* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prodrugs - ISpatula
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cephalosporins wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
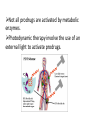
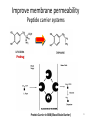
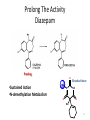
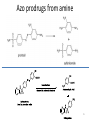
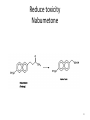
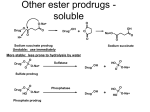
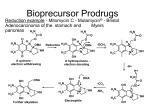
Prodrugs Medicinal Chemistry I 1 Prodrugs Are inactive compounds converted to the active form in vivo. Useful for drugs with undesirable physicochemical property. 2 Undesirable Properties • Physical Properties: a) Poor aqueous solubility b) Low lipophilicity c) Chemical instability d) Acid Sensitivity e) Poor Membrane Permeability (poor absorption) f) Toxicity (non-selective bioactivity) g) Bad Taste h) Short Duration of Action i) Non-site specific 3 Prodrugs activation mechanisms • Variety of mechanisms by which prodrug can be converted into active drug: 1. Metabolizing enzymes (phosphotase, esterases, peptidase) • Interpatient variable 2. Chemical activation (Hydrolysis, decarboxylation, light activation) • Stability issues 3. Mixture of both • Two important points: 1. The prodrug should be effectively converted to the active form once absorbed in the blood. 2. Cleavable groups are non toxic. 4 Not all prodrugs are activated by metabolic enzymes. Photodynamic therapy involve the use of an external light to activate prodrugs. Prodrugs classification • Can be classified into three categories: 1. Carrier-linked prodrugs - Carrier-linked prodrugs are drugs that have been attached through a metabolically labile linkage to another molecule, the so-called promoiety, which is not necessary for activity but may impart some desirable property to the drug 6 Prodrugs classification 2. Mutual prodrugs - In this type, both the drug and the carrier has activity 7 Produrgs classification 3. Bioprecursor prodrugs - contain no promoiety but rather rely on metabolism to introduce the functionality necessary to create an active species 8 Carrier-linked prodrugs Prodrugs functional groups 9 Prodrugs functional groups - Esters The most common type of prodrug because of the ease with which the ester can be hydrolyzed or formed. Esterase enzymes present in plasma and other tissues that are capable of hydrolyzing a wide variety of ester linkages Can add lipophilicity or hydrophilicity to the drug Increasing lipophilicity of the compound may yield a number of benefits, including increased absorption, decreased dissolution in the aqueous environment of the stomach, longer duration of action, and reducing bad taste 10 Improve membrane permeability • Problem: - Epinephrine is poorly absorbed through eye tissues - Catechols are unstable • Solution: The increased lipophilicity relative to epinephnine allows the drug to move across the membrane of the eye easily and achieve higher intraocular concentrations • The steric bulk of pivalic acid slows down the hydrolysis 11 Improve Membrane Permeability Ampicillin is poorly absorbed from the GI tract (~30% absorbed) WHY??? The carboxylic acid functional group (COOH): Binds the drug to a receptor via ionic or hydrogen bonding. An ionizable group may prevent drug from crossing a fatty cell membrane. Solution: Convert the acid function to an ester moiety. The less polar ester can cross fatty cell membranes. The ester group will be hydrolyzed back to the free acid by the esterase in the blood. 12 Ampicillin activation In Vivo 13 Masking bad taste • Problem: Water soluble drugs when dissolve in the mouth could lead to bad taste - This cause low compliance (pediatric) • Solution: A prodrug with reduced water solubility does not dissolve to any appreciable extent in the mouth and, therefore, does not interact with taste receptors. 14 Prodrugs for stability • Problem: propanolol undergo extensive first pass metabolism (glucuronidation) • Solution: adding ester group on the alcohol will protect it from metabolism Prodrugs for stability Increasing hydrophilicity • Increase the water solubility of drugs, making them more suitable for parenteral or oral administration when high water solubility is desirable Clindamycin Phosphate 17 Improve membrane permeability Peptide carrier systems Improve membrane permeability Peptide carrier systems Prodrug Protein Carrier in BBB (Blood Brain Barrier) 19 Drugs with amine moiety • The amide derivative is not a suitable choice in most of the case (WHY?)….Stable bond toward hydrolysis compared to the ester bond. Drugs with amine moiety Prodrug to increase lipophilicity 21 Drugs with amine moiety Prodrugs to increase water solubility Prolong The Activity Diazepam Prodrug O •Sustained Action •N-demethylation Metabolism Hexobarbitone Me N O NH O Me 23 Prodrugs to mask toxicity and side effects Cyclophosphoramide for phosphoramide mustard (anticancer agent) NH O P O 1. Cyt P450 2. Phosphoramidase Cl (liver) H2N Cl P HO N O N Cl Cl Cyclophosphoramide Phosphoramide mustard • • • Non toxic Orally active Alkylating agent Azo prodrugs from amine 25 Prodrugs used to target drugs Example: Hexamine N N N N • • • • Stable and inactive at pH>5 Stable at blood pH Used for urinary infections where pH<5 Degrades at pH<5 to form formaldehyde (antibacterial agent) Bioprecursor prodrugs • Bioprecursor prodrugs mostly use either oxidative or reductive activation reactions. • The main activation pathways are: 1) Proton activation. 2) Hydrolytic activation 3) Elemination activation 4) Oxidative activation 5) Reductive activation 6) Nucleotide activation 7) Phosphorylation activation 8) Sulfation activation 9) Decarboxylation activation 27 Reduce toxicity Nabumetone 28 Reduce toxicity Idoxuridine phosphorylation 29 Most other antiviral requires the same activation mechanism N HO N N N N PO Vi ral NH2 thymidi ne kinase Penciclovir OH N N N N NH2 P P PO N N N NH2 Cell kinases OH OH 30 Proton Pump Inhibitor Activation Omeprazole 31 32 Bioluminescent Red Tide 33 34