* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 1 – construction of logic gates
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
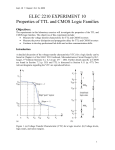
1.0 INTRODUCTION Characteristics of the active electronic components that determine the internal construction and operation of electronic circuitry of a logic gate. +5V 1k Y=0 10k A=1 2 1.1 Types of logic gates NOT AND OR XOR 3 1.1 Types of logic gates (cont.) NAND NOR XOR 4 1.2 Diode as a voltage controlled switch p-n junction component Two type material: p-type & n-type Operation: forward biased & reverse biased Knee voltage: 0.7V (Si) n 0.3V (Ge) 5 1.2 Diode as a voltage controlled switch (cont.) Operation 0V – knee voltage Small current’s flow Beyond knee voltage Negative voltage Leakage current More negative voltage Zener voltage 6 1.2 Diode as a voltage controlled switch (cont.) Forward biased vs. reverse biased 7 1.2 Diode as a voltage controlled switch (cont.) Diode works as a logic ON/OFF switch 8 1.2 Diode as a voltage controlled switch (cont.) Voltage range of logic level for TTL digital IC 9 1.2 Diode as a voltage controlled switch (cont.) Simple 2-input OR gate 10 1.3 Transistor as a voltage controlled switch p-n junction component Two type: PNP & NPN 11 1.3 Transistor as a voltage controlled switch (cont.) B-E junction as switch 12 1.3 Transistor as a voltage controlled switch (cont.) Not gate 13 1.4 Diode controls switching speed Speed limitation when switching diode from ON to OFF and vice versa Minority-carrier density Reverse biased (OFF) Forward biased (ON) 14 1.5 Switching time Rise and fall time Time taken for a signal to go from LOW to HIGH and vice versa. Tr and Tf 15 1.5 Switching time (cont.) Storage time (c) (a) Circuit (b) Input waveform (c) Diode current (d) Diode voltage (e) Minority carrier (d) (e) 16 1.5 Switching time (cont.) Propagation delay Time interval between the application of an input pulse and the occurrence of the resulting output pulse. Cumulative time delay when gates are cascaded. Limits the max freq at which a gate can operate. For propagation delay of 40ns; max freq operation is 25MHz For propagation delay of 25ns; max freq operation is ??? 17 1.5 Switching time (cont.) Propagation delay (cont.) Two types: TPLH - delay time from logic 0 to logic 1. TPHL - delay time from logic 1 to logic 0. Measured at 50% on rising and falling edges of the input and output. Total propagation delay? 18 1.6 TTL family TTL Series: 74 Series – First line of standard TTL ICs 74L Series – low-power version 74H Series - high-speed version 74S Series – Schottky TTL, reduce storage time delay 74LS Series – Low-Power Schottky TTL 74AS Series – Advanced Schottky TTL 74ALS Series – Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL 74F Series – Fast TTL 19 1.6 TTL family (cont.) TTL NAND Gate Operation Schottky TTL 74S Low-Power Schottky TTL Advanced Schottky TTL, 74AS Series (AS-TTL) Current-Sourcing and Current-Sinking Action Totem Pole TTL Tristate (Three-state) TTL TUGASAN 1 : PETA MINDA. TARIKH AKHIR HANTAR : 12 FEB 2010 NO PLAGIARSM!!! 20 1.7 CMOS family CMOS INVERTER GATE 21 1.7 CMOS family CMOS NAND GATE 22 1.7 CMOS family CMOS TRANSMISSION GATE Pass signal in both direction. Useful for digital and analog application. 23 1.8 Comparison of CMOS and TTL TTL CMOS Noise Margin 0.4V (standard) 1.5V (30% of VDD) Typically 45% Power dissipation mW nW Propagation delay TPLH is 11ns – 22ns TPHL is 7ns – 15 ns 30 - 50ns Fan-in Depends on number of unit loads it can handle. Usually 3. Depends on number of unit loads it can handle Fan-out Typically 10 Typically 50 24 1.9 Interfacing TTL and CMOS ICs Connecting the output(s) of one circuit of system to the input(s) of another circuit that has different electrical characteristics. Why? Two things to consider: Utilize strong points of different logic families. Ex: 74AS used in parts need for highest frequency 741 used in slower parts NMOS for LSI parts of the system. Voltage Current Where? – device data sheets 25 1.9 Interfacing TTL and CMOS ICs (cont.) CMOS driving TTL Input current for CMOS are low compared to output current TTL no prob. Input voltage for CMOS are higher than output voltage TTL pull-up resistor. 26