* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP European History Curriculum Map
Societal collapse wikipedia , lookup
Historical revisionism wikipedia , lookup
Historical materialism wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Homer wikipedia , lookup
Origins of society wikipedia , lookup
Early modern period wikipedia , lookup
Modern history wikipedia , lookup
Historiography wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of history wikipedia , lookup
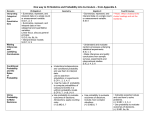
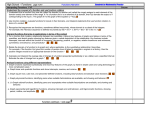
AP European History Curriculum Map 11-12 PLCS Connections A/H Connections Writing/Literacy Connections Date Aug. 912 Content Class Introduction Yearly Overview Geography Skills, Concepts, & Terminology Early Civilizations Late Middle Ages Core Content & Academic Expectations Addressed SS-HS-4.1.1- Using geographic tools (DOK 3) SS-HS- 4.2.2Advantages and disadvantages for human activities (DOK 2) SS-HS-4.3.1- Push/Pull Factors (DOK 3) SS-HS-4.3.2Geography & economic interdependence (DOK 2) SS-HS-4.4.2Modification of Environment (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human Skills Define & explain key terms Explain and analyze the reasons for the distribution of physical and human features on Earth's surface Explain and evaluate how physical and human characteristics of regions create advantages and disadvantages for human activities Describe movement and settlement patterns of people in various places and analyze causes of that movement and settlement Explain, analyze & evaluate how technology has facilitated the movement of goods, services, and populations; increased economic interdependence at all levels and influenced development of centers of economic activity Explain how human modifications to the physical environment, perspectives on the use of natural resources and natural disasters may have possible global effects in the modern world Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Activities/Assessments Lecture/Discussion Syllabus Homework Create overview posters Poster Presentations Geography Discussion Watch & Discuss “Plato’s The Republic Video” Guided Open Response Question/Score a 4! McKay Text Online Activities Chapter 12 Summer Work Test Key Terminology Socratic Method Socrates Plato Aristotle Civil Disobedience “Great Famine” Black Death Hundred Years’ War Joan of Arc Crecy Agincourt nd 2 Babylonian Captivity Conciliarists Jacquerie Aug. 1526 Renaissance behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.1Renaissance (DOK 2) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Chapter 13 Study Guide & Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 1 Sec 1 &2 McKay Text Online Activities Key Terms Handout Renaissance: New Directions Activity Rise of National Monarchs Activity States of Italy During the Renaissance Map Activity “Perfect Courtier” Primary Source Reading & Discussion “Oration on the Dignity of Man” Primary Source Reading & Discussion “Praise of Folly” Primary Source Reading & Discussion Renaissance Dante & The Divine Comedy vernacular Louis XI War of the Roses Fuggers Bourgeoisie Charters Guilds Lorenzo the Magnificent Quintilian Humanism Petrarch Secularism Printing press Johann Gutenberg Signori Oligarchies Individualism Aug. 29Sept. 9 Reformation Religious Wars Exploration AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.1Reformation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.2Exploration (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.1.1- Scarcity (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.2.1- Economic Systems (DOK 2) Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, analyze, and evaluate how humans began to rediscover the ideas of the Classical Age and to question their place in the universe Lives & Activities of Women Handout & Discussion “Utopia” Primary Source Reading & Discussion The Renaissance: Challenging Traditional Periodization Reading & Discussion Vendetta as Private Justice Reading & Discussion Lecture/Discussion History Alive Artwork Analysis Activity History Alive Tour of Florence Activity or Renaissance Project Watch & Discuss “Machiavelli’s The Prince Video” Watch & Discuss “All About the Renaissance Parts 1 & 2 Videos” Open Response Question Renaissance Assessment Humanism Secularism Michelangelo Castiglione & The Courtier Watch & Discuss “Reformation: Just the Facts” Video” or “Protestant Reformation Video McKay Text Online Activities History Alive Indulgence Activity Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 1 Sec. 3 & 4 Modern World History Study Guide Ch 3 & 4 Sec.1 Chapter 14 Study Guide & Key Terms “Luther: Giant of His Time & Ours” Reading & Discussion 95 Theses Analysis Luther: Reformer or Reformation Thomas à Kempis & The Imitation of Christ John Wycliff Jan Huss Mysticism Girolamo Savonrola Martin Luther 95 Theses Indulgence Pope Leo X Johann Tetzel Charles V Diet of Worms Edict of Worms Protestant Sola scriptura Machiavelli & The Prince Christian humanists Thomas More & Utopia Erasmus & In the Praise of Folly SS-HS-3.2.3- Free Enterprise System (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.4.2- Increasing Productivity (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.4.3- Economic