* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geology
Meteorology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
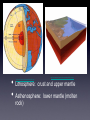
Warm-up 1/27/15 • Take out your Measurement lab from yesterday, the M & M lab if you fixed it and your Info sheet if you still have it. • 1. Keep working on the Reading Guide that you received yesterday. • 2. Make sure that you grab the 1.1/1.2 Reading guide at your table. • We will be taking notes in about 10 minutes. Branches & Spheres Introduction to Earth Science http://recycle4acause.files.wordpress.com/2009/12/earth.jpg • Earth Science: the name for group of sciences that deals with Earth & its space neighbors • Major categories of Earth Science: • Geology • Oceanography • Meteorology • Astronomy • Geology: • • = science that examines Earth, its form & composition, and the changes it undergoes 2 Main Categories: • • • • Physical Geology: study of the materials that Earth is made of; examines the present-day processes that shape our planet. Historical Geology: study of the earth’s geologic history. http://www.evk2cnr.org/WebCams/PyramidOn e/everest-webcam.html http://evk2.isac.cnr.it/ • Oceanography • study of the oceans and oceanic phenomena. • composition of seawater, the movement of water changes in coastline, marine life, and sea-floor topography. •Meteorology • study of the atmosphere and atmospheric phenomena; study of weather and climate. • Involves forecasting of weather, climatology, and the study of the atmosphere. Astronomy • = study of the universe. • Includes the understanding of the origins of our universe, galaxy, and solar system. http://www.fourmilab.ch/earthview/sat ellite.html A View of Earth http://burro.astr.cwru.edu/stu/media/earth.jpg •4 Spheres of Earth • Hydrosphere • Atmosphere • Geosphere • Biosphere Hydrosphere • = water portion of our planet. • Oceans = 97% of all the water on the Earth. • leftover 3% is freshwater • groundwater, streams, lakes and glaciers. Atmosphere • = life-sustaining, thin, gaseous envelope that surrounds the Earth. • exists only 16 km from the Earth’s surface. • Provides the air we breathe; protects from the sun’s heat and radiation. • production of weather and climate. http://www.metoffice.gov.uk/education/teachers/images/enlarge/teachers_factfile_atmosphere.jpg Geosphere • = layer of Earth under both the atmosphere and the oceans. • Composed of the core, the mantle and the crust. • Core: dense, heavy inner sphere • Mantle: less dense • Crust: lighter, thin portion • Not uniform in thickness (thin beneath oceans, thick beneath continents) • Lithosphere: crust and upper mantle • Asthenosphere: lower mantle (molten http://www.planetaryvisions.com/libsamples/GREA_003.jpg http://scienceprep.org/images/earthslayers.jpg rock) Biosphere • = all life of Earth. • Place where living things can be found. • Important to all the other spheres on Earth. • Today’s image of the Earth is VERY different than images from many years ago. • Grand Canyon, Rocky Mountains, Appalachain Mountains, etc. • Different forces have affected the Earth. • • Destructive Forces: forces that wear away parts of the Earth (weathering, erosion). Constructive Forces: forces that work to build up parts of the Earth (mountain building, volcanism) Vocabulary, due Fri. • Geology • • • • • • Independent variable Dependent variable Qualitative Quantitative Scientific theory Scientific law • • • • • • • • • Oceanography Meteorolgy Astronomy Geosphere Hydrosphere Atmosphere Biosphere Lithosphere Asthenosphere