* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download powerpoint
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Citizen Lab wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
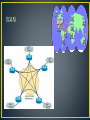
Unit 5 Introduction to Networking • Group of computers connected together in such a way as to allow resources to be shared. • What do you know about networks? • Describe a network – what are components? • Compare a stand-alone PC to a network PC. • Two or more computers that are linked together in order to: • share resources (such as printers and CD-ROMs) • exchange files • allow electronic communication. • • • • Cables Telephone lines Fiber Optic (visible light) Radio waves (WiFi - Wireless local area network that uses radio signals to transmit data) • Satellites (GPS) Cables Network Interface cards Modem A device that allows computers to communicate over telephone lines A card installed in a computer that allows you to connect to a network (can be Ethernet, telephone, or wireless) Switches Hubs like a tiny telephone company that lets pairs of devices make direct connections. simply connects all of the devices on its ports together Router Server a device that transfers data from one network to another in an intelligent way computer or device on a network that manages network resource • LAN • MAN • WAN • Local Area Network • Confined to a relatively small area •Generally limited to the same building • Computers can be no more than a mile apart • A file server – stores all of the software that controls the network, as well as the software that can be shared by the computers attached to the network • A workstation – computer connected to the file server • Cables – used to connect the network interface cards in each computer • Metropolitan (Metro) Area Network • Covers small geographical areas, such as cities •Often used by libraries and government agencies to connect to citizens and private business industries • Wide Area Network •Connects larger geographical areas •Examples include: RCSD and Internet • Each ICT I lab and ICT II lab have switches in them that control the data that flows in and out of the lab. • There is a hub switch in all the ICT II labs. The cable from each lab’s switch plugs in to a port on the hub switch. The hub is connected to the ICT server which is located in the main office. • The ICT server is connected to a router that gives us access to the Internet. • All of the computer labs & all of the individual computers in other classrooms make up the OGMS LAN. • Mrs. Lanyon’s lab, Mr. Lee’s lab, and Mrs. Weathersby’s lab (and all of the ICT I labs) are considered LAN segments because the computers in each lab are connected together in a kind of smaller network. • The computer workstations in each ICT I lab and each ICT II lab are connected by ethernet cables. The cables plug into the network card in each computer. • The main server at OGMS is connected to the main server at the county office. • All of the schools in the Lamar County School District are connected to the main server in the technology building at Jefferson Todd which makes LCSD a WAN.