Interdependence (DOK 2) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Explain, analyze, and evaluate how humans began to rediscover the ideas of the Classical Age and to question their place in the universe Explain and give examples of how new ideas and technologies led to an Age of Exploration by Europeans and analyze its impact on the absolute monarchies and caused significant political, economic and social changes Give examples of and explain how scarcity of resources necessitates choices at both the personal and societal levels in the modern world Compare and contrast economic systems based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security, and growth in the modern world Explain how individuals attempt to maximize their profits based on their role in the economy Describe and give examples of how factors have increased productivity in the world Explain and give examples of how interdependence of personal, national, and international economic activities often results in international issues and concerns in the modern world Catholic Discussion Two Interpretations of the Reformation Reading & Discussion Calvin’s TULIP Discussion “Who in the World was John Calvin?” Reading & Discussion John Calvin Handout Reading & Discussion Trial of Anne Boleyn Reading & Discussion “Address to the German Nobility” Primary Source Reading & Discussion Teresa of Avila Handout Reading & Discussion Protestant Revolt: A Move Towards the Unknown Activity Peasants: The Other Side of Civilization Activity History Alive Reformation Spoke Diagram Activity Chapter 15 Study Guide & Key Terms Auto-de-Fe Reading & Discussion Thirty Years’ War: The European World at War Activity Edict of Nantes Primary Source Reading & Discussion Chapter 19 Study Guide (pgs. 643-656 only) Lecture/Discussion Watch & Discuss “Age of Exploration: Just the Facts Video” History Alive Sunken Ship Activity History Alive Monument to Exploration Activity Transubstantiation Consubstantiation Diet of Speyer Peace of Augsburg Ulrich Zwingli John Calvin Anabaptists Henry VIII Act of Annates Act of Appeals Act of Supremacy Elizabethan Settlement Act of Uniformity St. Ignatius Loyola & the Jesuits Council of Trent Index of Prohibited Books Treaty of CateauCambrésis Concordat of Bologna Huguenots St. Bartholomew’s Day Massacre Politiques Henry IV & The Edict of Nantes Spanish Armada Thirty Year’s War Peace of Westphalia Henry the Navigator Bartholomew Diaz Caravel Compass Astrolabe Christopher Columbus Ferdinand Magellan Sept. 12-23 Absolute Monarchies SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.2- Absolute Monarchies (DOK 2) SS-HS-1.1.1- Types of Government (DOK 3) AE 2.14- Democratic Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Columbus Document Reading & Discussion Westward Ho! Geography Application Handout Atlantic Salve Trade Map Activity Exploration & Colonization Map Activity Exploration & Empires Map Activity Bartolome de las Casas Primary Source Reading & Discussion Severity of Spanish Rule Reading & Discussion Commercial Revolution Activity Aristocracy Plays at War Activity Columbian Exchange Video & Packet Epidemic Disease Video & Packet Reformation & Religious Wars Assessment Age of Exploration Open Response Question Hernando Cortes Francisco Pizzaro John Cabot Columbian Exchange Witchcraft Skepticism Essay & Michel de Montaigne William Shakespeare Baroque Mercantilism Navigation Acts Atlantic Slave Trade Adam Smith & Wealth of Nations Lecture/Discussion Chapter 16 Study Guide & Key Terms McKay Text Online Activities Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 5 Sec. 1-5 Assessing Elizabeth I Reading & Discussion Elizabeth I Reading & Discussion Viewpoints of Elizabeth I Reading & Discussion th 17 Century French Leaders Handout Sovereignty Henry IV Cardinal Richelieu Fronde Louis XIV Palace of Versailles Parlements Supreme Council Intendants Jean-Baptiste Colbert & mercantilism Revocation of the Edict of Nantes “Hapsburg Ring” principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Compare and contrast various forms of government in the world and evaluate how effective they have been in establishing order, providing security, and accomplishing common goals Speech of a Queen Priamry Source Reading & Discussion Two Views of Versailles Primary Source Reading & Discussion Babington Plot Reading & Discussion Virginia Company Primary Source Reading & Discussion “Pilgrims and Puritans: The Struggle for Religious Freedom in England (15171692)” Video & Discussion “Trials for Treason Act” Primary Source Reading & Discussion Glorious Revolution Packet Chapter 17 Study Guide & Key Terms “In Praise of Peter” Primary Source Reading & Discussion “Vienna: A Bustling City” Primary Source Reading & Discussion Europe, 1560 Map Activity Europe, 1648 Map Activity Elbe-Triste Line Activity Absolute Monarchs WebQuest Absolutism & Constitutionalism Assessment War of Devolution Treaty of Aix-laChapelle Franco-Dutch War Reunions William of Orange & League of Augsburg War of the League of Augsburg Treaty of Ryswick War of Spanish Succession Treaty of Utrecht Constitutionalism James I & Trew Law of Free Monarchies Puritans Authorized Bible Charles I “Grand Remonstrance” Oliver