* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download plant circulation
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
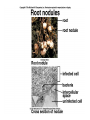
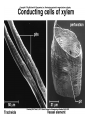
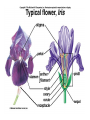
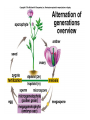
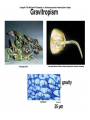
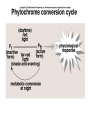
Plant Circulation and Transport • • • • Mycorrhizae Root hairs Macronutrients for plants C, H, O, N, K, Ca, P, Mg, S • Micronutrients for plants • Fe, Cl, Cu, Mn, Zn, Mo, B • • • • • • • • • Xylem Vessel Member Tracheids Transpiration Factors that Affect Humidity Temperature Sunlight Wind Plant Circulation and Transport • • • • • • • • Phloem Sieve-tube members Companion cells. Phloem loading Active transport Role of xylem and water Source to Sink flow Translocation Plant Reproduction • • • • • • Importance of flowers Importance of pollen Importance of seeds Sepals Petals Stamen – Anther – Filament • Pistil – Stigma – Style – Ovary Pollen must physically fit the stigma for pollination to occur. Important for species recognition. The Flower • • • • • • • • Adaptations Coevolution UV markings Nectaries Perfect Flowers Imperfect Flowers Monoecious Diecious Angiosperm Reproduction • Meiosis • Occurs in anthers and ovaries. • Forms haploid spores. • Microspores in the anthers. • Megaspores in the ovaries. • These divide by mitosis to form haploid, multicellular gametophytes. • These form embryo sacs and pollen grains. • Fertilization • Pollen tube • Ovule develops into a seed. • Ovary develops into a fruit. Other information concerning plants • • • • • Seed dispersal mechanisms Seed coat Germination Cotyledons Vegetative propagation Plant Hormones • Auxins--Promote cell elongation; stimulates division in the vascular cambium, promotes flowering and fruit formation. • Gibberellins—Stimulate cell division and elongation, inhibit seed formation, stimulate flowering and pollen-tube growth, ends dormancy, increases fruit size. • Cytokinins—Promote cell division in stems; facilitates healing of wounds, prolongs life of leaves, flowers, and fruits. • Ethylene gas—regulates metabolism, promotes fruit ripening, regulate shedding of leaves and flowers. • Abscisic Acid—Inhibits growth, promotes dormancy & stomate closure. Plant Responses • • • • • • • Photoperiodism Phytochrome Tropisms Phototropisms Role of auxins Gravitropism Positive and negative examples • Thigmotropism • Tendrils