* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ekaterina Dadachova, Ph.D.
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
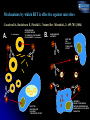
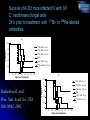
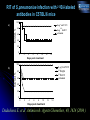
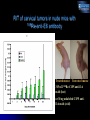
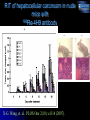
Novel approaches to therapy of infectious diseases Ekaterina Dadachova, Ph.D. Sylvia and Robert Olnick Faculty Scholar in Cancer Research Associate Professor Departments of Nuclear Medicine and Microbiology and Immunology Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY Production of radionuclides Preparation of 225Ac generators in a glovebox at the Institute for Transuranium Elements, EC (source ITU website) Higher levels of radioactivity are handled in “hot cells”. Hot cell (operator side with manipulators for remote-controlled work is shown on this photo. (source European Nuclear Society website) Radioactive substances really glow in the dark – a vial with 50 milliCurie of 225-Actinium which we use in our research Courtesy of Dr. J. Harvey, Northstar Nuclear Medicine What is ionizing radiation? The following kinds of ionizing radiation are used in nuclear medicine: electrons, positrons, alpha particles, gamma rays. Electron (beta-particle) has a mass of nearly 1/2000 of the mass of a proton or neutron. Depending on its energy, an electron can traverse different distances in water-less than 1 mm for 3H to ~1 cm for 32P. Positron is an antiparticle of an ordinary electron. It loses its kinetic energy the same way as an electron and has the same range in water. It then combines with an electron in annihilation reaction, in which its mass and that of electron are converted into the energy of two 511 keV annihilation photons emitted in exact opposite directions (180o apart). An alpha particle is a nucleus of 4He. Because of its large mass and positive charge, an alpha particle can usually pass only 20-100 m in water. A gamma ray is an electromagnetic wave, a gamma ray is similar to ordinary visible light but differs in energy and wavelength. Gammas penetrate several cm into the body. Mechanisms by which RIT is effective against microbes Casadevall A, Dadachova E, Pirofski L. Nature Rev. Microbiol., 2: 695-703 (2004) A. C. neoformans RADIOLABELED ANTIBODY BOUND TO SHED POLYSACCHARIDE KILLS NEARBY C. neoformans INFECTED MACROPHAGE KILLED BY ‘CROSS-FIRE’ EFFECT B. RADIOLABELED ANTIBODY INFECTED CELL KILLED BY ‘CROSS-FIRE’ EFFECT ANTIBODY BOUND TO MICROBIAL ANTIGEN EXPRESSED ON SURFACE KILLS CELL WITH RADIATION Radioimmunotherapy of experimental fungal infection Survival of A/JCr mice infected IV with 105 C. neoformans fungal cells 24 h prior to treatment with 213Bi- or 188Re-labeled antibodies a) 100 188 % survival 80 60 Re-18B7, 50 Ci 188 Re-18B7, 100 Ci 188 Re-18B7, 200 Ci PBS 40 "cold" 18B7, 50 g 188 20 Re-MOPC21, 100 Ci 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 b) Days post-treatment 100 213 213 Dadachova E. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:10942, 2003. % survival 80 Bi-18B7, 50 Ci Bi-18B7, 100 Ci 213 60 Bi-18B7, 200 Ci PBS "cold" 18B7, 50 g 40 213 Bi-MOPC21,100 Ci 20 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Days post-treatment 70 80 RIT for treatment of fungal biofilms Percentage of Metabolic Activity (492 nm) 120 B3501 Biofilms 100 B3501 Planktonic p<0.05 * 80 60 40 * 20 Percentage of Metabolic Activity (492 nm) The use of indwelling medical devices — pacemakers, prosthetic joints, catheters — is rapidly growing and is often complicated by infections with biofilm-forming microbes that are resistant to antimicrobial agents and host defense mechanisms. B3501 Planktonic 100 80 15 30 MAb 18B7-Bismuth-213 (µCi) p<0.05 * 60 40 * 20 0 0 B3501 biofilm 120 200 400 MAb 18B7-Rhenium-188 (Ci) L.R. Martinez et al Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 50(6):2132-2136 (2006) Radioimmunotherapy of experimental bacterial infections RIT of S.pneumoniae infection with 213Bi-labeled antibodies in C57BL/6 mice 100 a) 5 ug "cold" D11 Survival, % 80 5 ug 213Bi-D11 untreated 60 40 20 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Days post-treatment 100 5 g "cold" D11 b) 213 Bi-IgM Survival, % 80 213 Bi-D11 untreated 60 40 20 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Days post-treatment Dadachova E. et al Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 48, 1624 (2004 ) Radioimmunotherapy of HIV RIT EFFECTIVE IN MICE HARBORING HIV-INFECTED HUMAN CELLS MODEL: SCID mice injected intrasplenically with HIV-1 infected hPBMCs 188-Re-246-D before infection 188-Re-246-D after infection 213-Bi-246-D after infection 188-Re-1418 irrel. mAb 213-Bi-1418 irrel. mAb "cold" 246-D mAb Untreated controls 1 10 100 6 TCID 50/10 splenocytes 1000 10000 THINKING BEYOND RIT OF HIV NEW OPTIONS FOR THE TREATMENT OF VIRAL DISEASES SUCH AS Hepatitis C virus, Epstein Barr virus, human papilloma virus etc. (A. Casadevall, H. Goldstein, and E. Dadachova Expert Opinion Biol. Therapy, 7:595-597, 2007) RIT POTENTIALLY APPLICABLE TO TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF CANCERS CAUSED BY ONCOGENIC VIRUSES SUCH AS HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA, CERVICAL CANCER, AND CERTAIN LEUKEMIAS AND LYMPHOMAS (E. Dadachova, X.-G. Wang, and A. Casadevall Cancer Biother. Radiopharm., 22: 303-308, 2007) RIT of cervical tumors in nude mice with 188Re-anti-E6 antibody Treated mouse Untreated mouse 315 uCi 188Re-C1P5 anti-E-6 mAb (hot) or 30 ug unlabeled C1P5 antiE-6 mAb (cold) RIT of hepatocellular carcinoam in nude mice with 188Re-4H9 antibody X-G. Wang, et. al. PLOS One 2(10): e1114 (2007).