Cromwell New Model Army Commonwealth Instrument of Government Protectorate Restoration Charles II Test Act James II Glorious Revolution William & Mary Bill of Rights Act of Toleration Act of Succession Cabinet System Robert Walpole Prime Minister Hohenzollern Family Frederick William Junkers Pragmatic Sanction Treaty of Karlowitz Peter the Great Westernization Holy Synod Table of Ranks Sept. 26Oct. 7 Scientific Revolution Enlightenment SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.3- Age of Revolutions (Scientific Revolution & Enlightenment, DOK 3) SS-HS-1.1.1- Types of Government (DOK 3) SS-HS-1.2.1- “Common Good” (DOK 3) SS-HS-1.2.2- Limited Government (DOK 3) SS-HS-3.1.1- Scarcity (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.2.1- Economic Systems (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.3.1- Supply & Demand (DOK 2) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Analyze how an Age of Revolution brought about changes in science, thought, government, and industry that shaped the modern world and evaluate the long range impact of these changes on the modern world Compare and contrast various Chapter 18 Study Guide & Key Terms Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 6 Sec. 1-3 McKay Text Online Activities Lecture/Discussion History Alive Scientific Revolution Activity The Scientific Revolution: The Search for Meaning Activity Isaac Newton Primary Source Reading & Discussion Trial of Galileo Reading & Discussion Dissecting the Human Corpse Reading & Discussion History Alive Island Government Activity Encyclopedia Primary Source Reading & Discussion Salon Handout Voltaire Primary Source Reading & Discussion Tormenta Reading & Discussion Beccaria Primary Source Reading & Discussion Voltaire Lisbon Earthquake Scientific Revolution Geo-centric Helio-centric Nicolas Copernicus Galileo Isaac Newton & gravity William Harvey Andreas Vesalius Enlightenment Rationalism Philosophes Thomas Hobbes John Locke “Natural Rights” Montesquieu Voltaire Rousseau “General will” Beccaria Physiocrats Adam Smith Salons Diderot & Encyclopedia Enlightened Absolutism Enlightened Despot Maria Theresa Joseph II Oct. 1728 Changes to Life during Early Modern Europe AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events forms of government in the world and evaluate how effective they have been in establishing order, providing security, and accomplishing common goals Analyze how powers of government are distributed and shared among levels and branches and evaluate how this distribution of powers protects the "common good" Interpret the principles of limited government and evaluate how these principles protect individual rights and promote the "common good.” Give examples of and explain how scarcity of resources necessitates choices at both the personal and societal levels in the modern world Compare and contrast economic systems based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security, and growth in the modern world Explain and give examples of how numerous factors influence the supply and demand of products Reading & Discussion How Enlightened Were the Philosophes? Reading & Discussion Scientific Revolution & Enlightenment Assessment Enlightenment Essay Question Frederick the Great Catherine the Great Louis XV SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.3- Age of Revolutions (DOK 3) Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and Chapter 20 Study Guide & Key Terms McKay Text Online Activities Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 4 Sec 2-4 Coffee House Society Primary Source Reading & Discussion th 17 Century Medicine Document-Based Question Family Life Children & Education Dietary changes Medical practice Religion Pietism John Wesley Methodists Popular Culture Carnival Blood Sports Oct. 31Nov.18 French Revolution AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Analyze how an Age of Revolution brought about changes in science, thought, government, and industry that shaped the modern world and evaluate the long range impact of these changes on the modern world SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.3- Age of Revolutions (French Revolution, DOK 3) SS-HS-1.1.1- Types of Government (DOK 3) SS-HS-1.1.2- Protection of Rights (DOK 3) SS-HS-1.2.1- “Common Good” (DOK 3) SS-HS-1.2.2- Limited Government (DOK 3) AE 2.14- Democratic Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are Chapter 21 Study Guide & Key Terms McKay Text Online Activities Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 6 Sec. 4 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 7 Sec. 1-4 Lecture/Discussion Paris Before Revolution Reading Changing Images of the King Handout Accomplishments of the Revolution Handout Trial of Louis XVI Reading & Discussion Radical Phase of the Revolution Handout Moniteur Headlines Handout Stamp Act Boston “Tea Party” Coercive Acts Thomas Paine & Common Sense Declaration of Independence Treaty of Paris Constitutional Convention Checks & Balances Estates System First Estate Second Estate Third Estate Marie Antoinette “Assembly of Notables” Abbé Sieyès & What is the Third Estate? principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Analyze how an Age of Revolution brought