* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transthoracic tissue Doppler study of right ventricular - Heart
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
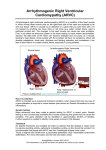
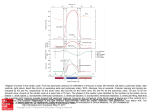
Downloaded from http://heart.bmj.com/ on May 8, 2017 - Published by group.bmj.com 980 Heart 2004;90:980 IMAGES IN CARDIOLOGY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . doi: 10.1136/hrt.2003.033340 Transthoracic tissue Doppler study of right ventricular regional function in a patient with an arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy A 45 year old man was admitted because of ventricular tachycardia. He was known to suffer from arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC). The rhythmic instability was quickly managed with amiodarone and atenolol. During evaluation of the patient’s cardiomyopathy, echocardiography was performed. Left ventricular global function was normal, but hypokinesia of the basal segment of the lateral wall was observed. The right ventricle was enlarged and appeared hypokinetic, especially at the apex in apical long axis view. The pulmonary infundibulum was enlarged (upper panel). We looked at the tissue Doppler characteristics of the right ventricle, especially the free wall, to quantify regional right ventricular function. We then used tissue Doppler velocity (TVI) curve analysis (lower panel) and observed the disappearance of the base–mid apex velocity gradient, and the presence of an isovolumic relaxation event on the TVI curves of the ARVC patient, contrary to what is seen in normal individuals. E Donal P Raud-Raynier [email protected] (A) Parasternal short axis view with the enlarged pulmonary infundibulum and the pulmonary valve regurgitation. (B) Same view looking at the left ventricle (LV) and the enlarged right ventricle (RV). (C) Same observation in apical view. (D) Dilated inferior vena cava. Tissue Doppler velocity (TVI) curve analysis and tissue tracking performed in one of the ARVC patients. There is no base–mid apex gradient, unlike in the control subject with normal right ventricular function. Note the presence of a negative isovolumic relaxation velocity in the ARVC patient (Q). The isovolumic relaxation is free of any event in the normal subject. www.heartjnl.com Downloaded from http://heart.bmj.com/ on May 8, 2017 - Published by group.bmj.com Transthoracic tissue Doppler study of right ventricular regional function in a patient with an arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy E Donal and P Raud-Raynier Heart 2004 90: 980 doi: 10.1136/hrt.2003.033340 Updated information and services can be found at: http://heart.bmj.com/content/90/9/980 These include: Email alerting service Receive free email alerts when new articles cite this article. Sign up in the box at the top right corner of the online article. Notes To request permissions go to: http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions To order reprints go to: http://journals.bmj.com/cgi/reprintform To subscribe to BMJ go to: http://group.bmj.com/subscribe/