* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 5
Musical analysis wikipedia , lookup
Circle of fifths wikipedia , lookup
Schenkerian analysis wikipedia , lookup
Chord names and symbols (popular music) wikipedia , lookup
Chord (music) wikipedia , lookup
Consonance and dissonance wikipedia , lookup
Figured bass wikipedia , lookup
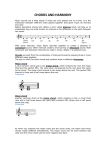
Instructor Anthony Johnson Course Music INTRODUCTION TO MUSIC HARMONY & TEXTURE MUSIC: HARMONY Harmony This is the most common term used by musicians to refer to the simultaneous sounding of musical notes sounding together in time. When working in conjunction with the melody we call that harmony or harmonization. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the "vertical" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the "horizontal" aspect. When we put these harmonies together to create depth in sound and emotional responses they are called chords. MUSIC: CHORDS Chords A chord in music is any harmonic set of two to three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. We also refer to the basic chord as a triad Triad The most frequently encountered chords are triads, because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give seventh chords, extended chords, or added tone chords. The most common chords are the major and minor triads. This referred to collectively as chordal "quality” MUSIC: CONSONANCE & DISSONANCE Consonance This is a term used to describe how harmony sounds to the ear. A consonant chord is a chord that sounds at rest or pleasant, it does noes not produce a feeling of tension. Dissonance This term is also used to describe a certain type of harmony or chord structure. A dissonant chord is a chord that sounds with tension or discorded, this particular style of chord causes uneasiness, unpleasantness or unrest. This is contradictory in human life but music thrives on this craziness. Play example MUSIC: TEXTURE Texture In music, texture is the way the melodic, rhythmic, and harmonic materials are combined in a composition thus determining the overall quality of sound. Texture is often described in regards to the density, or thickness, and range, or width between lowest and highest pitches, in relative terms as well as more specifically distinguished according to the number of voices, or parts, and the relationship between these voices A piece's texture may be affected by the number and character of parts playing at once, the timbre of the instruments or voices playing these parts and the harmony, tempo, and rhythms used. MUSIC: TEXTURE Four types of Textures Monophony Homophony Polyphony Imitation MUSIC: TEXTURE Monophony This is the simplest type of texture, it is a single unaccompanied melody. This can be found in Gregorian chant, or as you sing in the shower in the morning. Another term you might see this referred to as is Monophonic. Play examples MUSIC: TEXTURE Homophony This is when there is a single melody of great importance or one that is quite prominent, playing over a sea of less prominent sounds or chordal structures. Another term for this term you may see is homophonic. This type of music can be thought of as a tight, smooth texture—like silk among textiles. MUSIC: TEXTURE Polyphony When two or more melodies are played, sung, or sounding simultaneously. Another term associated with this is called polyphonic. This style of music makes for a more interesting listening experience, with greater depth of chord structures and plays more into dissonance listening. Yet we have greater pleaser when the chords resolve or become consonant. Another term to be aware of when dealing with this music is counterpuntal which is derived from the word counterpoint. This is the the technique of writing to or more melodies that MUSIC: TEXTURE Imitation This happens when various lines sounding together use the same or similar melodies, with one melody coming in shortly after the entrance of the previous. We also have non imitative polyphony Same as above with the melodies not be similar in any way. QUESTIONS & DISCUSSION Counterpoint is closely related to? Polyphony The effect of chords used with melody is what? Harmony Another name for a chord or how a chord is constructed is called? Triad What term is used for a dischorded or tension sounding chord is used? Disonance