about changes in science, thought, government, and industry that shaped the modern world and evaluate the long range impact of these changes on the modern world Compare and contrast various forms of government in the world and evaluate how effective they have been in establishing order, providing security, and accomplishing common goals Explain and give examples of how democratic governments preserve and protect the rights and liberties of their constituents through different sources Analyze how powers of government are distributed and shared among levels and branches and evaluate how this distribution of powers protects the "common good" Thoughts of Napoleon Activity Napoleon Giant or Midget Activity Napoleon’s Coronation Primary Source Reading & Discussion Napoleon’s Russian Campaign Geography Application Worksheet French Revolution, 17891793 Map Activity Summer of Riots Primary Source Reading & Discussion Declaration of the Rights of Man & Citizen Primary Source Reading & Discussion History Alive Experiential Exercise or Watch & Discuss “French Revolution Parts 1 & 2” Video French Revolution Assessment National Assembly Tennis Court Oath Bastille Emigrés Great Fear Declaration of the Rights of Man & Citizen Constitution of 1791 Civil Constitution of the Clergy Assignants Brunswick Manifesto Declaration of Pillnitz First Republic Jacobins Girondists Sans-culottes Committee of Public Safety Robespierre Reign of Terror Thermidorian Reaction Directory Napoleon Brumaire Coup Constitution of 1799 Plebiscite Napoleonic Code Concordat of 1801 Confederation of the Rhine Continental System Orders in Council Milan Decrees Peninsular War Battle of Nations Duke of Wellington Elba Hundred Days Battle of Waterloo St. Helena Congress of Vienna Klemens von Metternich Balance of Power Quadruple Alliance Holy Alliance Nov. 21Dec. 20 Agricultural Revolution Industrial Revolution SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.3- Age of Revolutions (Agricultural & Industrial Revolutions, DOK 3) SS-HS-3.1.1- Scarcity (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.2.1- Economic Systems (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.2.3- Free Enterprise System (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.3.1- Supply & Demand (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.4.2- Increasing Productivity (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.4.3- Economic Interdependence (DOK 2) SS-HS-4.3.1- Push/Pull Factors (DOK 3) SS-HS-4.3.2- Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Analyze how an Age of Revolution brought about changes in science, thought, government, and industry that shaped the modern world and evaluate the long range impact of these changes on the modern Lecture/Discussion McKay Text Online Activities Chapter 19 (pgs. 629-643 only) Study Guide & Key Terms Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 9 Sec. 1-3 Industrial Revolution: England’s Advantages Activity Chapter 22 Study Guide & Key Terms Industrial Revolution: Human Side Activity Industrial Revolution Video Living During the Industrial Revolution Video Importance of English Tradespeople Primary Source Reading & Discussion Beginner’s Luck Primary Source Reading & Discussion British Class System Image Analysis Plight of the Miners Primary Source Reading & Discussion Technology Transforms an Open-field system Three-field system Agricultural Revolution Crop Rotation Jethro Tull Enclosure Industrial Revolution Cottage industry/”putting out” system James Hargreaves Richard Arkwright Samuel Crompton Edmund Cartwright Eli Whitney Urbanization Steam Engine James Watt Matthew Boulton Henry Bessemer Bessemer Process Thomas Telford John MacAdam James Brindley LiverpoolManchester Railroad George Stephenson Geography & economic interdependence (DOK 2) SS-HS-4.4.2Modification of Environment (DOK 2) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events world Give examples of and explain how scarcity of resources necessitates choices at both the personal and societal levels in the modern world Compare and contrast economic systems based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security, and growth in the modern world Explain how individuals attempt to maximize their profits based on their role in the economy Explain and give examples of how numerous factors influence the supply and demand of products Describe and give examples of how factors have increased productivity in the world Explain and give examples of how interdependence of personal, national, and international economic activities often results in international issues and concerns in the modern world Describe movement and settlement patterns of people in various places and analyze causes of that movement and settlement Explain, analyze & evaluate how technology has facilitated the movement of goods, services, and populations; increased economic interdependence at all levels and influenced development of centers of economic activity Explain how human modifications to the physical environment, perspectives on the Age Video & Packet Industrialization & Urbanization in Europe Map Activity Manchester Geography Application Worksheet Steam Engine Primary Source Reading & Discussion Industrial