* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blocks of the ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
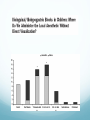
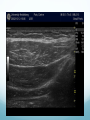
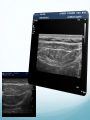
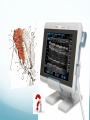
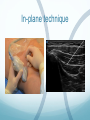
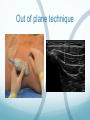
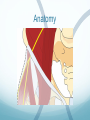
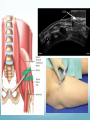
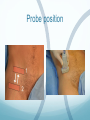
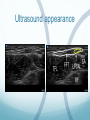
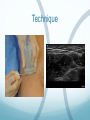
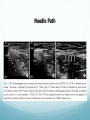
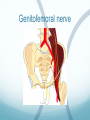
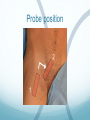
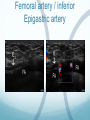
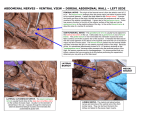
Ilioinguinal, Iliohypogastric and LCNT & Genitofemoral Dr Barry Nicholls. Taunton UK Faculty Disclosure X No, nothing to disclose Yes, please specify: Company Name Honoraria/ Expenses Consulting/ Advisory Board Funded Research Royalties/ Patent Stock Options Ownership/ Equity Position Employee Other (please specify) Ilioinguinal & Iliohypogastric nerves Anatomy The anterior primary rami of L1 divides into the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves. The nerves enter the abdomen posterior to the medial arcuate ligament(what's this) ?from the diaphragm They pass anterolateral to quadratus lumborum and pierce the Transversus Abdominis muscle close to the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS). The nerves pass close to the ASIS in the neurovascular plane (between Transversus Abdominis and internal oblique), before piercing the external oblique to reach the superficial tissues They supply the muscles and skin of the inguinal and pubic regions. The anterior primary ramus of L1 may divide as far anterior as the ASIS, with only one nerve crossing the posterior abdominal wall The subcostal nerve arises from T12, courses in the same plane as above, and divides into a branch which supplies the upper border of the postero-lateral thigh and buttock. ..., Indications n = 11265 Chronic Pain: 12% Br J Anaesth 2006 Aug;97(2):238-43 In-plane technique Out of plane technique Lateral Cutaneous Nerve of the Thigh (LCNT) Anatomy The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a pure sensory nerve, It arises from the dorsal rami of L2 and L3 (lumbar plexus). It emerges from the lateral border of psoas major, below the iliac crest, and crosses the iliacus muscle anteriorly (deep to its fascia) obliquely towards the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS). It passes under the inguinal ligament at a variable distance from the ASIS (typically 1cm - Range: 3mm to 7cm), and crosses over the sartorius muscle in the thigh. (Range: 2 to 11cm distal to the ASIS) It divides into anterior and posterior branches to supply the skin of the lateral thigh. Anatomy Probe position Ultrasound appearance Technique Needle Path Genitofemoral nerve Indications Genitofemoral neuralgia Anatomy The genitofemoral nerve (GFN) arises from the roots of L1 and L2 (lumbar plexus) within the psoas muscle. It penetrates the psoas muscle at L3/4 to lie on its anterior surface. It divides into a genital and femoral branch at a variable distance above the inguinal ligament. (Approximately 1-1.5cm) Femoral branch: Follows the external iliac artery and passes under the inguinal ligament superficial to the femoral sheath. (Sensory: skin - upper medial aspect of the thigh). Genital branch: The nerve lies lateral to the inferior epigastric artery at 1 - 1.5 cm above the inguinal ligament. It passes through the deep (internal) inguinal ring and inguinal canal and lies within the spermatic cord.. (Sensory/motor - anterolateral aspect of the scrotum and cremaster muscle). Genitofemoral nerve Probe position Femoral artery / inferior Epigastric artery Approach Thanks to Dr his slides . Jens Keesler for permission to use