* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
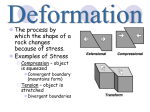
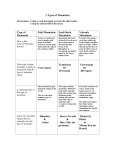
Chapter 11 Deformation of the Crust Standards SCSh3c. Collect, organize and record appropriate data SCSh6a. Write clear, coherent laboratory reports related to scientific investigations. SES2b. Relate modern and ancient geologic features to each kind of plate tectonic sett selection Vocab Section 1 – How Rock Deforms Deformation Isostasy Stress Strain Fold Fault Section 2 – How Mountains Form Mountain range Folded mountain Fault-block mountain Dome mountain Outline Section 1 Tectonic plate movement and iostatic adjustments cause stress on the rock in Earth’s crust. Isostatsy - gravitational and buoyant equilibrium between Earth’s lithosphere and asthenosphere. Isostatic adjustments – erosion of a mountain reduces the weight of the lithosphere causing it to rise. Deposition of sediment in the ocean increases weight causing it to sink Stress (force per unit area) can squeeze rock together (compression - @ convergent boundaries), pull rock apart (tension - @ divergent bondaries), and bend and twist rock (sheer - @ transform boundaries) Stress on rock can cause strain, or the deformation of rock. Rock can deform by folding (ductile) or by breaking (brittle) to form fractures or faults. Three types of faults occur in rock – break in rock where one block slides relative to the other Normal faults – hanging wall moves downward – divergent zones – form steep, step-like landforms Reverse faults – hanging wall moves upward – steep mountain ranges Strike-slip faults – planes slide horizontal to each other - transform boundaries Section 2 Mountains make up mountain ranges, which, in turn, make up mountain systems. Two major mountain belts: circum-Pacific belt, Eurasian-Melanesian belt – at convergent boundaries Mountains commonly form as the result of collision of tectonic plates Continental + Oceanic crust – large volcanic mountains Oceanic + Oceanic crust – volcanic mountains on the ocean floor Continental + Continental – collision – large mountain ranges (Himalayas –still growing) A mountain is classified according to the way in which the crust deforms when the mountain forms. Four types of mountains: Folded mountains - a mountain that forms when rock layers are squeezed together and uplifted Fault block mountains - a mountain that forms where faults break Earth’s crust into large blocks and some blocks drop down relative to other blocks Dome mountains - a circular or elliptical, almost symmetrical elevation or structure in which the stratified rock slopes downward gently from the central point of folding Volcanic mountains – •Mountains that form when magma erupts onto Earth’s surface are, which commonly form along convergent plate boundaries.