* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SCI 111
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic generator wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
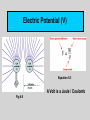
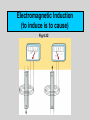
Chapter 6: Electricity and Magnetism Electric Charges Fig 6.3 Electrostatic Charge • Stationary charge confined to an object • Charging mechanisms – Friction – Contact with a charged object – Induction Electrical Conductors and Insulators Measuring Electric Charge • Unit of charge – – – – Coulomb (C) Equivalent to charge of 6.24x1018 electrons! Fundamental metric unit FYI: Equation 6.1 Measuring Electrical Forces Coulomb’s law • Relationship giving force between two charges • Similar to Newton’s law of gravitation but… • Ratio of “k” versus “G” implies gravity weaker. 2 Force “Fields” • Charges surrounded by electric fields • Fields and charges inseparable • Fields act on other charges. Electric Potential (V) Equation 6.3 A Volt is a Joule / Coulomb Fig 6.8 Electric Current (I) • Flow of charge • Reason for charge flow: – Potential differences (voltage) • Charge per unit time – Thus, a “rate” • Units? – Coulomb per second [C/s] – Amperes [Amps]. The Nature of Current (3 Fundamental Conclusions ; see Fig 6.12 caption) Fig 6.12 Fig 6.14 Electric Circuits Fig 6.10 DC versus AC Direct current (DC) • Charges move in one direction • Batteries ; Solar Cells How Stuff Works Homepage Alternating current (AC) • Charges rapidly change directions • Household circuits ; Transformers. FSU Homepage Electrical Resistance (R) Electrical Power and Work Power in circuits Electric bills Cost of operating these items? First: Determine how many Watts (P=IV) Then: Household Circuits and Safety Circuit Breaker • Three-Pronged Plug • Polarized Plugs • GFCI Magnetism A Property of Electricity Magnetic Poles and Fields Fig 6.19 No matter how you cut it, it keeps coming up a “dipole” Fig 6.20 Earth’s Magnetic Field Fig 6.22 Fig 6.21 Magnetic Declination Electric Currents and Magnetism: Current Loops Fig 6.27 Fig 6.25 Current Loops: Basis of a Solenoid Note: Magnetic field is like that of a bar magnet. Electromagnets Widely used “device” Electric Meters Galvanometer Fig 6.28 Electric Switches: Relays and Solenoid Switches Fig 6.29 Electromagnets Other Uses? Telephones and Speakers Electric Motors Fig 6.30 Fig 6.31 Electromagnetic Induction (to induce is to cause) Fig 6.32 Generators Fig 6.33 How does “power” get to your house? Transformers Step-down Fig 6.34 Fig 6.35 Step-down Step-up Step-up Next: Exam 2