Revolution Assessment Industrial Revolution Open Response Question Industrial Revolution Essay Question Industrial Revolution DBQ Rocket Thomas Malthus & Esssay on the Principle of Population Fredrich Engels & Condition of the Working Class in England in 1844 Factory Act of 1833 “Luddites” “Peterloo Massacre” Crystal Palace David Ricardo & “iron law of wages” Tariff protection Economic nationalism Mines Act of 1842 Combinations Acts Grand National Consolidated Trades Union use of natural resources and natural disasters may have possible global effects in the modern world Jan. 413 Europe 1815-1848 (Age of Metternich, 1830 Revolutions, 1848 Revolutions) SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.3- Age of Revolutions (Political Upheavals, DOK 3) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Analyze how an Age of Revolution brought about changes in science, thought, government, and industry that shaped the modern world and evaluate the long range impact of these changes on the modern world Lecture/Discussion McKay Text Online Activities Chapter 23 Study Guide & Key Terms Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 7 Sec. 5 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 8 Sec. 2 & 4 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 9 Sec. 4 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 10 Sec. 1 Metternich System Analysis Activity Emerging Political Spectrum Activity Revolutions of 1848 : A Case Study in Nationalism Activity In Search of an Economic View of the World: Smith to Marx Activity Metternich’s Views Primary Source Reading & Discussion Failure of the National Workshops Primary Source Reading & Discussion Communist Manifesto Primary Source Reading & Discussion Changing Threads of Unity Activity Britain: A Case Study in the Quadruple Alliance Holy Alliance Carlsbad Decrees Conservatism Edmund Burke Liberalism Laissez-faire Utilitarianism Jeremy Bentham David Ricardo & Principle of Political Economy & Taxation Nationalism Radicalism Romanticism William Wordsworth John Constable Francisco Goya Feminism Olympe de Gouges Mary Wollstonecraft Socialism Utopian Socialism Robert Owen Count Henri de Saint-Simon Charles Fourier Practical Socialism Louis Blanc National Workshops Marxist Socialism Karl Marx Communist Jan 17Feb. 3 Europe 1848-1914 SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of Evolution of Democracy Activity Europe 1815-1848 Assessment Manifesto Eugene Delacroix Ferdinand VII Battle of Navarino Decembrists Alexander I Nicolas I Russification Ultras Charles X Four Ordinances Louis-Philippe “Bourgeoisie Monarchy” Polish November Rising Reform Bill of 1832 Catholic Emancipation Act Corn Laws Anti-Corn Law League Chartist Movement “June Days” Louis-Napoleon Zollverein Frederick William IV United Landtag Grossdeutsch Kleindeustch Declaration of the Basic Rights of the German People Giuseppe Mazzini Lecture/Discussion McKay Text Online Activities Chapter 25 Study Guide & Key Terms Modern World History Second French Empire Napoleon III Piedmont-Sardinia Victor Emmanuel II Camilio di Cavour SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.4- Isms (DOK 3) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Analyze how nationalism, militarism, and imperialism led to world conflicts and the rise of totalitarian governments Reading Study Guide Ch. 10 Sec. 3 & 4 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 8 Sec. 3 Bismarck Telegram Analysis Dreyfus Affair Primary Source Reading & Discussion Dreyfus Affair Reading Chapter 24 Study Guide & Key Terms Humanitarianism: A Better World Activity Progress of Decline Primary Source Reading & Discussion Social Darwinism Primary Source Reading & Discussion Nietzsche’s Last Man Primary Source Reading & Discussion Belle Epoque Image Analysis English Social Life Handouts Soccer Stadium Handout History Alive Scramble for Land Activity Chapter 26 Study Guide & Key Terms Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 11 Sec.1-5 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 12 Sec. 1-3 History Alive Imperialist Motives Activity Imperialism: Taking up the White Man’s Burden Activity Victoria Takes the Reigns Primary Source Reading & Treaty of Turin Giuseppe Garibaldi Wilhelm I Otto von Bismarck Realpolitik Autsro-Prussian War North German Confederation Franco-Prussian War Ems Dispatch Francis-Joseph I Dual Monarchy Augsleich of 1867 Alexander II Edict of Emancipation Zemstvos Alexander III “Bloody Sunday” October Manifesto Duma Adolphe Theirs Paris Commune Home Rule Irish National Land League Easter Week Uprising Ulster Irish Republican Army Pogroms Houston Stewart Chamberlain Karl Leuger Dreyfus Affair Zionism Thedor Herzl Chaimm Weismann Kulturkampf Feb. 624 World War I Russian Revolution SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect Discussion No Need for Western Learning Primary Source Reading & Discussion Opium Trade Handout Commodore Perry & Japan Handout Migration Geography Application Worksheet Africa, 1914 Map Activity Europe 1848-1914 Assessment European Sports DBQ Revisionism Smallpox Edward Jenner Cholera John Snow Germ theory of disease transmission Louis Pasteur Robert Koch Antisepsis Joseph Lister Anesthesia Children’s Act of 1908 