* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Byzantine and Sassanid Empire around 600 CE
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Liberalism and progressivism within Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Islamic extremism in the 20th-century Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam in southern Italy wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in South Africa wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
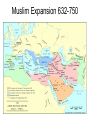
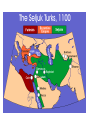
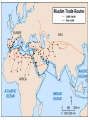
•The Spread of Islam Arabia Before Muhammad • Pastoral nomads (Bedouins), farmers in oasis – depend on each other • Tribal society • Caravan trade important (incense), involved in trade network Mediterranean, Middle East, East Africa, India • Mecca major economic and religious center • Arab tribes under political influence of Byzantine (Christian) and Sasanid empire (Zoroastrian) Byzantine and Sassanid Empire around 600 CE Muhammad´s Life and Teachings • Muhammad former merchant, began to have revelations by archangel Gabriel • Main features: Arab decent traced to Ishmael, Abraham´s son, strictly monotheistic, promise of heaven after death, five pillars (fasting, prayer 5 times a day, almsgiving, confession of faith, pilgrimage to Mecca), universal religion, egalitariansim • Elite in Mecca forces Mohammed to flee to Medina (622 CE, HIJRA, beginning of Muslim calendar) • Describe the origins of Islam. When and where was it created? What geographic features had an impact on it? What other cultures impacted Islam? How? • What are the main beliefs of Islam? Muslim Expansion • Muhammad unites Arab tribes, conquers Mecca in 630, dies 632 • First four succesors (caliphs) expand territory to Middle East, North Africa, Persia • Caliphs are leaders of all Muslims, political and religious (theocracy) • Success possible because of exhausting war between Persia and Byzantium, motivated soldiers, ingenious military leadership, indifferent population • Quarrels over succession lead to split into Sunni and Shia (Ali´s followers) • Shia: mostly in Persia, southern Iraq • Sunni: majority of Muslims Muslim Expansion 632-750 Umayyad Dynasty (652-750) • Capital in Damascus • Wars against Byzantium • Conquest of Spain, further advances stopped by Franks in 732 • Arabic official language of government • Conversions encouraged • Non-Muslims pay a special head tax, but not forced to convert • Judaism and Christianity tolerated Great Mosque in Damascus Abbasid Dynasty (750-1258) • Supported by mawali and Shiites, although Sunni temselves • New capital Baghdad (close to Persia) • First 100 years golden age of Muslim culture • Argument between ulama and caliph about who should have the final say in religious matters • Caliph renounces his final authority in religious matters • Counter caliph in Cordoba, Spain • Regional loyalties, problems with Shiites,rise of new dynasties, and difficulty to control a large empire lead to gradual decline Government • • • • • Rulers legitimate power by upholding shari’a law Caliph is Muhammad’s successor Arab military camps control conquered areas Non-Muslims pay head tax After conquest of Persia, Abbasids rely on Persian bureaucrats • Taxation of agricultural production • Adopt pomp and ceremonies of Persian court Islamic Law • Sunna: tradition of the prophet • Hadith: collection of Muhammad’s words and deeds, several different strands • Quran and Hadith basis for Shari’a • Muslim ruler required to live by and enforce shari’a • Unifying effect on Muslim world, Ibn Battuta could be judge in Africa as well as in India • Countries under Muslim law: Dar al Islam Ibn Battuta´s Travels • Describe the first 100 years of Muslim expansion. How far did their empire reach? • What made the Muslim armies so successful? • How was government organized under the Caliphate? What was new about that? What was adopted from previous cultures? • How important was Islamic law? Political Fragmentation • • • - In 10th century third caliph in Cairo, Egypt North Africa: Berbers (11th cent.) Turkey, Iraq, Syria: Abbasids rely increasingly on mamluks Turkic slave soldiers gain political power Seljuk Turks (11th century) create empire, are „protectors“ of the caliphs, but hold defacto political power • Turkey, Holy Land, Syria: Crusading states(1099-1250), do not survive permanently • Middle East: Mongols (1258 sack of Baghdad, end of Caliphate) • What led to the fragmentation of the Muslim Empire? Cities • New cities and former military camps (Baghdad, Basra, Kufa, Fustat, Qayrawan) • Grow because of conversions and economic growth • Many large cities from Byzantine and Sassanid times, they decline however • Centers of Islam: mosques, schools, universities • Centers of production: Cloth, metal goods, ceramics, glass Economy • International trade dominated by Muslim merchants • Banking system, checks, credit, crucial for long distance trade • Big cities provide markets for trade • Business partnerships (often with Jewish and Christian merchants) • Common currency (dinar) Agriculture • Independent landowners, large estates with slaves, tenant farmers • Production for market, cash crops (sugar, citrus fruits, cotton, rice – from India and China) • Use of fertilizers, water pumps, mills, improved irrigation • Slaves used for sugar cane production • Analyze trade and economic innovations under the Muslim empires. • Analyze the role of cities. • Give examples of economic production in the Muslim Empire. Science and Medicine • House of wisdom in Baghdad (Greek, Indian, Persian, Mesopotamian texts translated into Arabic) • Ibn al Haytham: Scientific Method, Book of Optics • Al-Khwarizmi: Algorithm, Algebra • Ibn Sina: Medical encyclopedia, contagious nature of diseases • Surgeons disinfect wounds, use surgical instruments, trained in hospitals Technology • Transfer between east and west: • Paper, astrolabe, compass, lateen sail, decimal system • Production of steel (swords from Damascus) Women and Slaves • Women veiled and confined to the house, already in Byzantine and Sassanid times • Legal protection of women under Quran, a woman´s soul was considered equal before Allah, but not equality to men (limited divorce rights, keep dowry if divorced by their husband, woman´s testimony in court weighs only half of a man´s, men can have up to four wives) • Slavery allowed, slaves from central Asia, Europe, Africa • Slaves used in households, as soldiers, in agriculture • Forbidden to enslave Muslims Sufism • In 12th and 13th century • Mystic brotherhoods looking for union with God through rituals, emotional sense of religion, personal relationship with Allah • Sufi saints worshipped in countryside • Important in spreading Islam to other countries and making it more popular Mosque in Samarra • Alhambra in Cordoba Arches • Arabesques • What cultural contributions were made under the Muslim empires? What earlier cultures had an impact on Muslim culture? Give examples of cultural transfer. Calligraphy