* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mountain Building
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
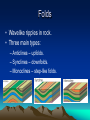
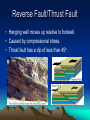
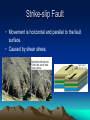
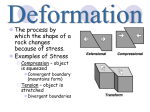
Mountain Building Chapter 11 Stress • Force per unit area on a solid. • Three Main Types: – Tensional Stress – pulls apart – Compressional Stress – squeezes together – Shear Stress – pulls in opposite directions Deformation of Rock • Any change in the original shape and/or size of a rock body. • Affected by: – Temperature – Pressure – Rock Type – Time Deformation of Rock • Two main types: Brittle Deformation: rock will fracture or break. Ductile Deformation: rock will fold or bend. Isostasy • Earth’s crust is floating in gravitational balance on the mantle. • When a change occurs, like erosion, the crust will establish a new level of gravitational balance (Isostatic Adjustment.) • This can cause uplift in the crust. Folds • Wavelike ripples in rock. • Three main types: – Anticlines – upfolds. – Synclines – downfolds. – Monoclines – step-like folds. Faults • Fractures in Earth’s crust where movement has taken place. • 4 main types: – Normal Faults – Reverse Faults – Thrust Faults – Strike-Slip Faults Normal Fault • Hanging wall moves down relative to footwall • Caused by tensional stress. Reverse Fault/Thrust Fault • Hanging wall moves up relative to footwall. • Caused by compressional stress. • Thrust fault has a dip of less than 45o. Strike-slip Fault • Movement is horizontal and parallel to the fault surface. • Caused by shear stress. Mountains • Orogenesis – mountain-building. • Types of Mountains: – Volcanic Mountains – Folded Mountains – Fault-block Mountains • Graben – downwarddisplaced block • Horst – uplifted block Other Landforms • Plateau – high elevation and level surface. • Dome – circular landform produced by upwarping. • Sedimentary Basin – Circular landform produced by downwarping. Convergent Boundary Mountains • Oceanic-Oceanic – forms volcanic mountains. • Oceanic-Continental – forms volcanic and folded mountains. – Accretionary wedge – sediments scraped from the subducting plate. • Continental-Continental – forms complex folded mountains. Mountains at Other Boundaries • Divergent Boundaries – forms fault-block mountains made of volcanic rock. • Non-Boundary Mountains – formed by hot spots or regional extension or stretching. Accretion • When crustal fragments collide with and stay connected to a continental plate. • Terranes – crustal fragments that have a geologic history different from the adjoining fragments.