Ferry Laws Domestic servants Edwin Chadwick British Public Health Act of 1875 Lord Leverhume Ebenezer Howard British Housing Act of 1890 Boy Scouts “The Woman Question” Imperialism Berlin Conference 1884-1885 White man’s burden Sepoy Mutiny Meiji Restoration Boxer Rebellion Chapter 27 Study Guide & Key Terms McKay Text Online Activities Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 13 Sec. 1-4 Modern World History Three Emperor’s League “two power rule” Dreadnought Hague Conventions 1899 & 1907 Triple Alliance SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.4- Isms (DOK 3) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Analyze how nationalism, militarism, and imperialism led to world conflicts and the rise of totalitarian governments Explain how people from different cultures with different perspectives view regions in different ways, sometimes resulting in conflict in the modern world Reading Study Guide Ch. 14 Sec. 1 Lecture/Discussion Trench Warfare Activity World War I: The War in Europe Video World War I: On the Homefront Video Taylor Outbreak of WWI Reading & Discussion Wilson’s 14 Points Handout Shell Shock Reading & Discussion Europe in World War I Map Activity Naval Blockades Reading & Discussion Tank in WWI Reading & Discussion Militarism Image Analysis Diplomatic Maneuvers Primary Source Reading & Discussion Poets View of War Primary Source Reading & Discussion Indictment of Germany Primary Source Reading & Discussion Alliance System: A Search for Security Activity The Great War: Sidney Bradshaw Fay Thesis Activity Treaty of Versailles: An Outside Perspective Activity Russian Revolution: The More Things Change Activity Plight of Russian Peasant Primary Source Reading & Discussion Lenin’s Return Primary Source Reading & Activity Triple Entente “powder keg of Europe” Archduke Franz Ferdinand Gavrilo Princip Black Hand “blank check” Trench Warfare Lusitania Total war War Raw Materials Board Wilfred Owen Rationing Spanish Flu Rasputin Petrograd Soviet Army Order No. 1 Lenin Bolsheviks Leon Trotsky Stalin Cheka Armistice League of Nations Big Four David Lloyd George Georges Clemenceau Vittorio Orlando Woodrow Wilson Fourteen Points Treaty of Versailles Paris Peace Conference Balfour Declaration Brest-Litovsk Primary Source Reading & Discussion Trial of Nicolas & Alexandra Reading Watch Animal Farm World War I & Russian Revolution Assessment Feb. 27Mar. 9 Between the Wars Era SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.4- Isms (DOK 3) SS-HS-3.1.1- Scarcity (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.2.1- Economic Systems (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.3.1- Supply & Demand (DOK 2) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Analyze how nationalism, militarism, and imperialism led to world conflicts and the rise of totalitarian governments Give examples of and explain how scarcity of resources necessitates choices at both the personal and societal levels in the modern world Compare and contrast economic Chapter 28 Study Guide & Key Terms McKay Text Online Activities Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 15 Sec. 1-2 World War I & Its Aftermath Video Lecture/Discussion Trial of Adolph Hitler Reading & Discussion Kellogg-Briand Pact Image Analysis Hitler’s Political Ideas Primary Source Reading & Discussion Munich Agreement Primary Source Reading & Discussion French Search for Security: An Elusive Goal? Activity Potpourri: A Look at the 20s & 30s Activity Between the War Assessment Prohibition Pope Pius XI Dadaism Surrealism TS Eliot James Joyce Franz Kafka Erich Maria Remarque Jaroslav Hasek Lumière Brothers Charles Pathé Marconi Proportional Representation Hitler Stalin Mussolini Weimar Republic Beer Hall Putsch Representation of the People Act (1918) Equal Franchise Act (1928) Sex Disqualification Act of 1919 Law of Property of 1926 Pension Act of 1925 Trade Disputes Act of 1927 Raymond systems based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security, and growth in the modern world Explain and give examples of how numerous factors influence the supply and demand of products Mar. 1230 World War II SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.4- Isms (DOK 3) SS-HS-1.1.1- Types of Government (DOK 3) SS-HS-1.1.2-Protection of Rights (DOK 3) SS-HS-3.1.1- Scarcity Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and Poincaré Ruhr Valley Great Depression National Insurance Act of 1911 Public Order Act of 1936 Stavisky Affair Friedrich Nietzsche Sigmund Freud Id Ego Superego Stream-ofconsciousness Frank Lloyd Wright Cubism Pablo Picasso Dawes Plan Mein Kampf New Deal Chapter 29 Study Guide & Key Terms McKay Text Online Activities Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 14 Sec. 2 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 15 Sec. 3-4 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 16 Sec. 1-5 World War II The Road to War Video World War II Map Activity Arming for War Video Kristallnacht Primary Reparations Dawes Plan Locarno Pact (1925) Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928) Spanish Civil War Anti-Comintern Pact Lebensraum Anschluss Appeasement Munich Conference Neville Chamberlain Polish Corridor Nazi-Soviet