* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.5 Powerpoint
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
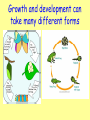
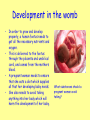
Key Area 2.5 Growth and development Starter Activity: What does each of these grow and develop into? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Apple seed Tadpole Kitten Caterpillar Maggot Potato Starter Activity: Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Apple tree Frog Cat Butterfly Fly Potato plant Lesson 1 Learning Intention: To investigate growth and development of different organisms Success Criteria: • Be able to compare growth and development of different plants and in terms of time scale and size • Be able to compare growth and development of different animals and in terms of time scale, size and organ development • Assess the growth of brine shrimp What is growth? • All living organisms grow. • Growth involves making new cells from existing ones by cell division. • This will cause the size and the mass (weight) of the organism to increase. Growth and development can take many different forms …and different lengths of time 9 months about 20 years Brain development • Humans take a long time to develop because of our large brain size. • This makes us the most intelligent of all the animals. Brain development in the womb • During the 40 weeks of pregnancy, the brain grows rapidly. • Our brains continue to grow from childhood until adulthood. (ml) Brain growth Examples of growth - plants • Plants grow from a an embryo plant inside the seed into a tiny plant called a seedling. • This then continues to grow into a fully grown adult plant. • Some plants are very small when fully grown and some are huge! Examples of growth - animals • Animals grow from a fertilised egg into an embryo, and then into a baby animal. • Some baby animals hatch out of eggs. Others are born from a womb. • The baby animal will then grow into a fully grown adult. This may take a few days, a few weeks, or many years. Activity 1 - Growth in brine shrimp 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Take a sample of water containing brine shrimp from the tank in a small glass beaker. Put a little tank water into a second beaker. Use the wide end dropper to transfer one shrimp to a watch glass sitting on a piece of graph paper. Estimate its size in mm and record in a table. Put this shrimp into the second beaker and select another shrimp to measure. Repeat until you have measured 20 shrimp. Results table Length of brine shrimp (mm) Tally mark Total number 1 2 3 4 5 6 Conclusion : Brine shrimp grow from ___mm when they hatch out to ___mm when they are fully grown. The most common size of brine shrimp in the tank is _____mm. Now draw a histogram of these results. Lesson 2 Learning Intention: To investigate growth and development of different organisms Success Criteria: • Understand the factors that can affect growth of plants • Understand the factors that can affect growth of animals • Understand the idea of a balanced diet and display the foods which make up a healthy balanced diet Growth in plants • The early stages of growth in plants is called germination. • This is when the embryo plant uses the energy from the food store to start growing. • Germination may take a few days or a few weeks. Successful germination • Germination will only be successful if the seed has all the things it needs. • What are the three requirements for successful germination? Growing healthy plants • Seeds need water, oxygen and warmth to germinate. • Seedlings and adult plants will only grow well if they have all the things they need. • What do adult plants need to grow well? • They need water, CARBON DIOXIDE, warmth AND LIGHT. • They also needs MINERALS (nutrients) from the soil like nitrogen, phosphorus and magnesium. What if these are not available? • If a plant does not get all it needs, it will not grow so tall, it may have less leaves, or may not be able to produce flowers and seeds to make the next generation. • In extreme cases the plant may die. Nutrient deficiency • If plants do not get the right minerals, they will not grow healthily. • These leaves show the results of lack of just one mineral. • Plant growers can add fertilisers to overcome these problems. Fungal infection in plants • Plants can suffer from fungal infections which affect their growth and development. • Fungal infections are more common when conditions are very damp or humid. • Farmers and gardeners can use fungicide chemicals to get rid of these infections. How rice plants are affected by salty water Increasing salt in the water • Salt can stunt the growth of rice plants. • The higher the salt content, the smaller the plant. • If rice fields get flooded with sea water this can happen. Effects of air pollution on plants • Acid rain caused by air pollution can harm