex World Out There Terms Ligand - Each of the atoms or groups attached to the central (usually the metal) atom of a co-ordination complex. (OED) Lewis Acids. Electron pair acceptors (Metal Ions) Lewis Bases. Electron pair donators – the ligands Terms Monodentate – one atom per ligand molecule. Multidentate – more than one ligand atom per ligand molecule. (Chelating ligand) Applied to a group (ligand) that loops round a central metal ion to be attached at two or more points, and also to the co-ordination compound so formed. Hence as n., a chelate compound. Chelate - Having chelæ or prehensile claws. Most Transition metals bind six ligand atoms. Examples of Ligands and complexes. Cyanide Ethylenediamine EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) Example of Complexing ligands in nature and Medicine Nonactin - an ionophore Ferrioxamine B EDTA Acid Base Properties EDTA is hexaprotic. pKa’s are 0.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.66, 6.16 and 10.24 First four are for carboxylate protons The neutral compound is tetraprotic. A common salt is Na2H2Y.2H2O The Y4- form is the one that binds EDTA Y4 The fraction in that form is: [Y 4 ] [ H 6Y 2 ] [ H 5Y ] [ H 4Y ] [ H 3Y ] [ H 2Y 2 ] [ H Y 3 ] [Y 4 ] Fractional Form Hn +++ PK Format Conditional Formation Constants n4 [ MY ] K Y 4 K f n [ M ][ EDTA] ' f Conditional Formation Constants Since these are a function of pH the control of pH allow us to determine the strength of the metal ligand complex. This can be seen in the EDTA titration of Ca2+ Most Metal Ions will form Hydroxides Auxiliary Complexing agents are used. Ammonia for zinc for example. Indicators Same function as with acid base indicators but with excess EDTA you remove a metal from the indicator thus changing its color. Techniques Direct Titration Back Titration (Al ion with excess EDTA) Titrate excess EDTA with Zn Displacement Titration – Metal ion is place in a solution with excess CaEDTA. The Ca displaced is then titrated with standard EDTA. Indirect Titration – SO4 _- Add Excess Ba – filter and boil solid with excess EDTA. Amount of excess EDTA determined by titration with Mg Techniques Masking Other ligands are added and block an interfering metal ion from reacting with the EDTA These systems can get very complex but and work quite well - Follow cook book procedures. You would want to validate you procedure.