Non- Apr. 920 Cold War (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.2.1- Economic Systems (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.3.1- Supply & Demand (DOK 2) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Analyze how nationalism, militarism, and imperialism led to world conflicts and the rise of totalitarian governments Compare and contrast various forms of government in the world and evaluate how effective they have been in establishing order, providing security, and accomplishing common goals Explain and give examples of how democratic governments preserve and protect the rights and liberties of their constituents through different sources Give examples of and explain how scarcity of resources necessitates choices at both the personal and societal levels in the modern world Compare and contrast economic systems based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security, and growth in the modern world Explain and give examples of how numerous factors influence the supply and demand of products Source Reading & Discussion Nazi-Soviet Image Analysis Japan’s Treachery Primary Source Reading & Discussion Two Views of the A-Bomb Primary Source Reading & Discussion Decision to Drop the Bomb Video Auschwitz Primary Source Reading & Discussion Nazi Propaganda Primary Source Reading & Discussion GI Handout Trial of Adolph Eichmann Reading & Discussion Atomic Bomb Reading & Discussion Concentration Camp Video Lecture/Discussion Educator’s Reference WWII Casualties Lesson Plan aggression Pact “scorched earth” policy Vichy France Henri Petain Free France Charles de Gaulle French Resistance Movement Final Solution Holocaust Concentration camps Wannsee Conference Conference Diplomacy “Big Three” Tehran Dumbarton Oaks Yalta Potsdam United Nations UN Charter UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights Totalitarianism Five Year Plan Fascism Lateran Agreement (1929) Nazism Enabling Act Blitzkrieg Hitler’s New Order Battle of Coral Sea Battle of Midway D-Day SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern Chapter 30 Study Guide & Key Terms McKay Text Online Activities Truman Doctrine “containment” Marshall Plan SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.5- Cold War (DOK 3) SS-HS-1.1.1- Types of Government (DOK 3) SS-HS-1.1.2-Protection of Rights (DOK 3) SS-HS-3.2.1- Economic Systems (DOK 2) SS-HS-3.4.3- Economic Interdependence (DOK 2) SS-HS-4.3.1- Push/Pull Factors (DOK 3) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Explain the rise of both the United States and the Soviet Union to superpower status following World War II, the subsequent development of the Cold War, and the formation of new nations in Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and the Middle East, and evaluate the impact of these events on the global community Compare and contrast various forms of government in the world and evaluate how effective they have been in establishing order, providing security, and accomplishing common goals Explain and give examples of how democratic governments preserve and protect the rights and liberties of their constituents through different sources Compare and contrast economic Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 17 Sec. 1-5 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 18 Sec. 1-5 UN Charter Primary Source Reading & Discussion Marshall Plan Primary Source Reading & Discussion Brezhnev Doctrine Primary Source Reading & Discussion Berlin Airlift Reading & Discussion Ping-Pong Diplomacy Reading & Discussion Cold War in Europe Map Activity The Cold War: Who was Responsible? Activity Berlin Wall Reading & Discussion Race to the Moon Reading & Discussion Lecture/Discussion Cold War Assessment Berlin Blockade NATO Warsaw Pact Mao Zedong Chiang Kai-shek Korea “domino theory” Brinkmanship Nikita Khrushchev Dwight D. Eisenhower Sputnik Space race Berlin Wall Cuban Missile Crisis Fidel Castro “quarantine” Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (1963) Ostpolitik Détente Sino-Soviet Split Ping-Pong Diplomacy Richard Nixon Decolonization Ghana Kenya Israel Vietnam Ho Chi Minh Dienbienphu Geneva Conference (1954) Ngo Dinh Diem Tonkin Gulf Resolution Tet Offensive Vietnamization Common Market GAmal Abdel Nasser systems based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security, and growth in the modern world Explain and give examples of how interdependence of personal, national, and international economic activities often results in international issues and concerns in the modern world Describe movement and settlement patterns of people in various places and analyze causes of that movement and settlement Explain how people from different cultures with different perspectives view regions in different ways, sometimes resulting in conflict in the modern world Apr. 23May 15 Collapse of Communism European Union Contemporary Problems SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools (DOK 3) SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect (DOK 3) SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition (DOK 2) SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation (DOK 2) SS-HS-5.3.6 Post WWII World (DOK 2) SS-HS-1.1.1- Types of Government (DOK 