* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 18.3 - CPO Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
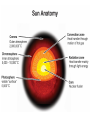
Astronomy Chapter Eighteen: Earth, the Moon, and the Sun • 18.1 The Earth and Its Moon • 18.2 Earth Cycles • 18.3 The Sun Investigation 18B Earth’s Seasons • What causes the seasons? 18.3 The Sun • The Sun is a star. • A star is a giant, hot ball of gas held together by gravity. • The Sun is mediumsized compared with other stars in the universe. Approximately 1 million planet Earths could fit inside the Sun! 18.3 The Sun • Gravity squeezes the atoms in the core of a star so tightly that they fuse together in a reaction called nuclear fusion. • In the process, huge amounts of energy are given off. 18.3 Anatomy of the sun • • The corona is the outermost layer of the sun’s atmosphere, extending millions of kilometers beyond the sun. Sunspots are areas of gas that are cooler than the gases around them. 18.3 Features of the sun • Occasionally, large “loops” of gas called prominences can be seen jumping up from groups of sunspots. 18.3 Features of the sun • Solar wind is an electrically charged mixture of protons and electrons. • Auroras, called the northern lights, occur when layers of our atmosphere are energized by solar winds. Research Connection Solar Observatory • The staff of Big Bear Solar Observatory study the sun, solar phenomena, and the solar atmosphere. Activity Distance from Earth to the Sun • Scientists have been studying the sun, its behavior and its relationship to the Earth. • Graph the month of the year versus the distance of Earth to the Sun using a spreadsheet program.