plants and even kill them. Effect of radiation on plants • Over exposure to radiation – for example the sun’s radiation – can cause damage to plants. PLANTS DAMAGED BY OVEREXPOSURE TO UV RADIATION FROM THE SUN LOW RADIATION HIGH RADIATION Human growth and development • In the same way as plants, humans will not be able to grow to their maximum height or weight if they do not get enough food. • We also need to get the right kinds of food. • This is called a balanced diet. H&W Balanced diet • A balanced diet contains the correct quantities of each of the main food groups. • We need lots of some types of food and only a little of others. • We should eat more of the foods at the bottom of the pyramid, and less of those at the top. Fats Proteins Fibre, vitamins and minerals Carbohydrates H&W Activity - Balanced diet plate 1. Use a ruler to measure and find the very centre of the paper plate. Mark a small dot here in pencil. 2. Draw one line from the centre dot to the edge. 3. Use a percentage pie chart measurer to mark off segments of the same size as shown in the diagram. 4. Write the name of the food group and % along the edge of the plate. 1. Cut out the foods on the handout sheet 2.Stick each picture onto the correct segment. 3.Now colour them in. • Understand the factors that can affect growth of plants Lesson 3 Learning Intention: To investigate growth and development of different organisms Success Criteria: • Know the main chemical food groups and their use in the body • Know about diseases caused by lack of vitamins and minerals • Know the effects on growth of starvation • Understand the effects of harmful chemicals on development of a human foetus Chemicals in food H&W Our food is a mixture of many different chemicals. These food chemicals can be split into groups. The three major groups are: Carbohydrates (starch and sugars) which are used for energy. Fats which are also for energy. Proteins which are used for growth and repair of cells and tissues. As well as these, our food also contains very small quantities of vitamins and minerals for health, fibre to keep food moving through the gut, and water for chemical reactions. Food Groups Food group H&W Use in the body Carbohydrate Fat Growth and repair For chemical reactions Fibre Vitamins and minerals Vitamins and minerals H&W • Vitamins A,B,C,D and K are all very important. The minerals we need include calcium and iron. • These chemicals or nutrients are needed in very small quantities, but are still very important • They help to maintain the health of the body. • Lack of any one of these can cause illness or disease. Deficiency disease • Lack of Vitamin C can cause a condition called scurvy which damages skin and teeth. • Lack of Vitamin D can cause a condition called rickets where bones are too soft and can bend. • Lack of iron can cause a blood condition called anaemia which reduces the number of red blood cells. H&W Not enough food H&W • People in some parts of the world simply do not get enough food. This causes stunted growth and serious health problems. Not enough food H&W • People who go hungry all the time are likely to be underweight, weighing significantly less than an average person of their size. • If malnourished as a child, their growth may also be stunted, making them much shorter than average. • In developing countries, 1 out of 4 children younger than age 5 are underweight. Starvation Development in the womb • In order to grow and develop properly, a human foetus needs to get all the necessary nutrients and oxygen. • This is delivered to the foetus through the placenta and umbilical cord, and comes from the mothers blood. • A pregnant woman needs to ensure that she eats a diet which supplies all that her developing baby needs. • She also needs to avoid taking anything into her body which will harm the development of her baby. What substances should a pregnant woman avoid taking? Effects of smoking on foetal development • Carbon monoxide in cigarette smoke causes less oxygen to get to the baby. • Nicotine causes less glucose to reach the baby. • These then slow down the growth of the baby. • On average, babies born to mothers who smoke are lighter than those of mothers who do not smoke. H&W Effects of alcohol on foetal development H&W Effects of drugs on foetal development • Drugs can be legal, like paracetamol or antibiotics. Other drugs are illegal, like cannabis and heroin. • Any kind of drug can harm a developing foetus. • The main effects are brain damage and limb malformation. • Babies of illegal drug users can be born addicted to the drug. Premature birth H&W • Smoking or drinking alcohol during pregnancy also increases the risk of the baby being born prematurely. • Premature babies have health issues which sometimes affect them throughout their whole life. Video clips • • • • Balanced diet Vitamin deficiencies Malnutrition World food shortage