2) SS-HS-1.1.2-Protection of Rights (DOK 3) SS-HS-3.2.1- Economic Systems (DOK 2) SS-HS-4.3.1- Push/Pull Factors (DOK 3) Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, De-stalinization Brezhnev Doctrine Watergate OPEC Chapter 31 Study Guide & Key Terms (pg. 1027-1051 only) McKay Text Online Activities Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 19 Sec. 3-4 Modern World History Reading Study Guide Ch. 20 Sec. 1-5 Glasnost & the Soviet Press Primary Source Reading & Discussion Lecture/Discussion Fall of Communism Video Collapse of Communism Assessment Chapter 31 Study Guide & Key Terms (pg. 1051-1061 only) Gorbachev Chernobyl Perestroika Glasnost Solidarity Lech Walesa Erik Honecker Brandenburg Gate “velvet revolution” CIS Slobodan Milosevic BosniaHerzegovina Ethnic cleansing Balkanization Globalization Alliance for Germany European Union SS-HS-4.3.2Geography & economic interdependence (DOK 2) SS-HS-4.4.2Modification of Environment (DOK 2) AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events SS-HS-5.1.1- Using historical tools SS-HS-5.1.2- Cause & Effect SS-HS-2.1.1- Culture as a system SS-HS-2.3.1- Conflict & Competition SS-HS-2.3.2Compromise & Cooperation SS-HS-5.3.6 Post WWII World SS-HS-4.3.1- Push/Pull Factors SS-HS-4.3.2Geography & economic interdependence SS-HS-4.4.2Modification of Environment interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Explain how the second half of the 20th century was characterized by rapid social, political, and economic changes that created new challenges in countries around the world, and give examples of how countries have addressed these challenges Compare and contrast various forms of government in the world and evaluate how effective they have been in establishing order, providing security, and accomplishing common goals Explain and give examples of how democratic governments preserve and protect the rights and liberties of their constituents through different sources Compare and contrast economic systems based on their abilities to achieve broad social goals such as freedom, efficiency, equity, security, and growth in the modern world Describe movement and settlement patterns of people in various places and analyze causes of that movement and settlement Explain, analyze & evaluate how technology has facilitated the movement of goods, services, and populations; increased economic interdependence at all levels and influenced development of centers of economic activity Explain how human McKay Text Online Activities Cultural Crossroads Video De Gaulle on European Unity Primary Source Reading & Discussion Fighting the Greenhouse Effect Primary Source Reading & Discussion Future of Medicine Primary Source Reading & Discussion Babushka at the Barricades Primary Source Reading & Discussion We the People Primary Source Reading & Discussion Madness in Bosnia Primary Source Reading & Discussion Speech to the European Parliament Primary Source Reading & Discussion Lecture/Discussion European Union & Contemporary Problems Assessment Maastricht Treaty European Federal Union Jean Monnet Paul-Henri Spaak BENELUX European Coal & Steel Community European Defense Community Treaty of Rome Euratom European Economic Community “Common Market” European Free Trade Association European Commission Council of Ministers European Parliament European Court of Justice Single European Act AE 2.14- Democratic principles AE 2.15- Describe & analyze governments AE 2.16- Analyze & interpret human behaviors AE 2.17- Multicultural cooperation AE 2.18- Economic principles AE 2.19- Apply geographical knowledge AE 2.20- Analyze & interpret historical events modifications to the physical environment, perspectives on the use of natural resources and natural disasters may have possible global effects in the modern world Define & explain key terms Analyze perceptions and perspectives of people and historical events in the modern world Analyze how history is a series of connected events shaped by multiple cause and effect relationships, tying past to present Explain, interpret, analyze, and evaluate how belief systems, knowledge, technology, and behavior patterns define cultures and help to explain historical perspectives and events in the modern world Explain reasons why conflict and competition develop as cultures emerge in the modern world Explain, justify, analyze, interpret, an evaluate how compromise and cooperation are characteristics that influence social interaction in the modern world Explain how the second half of the 20th century was characterized by rapid social, political, and economic changes that created new challenges in countries around the world, and give examples of how countries have addressed these challenges Describe movement and settlement patterns of people in various places and analyze causes of that movement and settlement Explain, analyze & evaluate how technology has facilitated the movement of goods, services, and populations; increased economic interdependence at all levels and influenced development of centers of economic activity Explain how human modifications to the physical environment, perspectives on the use of natural resources and natural disasters may have possible global effects in the modern world