* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Why We Do What We Do - Lifelong Learning Academy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
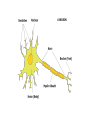
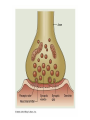
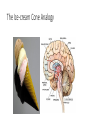
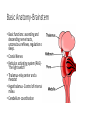
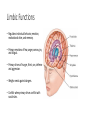
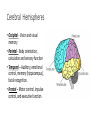
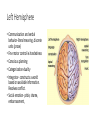
Why We Do What We Do Alan B. Grindal MD In order to overcome our failures and vulnerabilities as both individuals and societies, we must first understand our biologic predispositions and the evolutionary behavioral traits which have made us human. Introduction The body has needs and the environment has resources. The brain attempts to match the two and create stability. Basic drives include individual and genetic survival. Outline • Introduction to the brain. • Human behavior and evolution • Morality • Free Will • Violence • Love and attachment Brain Complexity • 100 billion neurons • 150,000,000,000,000 (150 trillion) synapses • 100,000 miles of nerve fibers • Prenatal brain makes 5000 new neurons a second. • 1 cubic millimeter of brain cortex contains 1 billion synapses. The brain is complicated. There are no simple answers. The Ice-cream Cone Analogy Basic Anatomy-Brainstem • Basic functions: ascending and descending nerve tracts, unconscious reflexes, regulation of sleep. • Cranial Nerves • Reticular activating system (RAS)”the light switch” • Thalamus-relay center and a rheostat • Hypothalamus- Control of internal milieu • Cerebellum- coordination Limbic Functions • Regulates instinctual behavior, emotion, motivational drive, and memory. • Primary emotions of fear, anger, sorrow, joy and disgust. • Primary drives of hunger, thirst, sex, defense and aggression. • Weighs needs against dangers. • Conflict when primary drives conflict with social rules. Cerebral Hemispheres • Occipital - Vision and visual memory • Parietal - Body orientation, calculation and sensory function • Temporal – Auditory, emotional control, memory (hippocampus), facial recognition. • Frontal – Motor control, impulse control, and executive function A Dichotomous Relationship Left Brain Right Brain • Expressive, verbal • Logical, detailed • Concrete • Social emotions • Factual Memory • “Left Hemisphere Interpreter” • Perceptual, spatial • Holistic, creative • Metaphorical • Primary emotions • Emotional autobiographical memory Left Hemisphere • Communication and verbal behavior-literal meaning, discrete units (prose) • Fine motor control ie.handedness • Conscious planning • Categorization-duality • Integrator- constructs a world based on available information. Resolves conflict. • Social emotion- pride, shame, embarrassment, Right Hemisphere • Close relationship to Limbic system and primary emotional valence and familiarity. • Sensitive to rhythm and repetition i.e.. poetry, music, and religion • Spatial orientation. • Self-monitoring and Ego boundaries. • Prosody and non-verbal expression. • Appreciation of humor. Interhemispheric Communication • Corpus Callosum • Coordinate and integrate. Ex# bimanual tasks. • Competitive and deactivating • Callosectomy- two minds Serial v. Parallel Processing • Serial- Information processed with increasing integration and complexity eg. A dot to a line to a shape. • Parallel- Independent serial processes can occur simultaneously and can combine and compete with each other. • Unconscious- parallel. Consciousserial • Emphasis on connectivity as well as location. Plasticity • Changeability and remodeling with learning and experience • Nerves that fire together wire together • Change in synaptic strength, sprouting of dendrites, new nerve cells • Braille readers, musicians • Limited capacity with aging Neuronal Pruning • Decrease connections- greater specificity and efficiency. • Primarily during late fetal stages and infancy- eliminates “noise” in the system. • “ Use it or lose it” • Neural Darwinism Small World Networks • Networks- Nodes, edges and hubs • Systems of functionality ( Sensory, attention, language, salience and executive) • Systems build in complexity and interactivity. • Autism- Increase connections in sensory systems • ADHD- Decrease connections – primarily in attention systems Glial cells • Astrocytes- Provide scaffolding, regulate synapse and control blood brain barrier- Brain tumors. • Oligodendroglia- Form myelin sheets to promote rapid conduction.- Multiple Sclerosis. • Microglia- Inflammatory response and scavengers.














![[SENSORY LANGUAGE WRITING TOOL]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014348242_1-6458abd974b03da267bcaa1c7b2177cc-150x150.png)







