* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download E-Government Toolkit for Developing Nations
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
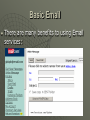
Internet & Email Presentation Overview Internet & Email I. Introduction II. The benefits of Internet & Email III. Understanding the Internet IV. Basic Email Part I. Introduction Introduction Information Technology (IT) primarily deals with the creation and manipulation of digital information being used by individuals in the home, school and virtually every sector. Making digital or Digitization refers to the ability to transform text, documents, books, pictures, voices, sound, music, television signals, movies and any other data into computer bits. Note: Computer bits simply refers to the data or the information represented by a series of 1’s and 0’s. Introduction ICT, in addition, deals with sending and receiving these computer bits, through the use of phone lines, copper & fiber optic cables, and wireless devices. The technology continues to become faster and cheaper, making it more widely used. Introduction Therefore, it can be said that ICT is made up of mainly the following: 1. The Information Highway (i.e. Phone lines, satellites and fiber-optic cables are the roads) 2. The Information Transport (i.e. computers, mobiles, and other network devices are the vehicles) Introduction There is no universal definition of ICT because it is always growing to include more and more tools and the skills needed to use them. For the scope of this presentation, we will only discuss the Internet & Email, their benefits, the different parts and how to troubleshoot Internet connections. Part II. The benefits of Internet & Email The benefits of Internet & Email There is an old famous saying that reads: “the future of the computer is the network.” That is to say that the computer alone is a very useful tool; but the tool will be even more useful when it is connected to a network of computers sharing information and other resources. The benefits of Internet & Email The Internet is a global network of computers, their interconnections, and the information that travels between them. Email or Electronic Mail is one of the most common services that can be accessed through the Internet, allowing users to send text messages and attachments (i.e. files) of limited size, depending on the service. The benefits of Internet & Email We live in the information age, and it is often said: “Information is power.” So the ability to store, retrieve, manipulate, send, and receive information, correctly and quickly, essentially makes individuals and organizations more productive. The benefits of Internet & Email Having easy and affordable access to the Internet allows us to benefit from all the information and services available. Note: This difference between those who have easy access to ICT and those who don’t is commonly known as ‘the digital divide.’ The benefits of Internet & Email In the words of Thomas L. Friedman, “the innovations in computerization, miniaturization, telecommunication and digitization have democratized technology”… and information. What this means is that because of all the advancements in the various fields, ICT equipment keeps getting faster, smaller, cheaper, and thus more easily accessible to the masses. The benefits of Internet & Email Subsequently, more and more of the world’s population is connected and has access to the tools needed for sharing lots of information, news, knowledge, books, pictures, music, movies, money and so much more, on a daily basis. With easy access to the Internet, individuals and the society at large can be empowered. The benefits of Internet & Email Thus, the Internet can greatly contribute as a driver for socioeconomic development. By using the Internet and its services, any sector can increase productivity and maintain efficiency, by storing, retrieving and sharing information with great speed and accuracy. The benefits of Internet & Email The Role of ICT in National Development 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Agriculture Health Education & Research Trade & Commerce Good Governance Environmental Management Tourism Gender Culture The benefits of Internet & Email 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Agriculture – To facilitate wide access to information and intensive sharing of knowledge among planners, policy makers, practitioners and researchers in the agriculture sector; To assist farmers on such areas as input supply, extension and use of local knowledge; To market agricultural products; To provide equitable access to new techniques for improving agricultural production; To reduce food storage losses through more efficient distribution. The benefits of Internet & Email 1. 2. 3. Health – To use virtual medicine and telemedicine to make it possible for patients located in rural areas to have access to medical experts located thousands of miles away; To enhance health administration and management through medical information system; To establish information “health profiles” and decision support system on federal, regional, zonal, woreda and kebele levels. The benefits of Internet & Email 1. 2. 3. 4. Education & Research – Provide equitable remote access to resources in support of both distance education and the strengthening of local educational capacity; Connecting schools, universities and research centers to national and international databases, libraries, research laboratories and computing facilities; Reducing communication and administrative costs by building communication networks linking all educational establishments; Promoting and supporting collaboration among teachers and researchers; The benefits of Internet & Email 1. Trade & Commerce – Linking chamber of commerce, trade associations and enterprises to both national and global trade; 3. Reduced commercial transaction costs; Online trade related information and import/export opportunities; 4. Improving management of federal income tax; 2. 5. Development and marketing of new products through electronic networks. The benefits of Internet & Email 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Good Governance – To strengthen the efficiency, accountability, and the transparency of government; To help the government design, implement, and assess policy reforms To enhance the public’s participation in the democratic process To provide the citizens with the ability to improve their interactions with each other and with the government. To yield large productivity increases in government service delivery. The benefits of Internet & Email 1. 2. 3. Environmental Management – Increase agricultural productivity by providing farmers with information on weather forecasts; Implementing networks which provide access to low cost terrestrial and satellite radio telecommunications in areas threatened by environmental degradation and natural disasters; Establishing problem monitoring information systems using geographic information system (GIS) technologies, to combine information on soils, hydro-geology and rainfall with socioeconomic data, allowing early warnings. The benefits of Internet & Email 1. 2. 3. 