* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
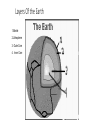
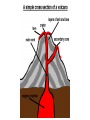
World Geography 3202 Unit One Land And Water Forms Introduction • Unit 1 introduces You to the concept that the earth’s surface is shaped by building-up and wearing away forces. • The unit will help You to examine the constituent parts of the physical environment, forces that created them, patterns in their distribution, and how they influence selected human activities. Patterns in the location of landforms on the earth’s surface Q#1 What category of landforms would be reflected in this type of diagram Q#2 What pattern can be seen from the diagram of landforms illustrated here? Relief map of North America Q#1 How would you describe the distribution of landforms illustrated in this map? Q#2 What type of landforms can you identify on this map? Q#3 Where in the Americas are you most likely to encounter: Mountains Large Lakes Plains and Plateaus Large Rivers River Deltas Questions for Review • Define the term topography. • Differentiate among the terms hill and mountain, and plain and plateau. • Identify: seismology; minerals; rocks; compounds; elements; Igneous rocks; Sedimentary rocks; metamorphic rocks; Valleys; • Describe the distribution of these landforms over the earth’s surface How did this distribution come about? • The earth’s landforms are never static: That is to say, they are constantly in a state of change due to forces at work that both wear down the land, as well as build up and shape the land. • First, we are going to look at forces that build up and shape landforms,…. Forces that shape the earth’s land formations • The face of the earth is shaped by tectonic activity. • Tectonic activity can be described as the movement of the earth’s crust, or “plates” as a result of the pull of gravity; convection currents, or the circulating movement of fluid rocky material in the mantle; and thermal plumes, or vertical columns of molten rocky material in the mantle. Crustal Movement Under the ocean How Plate Tectonics Explains the shaping of landforms • The theory of plate tectonics was formulated during the early 1960s, and it revolutionized the field of geology. • Scientists have successfully used it to explain many geological events, such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions as well as mountain building and the formation of the oceans and continents. What are Tectonic Plates? • Tectonic plates are made of either oceanic or continental crust and the very top part of the mantle, a layer of rock inside the earth. • This crust and upper mantle form what is called the lithosphere. • Under the lithosphere lies a fluid rock layer called the asthenosphere. • The rocks in the asthenosphere move in a fluid manner because of the high temperatures and pressures found there. • Tectonic plates are able to float upon the fluid asthenosphere because they are made of rigid lithosphere. Layers Of the Earth 1.Mantle 2.Lithosphere 3. Outer Core 4. Inner Core How compressional forces are caused. • Compressional / Destructive (subduction zones) plate boundaries occur when an oceanic plate is forced under (or subducts) a continental plate • What do you think could be the result of this type of force? Compression at Work: How tensional forces are caused • Tensional / Constructive (divergent ) plate boundaries occur when two plates move away from each other • What do you think could be the result of this type of force? Relate selected plate movements to compressional and tensional forces • An earthquake is a sudden movement of the earth's surface. • Earthquakes are caused by the movement of the earth's tectonic plates. • Earthquakes occur where the earth's plates meet along plate boundaries An example of the cause of an Earthquake • For example as two plates move towards each other, one can be pushed down under the other one into the mantle. • If this plate gets stuck it causes a lot of pressure on surrounding rocks. • When this pressure is released it produces shock waves. These are called seismic waves. This is an earthquake. • The waves spread out from the point where the earthquake started - the focus. More damage is done near the focus. • The point on the earth's surface directly above the focus is the epicentre. Volcanoes • A volcano is a conical hill or mountain formed by material from the mantle being forced through an opening or vent in the Earth's crust. Volcanoes are found in three states - extinct, dormant and active. • An extinct volcano will never erupt again. • A dormant volcano has not erupted in 2000 years. • An active volcano has erupted recently and is likely to erupt again. • Volcanoes are found along destructive (subducting) plate boundaries, constructive (divergent) plate boundaries and at hot spots in the earth's surface.