* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Dominion of New England wikipedia , lookup
Province of Massachusetts Bay wikipedia , lookup
Colonial period of South Carolina wikipedia , lookup
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
Colonial American military history wikipedia , lookup
Shipbuilding in the American colonies wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
Slavery in the colonial United States wikipedia , lookup
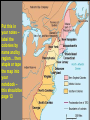
Motives for European Exploration 1. Crusades = by-pass intermediaries to get to Asia. 2. Renaissance = curiosity about other lands and peoples. 3. Reformation = refugees & missionaries. 4. Monarchs seeking new sources of revenue. 5. Technological advances. 6. Fame and fortune. REASONS FOR COLONIZATION Seek Refuge: Many people sought refuge in the New World to get away from persecution from their homeland. Religious Freedom: New World would provide an opportunity for them to practice the religion they wanted. Economic Opportunity: Many people who came over were poor in the Old World and New World offered a chance at making a better life. Progressive Gov’t: Moved away from a nonrepresentative and elitist gov’t into a more democratic system. A time of rebirth in Western Civilization “intellectual enlightenment” Direct Causes = 3 G’s Become a world power through gaining wealth and land. (GLORY) Economic: Search for new trade routes with direct access to Asian/African luxury goods would enrich individuals and their nations (GOLD) Religious: spread Christianity and weaken Middle Eastern Muslims. (GOD) Political: The 3 motives reinforce each other EUROPEAN European COLONIZATION Colonization When the New World is discovered, the Big 4 four European countries start to compete for control of North America and the world: Spain English France Portugal EUROPEAN COLONIZATION The Portuguese were the first to begin searching for an all water route to Asia….. • Prince Henry the Navigator – 1450’s Colonized the South America in the area of what would become Brazil EXPLORERS SAILING FOR PORTUGAL Prince Henry the Navigator - Portugal Funded Exploration down coast of Africa - 1419-1460 Vasco da Gama - Portugal - Opened trade with India - Placed Portugal in position to dominate trade with India 1498 Pedro Cabral - Portugal - Claimed present day Brazil for Portugal – 1500 Started in Caribbean, then Central and South America—most important was conquest of Aztecs by Cortez (1521) and Incas by Pizzaro (1531) First permanent colonies in what will become United States are founded by Spain • St. Augustine (Florida) is founded (1565) to protect Spanish treasure fleets Explorers Sailing For Spain Columbus - Italian sailing for Spain Landed in the “West Indies” - 1492 Magellan - Portuguese sailing for Spain 1st to circumnavigate the world - 1522 OTHER SPANISH EXPLORERS Ponce De Leon - Established colony at Puerto Rico - Sailed north looking for Fountain of Youth Discovered Florida - 1508 Vasco de Balboa - Established settlement in Panama - 1st European to see Pacific Ocean - 1513 Francisco de Coronado - Explored north from Mexico; up Colorado River; saw Grand Canyon 1540 Hernando de Soto - Explored Florida into Carolina’s and west to the Mississippi River - 1541 EXPLORERS SAILING FOR SPAIN & PORTUGAL Amerigo Vespucci - Italian sailing for both Spain and Portugal - Sailed to the America’s - Amerigo is his first name (where we get “America”) 1501 SPAIN COLONIES IN AMERICA The Spanish gov’t operated strict control over her colonies Conquering of the Americas allowed Spain to become the most powerful country in the 16th century “We came here to serve God and King… and to get rich” Not only disease, but civil wars and religious superstitions also allowed the Europeans, namely the Spanish, to conquer the Native Americans (who GREATLY outnumbered the explorers) The advanced technology of the Europeans offered an incredible advantage in combat • Gunpowder, cannon, and bullets vs. bows and arrows • Horses (transport and cavalry) and also pigs, cattle, and goats (foodstuffs) played a very important role in conquest THE SPREAD OF CATHOLICISM Catholic missionaries quickly spread to the Americas in the wake of the conquistadors’ victories The Natives were viewed as pagans and the Catholic religion was in turn imposed upon the people • The spreading epidemics were seen as the wrath of God upon the pagans and justified the actions of the god-fearing Spanish Spain would never develop successful settlements (in terms of trade and power) in US territory mainly due to its primary lust for gold and silver instead of developing centers of trade FRANCE COLONIES IN AMERICA The French government strictly controlled the colonies but made little effort to encourage settlement Because the fur trade was the basis of the colonial economy, Indians became valued trading partners (not exploitive like Spain) Like the Spanish gov’t, the French were encouraged to marry; mixed blood ENGLISH COLONIES IN AMERICA • English colonization differed from Spanish & French because the English gov’t had no desire to create a centralized empire in the New World • Period of “Salutary Neglect” • Different motivations by English settlers led to different types of colonies • New England, Middle and Southern Colonies ENGLISH COLONIES IN AMERICA • Jamestown 1607 is the very first settlement • Becomes 1st permanent colonial town • Powatan who inhabit the land… • Coexist with Whites for a time • Eventually, more and more whites come leading to conflict • are not as easily overcome • Life is Jamestown is very very very tough CONTRIBUTIONS TO MOTHER COUNTRY 1. England -- Democratic forms of local government; tradition of hard-working, zealous individuals, English language 2. France -- Language, culture, and religion introduced to Canada and Louisiana and many Indians west of Appalachians; large-scale trade with Indians 3. Spain -- Schools, hospitals, and printing presses established by missionaries; Spanish language in the Southwest; teaching of Christianity and handicrafts to Native Americans. Put this in your notes – label the colonies by name and by region… then staple or tape the map into your notebook – this should be page 13 NEW ENGLAND COLONIES A. Consisted of Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut and Rhode Island B. Geography: Soil was rocky and weather was cold thus growing season was short C. Economy: Terrain did not allow for farming but fishing became the thriving part of the coloy D. Gov’t: No separation of church and state; took religion to the extreme (Separatists and Puritans) “Town Meetings” offered a version of direct democracy E. The New England colonies were established for the purpose of religious freedom, not profit MIDDLE COLONIES A. Consisted of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware B. Geography: Weather was warmer and growing season longer Terrain was not rocky; ideal for farming. C. Economy: Called “bread colonies” due to high grain export. Wheat, rye, corn, oats, barley and flour. D. Gov’t: Assembly that had all legislative power. They were elected by members of colony (rich). Adopted “The Charter of Privileges” guaranteed the principle of religious toleration to all Protestants SOUTHERN COLONIES A. Consisted of Maryland, N. Carolina, S. Carolina, Virginia, and Georgia. B. Geography: Terrain was flat. Weather was hot and humid, thus growing season was very long. C. Economy: Had the warmest colonies than the others; farmers had great plantations where they grew tobacco and rice. Supported by slave labor and farming. Primary seaport for the southern colonies was Charleston, S.C; growth of commerce. D. Gov’t: Positions in gov’t were dominated by planters and farmers and consisted of only men and landowners WHAT DID THE ENGLISH COLONIES LOOK LIKE AT THE END OF THE 17TH CENTURY? TYPES OF COLONIES Joint Stock – colonies granted to private companies in the hopes of creating profits from colonization • Proprietary – land granted to individuals for the purpose of creating colonies; the individuals had the right then to grant land to whomever they chose • Royal – colonies headed by the English crown/government itself JAMESTOWN First successful colony establish in 1607 The Profit Dilemma – VA was a joint stock colony, and therefore the Virginia Co. of London demanded immediate profits • Settlers were pressured to look for gold and silver rather than farm and hunt • This bungling of priorities led to times of starvation Starving Time) John Smith- “If you don’t work, you don’t eat” (The MONEY……FINALLY • John Rolfe and Tobacco – Around 1613 Rolfe would develop a process for curing tobacco that would remove most of its bitterness, making it much more pleasant to smoke – The demand for tobacco would quickly grown throughout England and Europe – The tobacco plant was very easy to grow in the VA climate and environment • Rolfe would also marry Pocahontas, bringing a very brief period of peace between VA and the Powhatans MERCANTILISM There was a fixed amount of wealth in the world. • Keeping trade completely within the Empire, becoming economically self-sufficient, was an effective means of protecting oneself from (and potentially dominating) one’s enemies. Because there was a fixed amount of wealth available in the world as a whole, countries increased their own share of this wealth only at the expense of their rivals. BACON’S REBELLION Indentured Servants • Labor Force • Serve 5-7 years for passage to New World Freedman unable to own land; moved westward into Indian territory • Indian Tribes resisted white expansion Governor Berkley refused to help freedman; Nathaniel Bacon’s militia massacred Indians and chased Berkley out of town Significance? ROOTS OF SLAVERY Slaves were originally treated as indentured servants but the growing black population in VA by 1672 prompted stricter slave laws: • Africans were defined as slaves for life; slave status was passed on to children • By 1700, slavery was based exclusively on skin color ORIGINS & DESTINATIONS OF AFRICAN SLAVES, 1619-1760 ENLIGHTENMENT Intellectual movement; emphasized reason, science, and observation and led to the discovery of natural laws • Generally we are good and it is our environment that influences us • The use of science and reason could answer life’s mysteries • Science and reason could also answer man’s questions concerning government and himself GREAT AWAKENING Revival of religion and an attempt to turn people back to God. • A series of religious revivals aimed at restoring devotion For the most part it was a reaction to the Enlightenment. • Encouraged ideas of equality and right to challenge authority • Birth of charity and charitable organizations • Ivy League Schools