4. Tourism Attracting more tourists and other visitors by offering high-quality information and telecommunication services in tourist resorts; Reducing the costs of international promotions for attracting tourists; Improving the image of the country through online promotional campaigns; Provision of tourism related information and indicators that encourage and facilitate investment in tourism projects. The benefits of Internet & Email 1. 2. 3. Gender – Improve the rights of women through access to information and indicators which may be used for tracking gender issues and elimination of stereotypes; Ensure equitable access of women to information, technology and technological education; Enhance the role of modern communications media to promote awareness of equality between women and men. The benefits of Internet & Email 1. 2. 3. Culture – Making national museums accessible to all parts of the regions as well as to the rest of the world; Electronic preservation and documentation of manuscripts and artifacts; Increasing accessibility of rare manuscripts and artifacts to researchers and the general public through the development of cultural CDROM products. Part III. Understanding the Internet Understanding the Internet So the Internet refers to the network of thousands of regional networks which enables the transfer of all kinds of information, in the form of computer bits or packets represented by series of 1’s & 0’s. Connecting to the Internet – There are mainly 2 ways of connecting to the Internet: - Dial up - Network Understanding the Internet Dial up – Most stand-alone computers use a modem and a phone line to dial into an Internet Service Provider's (ISP) server, which provides access to the Internet. ISPs will typically charge a monthly fee based on the number of hours of access to the Internet. The speed of the Internet connection, also known as bandwidth, is not more than 56 kilobytes per second (kbps). Understanding the Internet Dial up Understanding the Internet Network – Universities, government offices and large companies usually have a network connection, which means that the computer is part of a network with a high-speed dedicated (leased-line) connection. This connection has high-speed bandwidth of 64 kbps or more, also known as Broadband. Understanding the Internet Understanding the Internet Computers on the Internet use client/server architecture. This means that the remote server machine provides files and services to a user's client machine when requested. IP address – an Internet Protocol address is a unique numeric identifier representing computers on the Internet. (e.g. 213.55.64.36) Using the Internet (cont.) Client/Server architecture Understanding the Internet Since an IP address is not easy for people to remember, the Internet uses domain names which correspond to the IP addresses. Therefore, a globally unified namespace (i.e., a system of names in which there is one and only one name for each server) is essential for the Internet to function. Understanding the Internet A domain name is a way to identify and locate computers connected to the Internet. A domain name must be unique; no two organizations on the Internet can have the same domain name. (i.e. www.yahoo.com is the Yahoo! Domain on the World Wide Web.) Therefore, a Domain Name Server (DNS) is needed to match a domain name to an IP address and vice versa. Understanding the Internet An IP address can be static or dynamic: - a static IP address does not change (e.g. Web servers, routers, etc.) - a dynamic IP address can change (e.g. dial-up computers) Understanding the Internet 213.55.64.36 Gateway 192.168.121.1 10.168.1.17 Understanding the Internet Local Area Network (LAN) settings: In an office LAN, the router or gateway used for accessing the Internet must have a static IP address. Note: The computers can have static or dynamic IP addresses. If the address is static, it is set manually. If it is dynamic, a DHCP server must assign IP addresses to computers automatically, as they connect to the network. Understanding the Internet Computers in the same network should have IP addresses in the same range, in order to communicate. (i.e. 192.168.121.1 up to 192.168.121.255) Usually, your gateway is assigned the first IP address in the range: 192.168.121.1 Note: Routers will have an internal and external IP address; only the internal IP address is discussed here. Understanding the Internet After making sure that the network cables are all connected properly, we first need to make sure that the Local Area Connection is enabled. To do so: 1. Click Start->Control Panel->Network Connections 2. Right-click Local Area Connection and select Enable Understanding the Internet Understanding the Internet To check the IP address of a computer and its gateway: 1. Click Start ->Run 2. Type ‘cmd’ in text box and click ok 3. At the command line, type: ‘ipconfig /all’ Understanding the Internet Understanding the Internet To check if the computer can communicate with the gateway: 1. Click Start->Run 2. Type ‘cmd’ in text box and click ok 3. At the command line, type: ‘ping [Gateway IP address]’ (e.g. ping 192.168.121.1) If the computer communicates with the gateway, usually, packets sent = packets received. Note: The ping command can be used to check connectivity between any computers in the same network. Understanding the Internet Understanding the Internet If the computer communicates with the gateway, it should be able to access the Internet. If they do not communicate, the problem is within your LAN. If they do communicate and you still cannot access the Internet, you may need to verify your browser settings in Internet Explorer. Understanding the Internet To verify browser settings: 1. Click Start->Internet Explorer 2. On the top menu, select Tools->Internet Options 3. Select the Connections tab and click LAN settings 4. Automatically Detect settings should be enabled. Part IV. Basic Email Basic Email Email – Electronic mail is generally of 2 types: 1. Internet email may travel and be stored on many other networks and machines. 2. Purely internal or intranet email systems, where the information never leaves the corporate or organization's network. Note: Most Web browsers include features that allow you to send and receive e-mail messages, or they enable you to link to another program that handles e-mail. Basic Email To send and receive e-mail you need an e-mail account, with username (user ID) and password. The concept is based on traditional mail, where the user has an inbox (like Post office box) to receive incoming emails. To send an email, the user must know the recipient's email address. E-mail addresses normally consist of a user ID followed by a domain name (usually the name of an organization), just like a Web address. Basic Email There are many benefits to using Email services: Basic Email It is fast and reliable It allows the user to send email to many users, at the same time You can store all the emails you send and receive to view them later You can use the address book for the people you communicate with frequently You can send different attachments, as long as they don’t exceed a certain file size Basic Email As part of the Federal and Regional ICT Action plan, all government offices will eventually require official email addresses. (e.g. [email protected]) Therefore, everyone should try to make regular use of Personalized emails to get the habit and improve faster communication Thank You