* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Student Lecture Notes CH 11 all
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
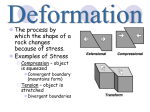
Lecture Notes - 11 Mountain Forming 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation temperature, confining pressure, rock type, and time. • Deformation - all ____________ original ___________ and/or size of rock body. Most crustal deformation occurs ______________________________. • Stress = force per unit area (_________________) Show Picture • Strain = change in shape/volume of rock from stress. Show Picture Temperature and Pressure • _____________________ by: _______ deformation and _______ deformation. Brittle deformation ________________once strength is exceeded. Ductile deformation = solid state _______ that produces a ________________________ without fracturing the object. Rock Type Mineral composition and texture affect deformation Time - rock will deform over a long period of time. Types of Stress _____________ stress, ____________ stress, and _____________ stress. Draw Pictures Folds (in sedimentary rock strata) • Anticlines upfolding, or ___________________ • Synclines linear ___________________________ found with anticlines • Monoclines large step-like folds. Faults Normal Faults - ___________ wall block ______________ relative to the footwall block Reverse Faults __________ Faults - hanging wall block ___________ relative to footwall Thrust Faults reverse faults with _____________________________) Strike-Slip Fault - movement is ___________ to the trend, or _____, of the fault surface. Joints - __________________ with no appreciable movement. 11.2 Types of Mountains Folded Mountains classified by processes that __________________. Orogenesis = _____________________________________________ Fault-Block Mountains Large-scale _____________________ fault-block mountains. • blocks of crust are __________________________ • Grabens - __________________________ of fault-bounded blocks. • __________ = elongated, ______________________ of crust bounded by faults. Domes and Basins - __________ or elongated structure (formed by _________ of the underlying ____________________.) Orogenesis refers to those processes that produce what? _______________________ 11.3 Mountain Formation - Mountain Building at Convergent Boundaries Colliding plates ___________ that _________________, and metamorphose thick layers of sediments ______________ at the edges of landmasses. Mountain Building at Convergent Boundaries ____________________ Convergence - produces ___________________________. Ocean-Continental Convergence - __________ mountains and __________________. • An ______________________________ = accumulation of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks (________ some scraps of ______________________). Mountain Building at Divergent Boundaries - along ocean ridges = ______ type mountains. Continental Accretion-process when ________ collide with & stay connected to a_______ Terranes • any crustal fragments that have a geologic history distinct (different) from adjoining fragments that _____ along the Pacific Coast. Principles of _____________________ - Isostatic Adjustment for Mountains • Earth’s _______________________ in gravitational balance upon mantle. • deformed and thickened crust will undergo regional uplift. • Isostatic adjustment = process of establishing a __________________________ DRAW The collision and joining of crustal fragments to a continent is called