* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Species Niche
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
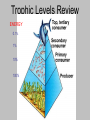
Description: Finish looking at the specific species interaction relationships. This is in the form of a multimedia notes/lecture period on PowerPoint. Goals: •Examine how interactions between a species and its environment define a species niche. •Explain how a species adapts to its niche. Objectives: Day 7 I. Explain the difference between parasitism and predation. II. Describe the major types of interactions between species Warm Up Based on the type of species interaction, where would you find the following examples on the trophic pyramid? 1. Predator 2. Prey A= 1. Consumer (Secondary & up) 2. Consumer (Primary & up except for the top consumer) Vocabulary Reminder New Terms: Predator- Previous Terms: Producer- Prey- Consumer- Mimicry- Herbivore- Parasite- Carnivore- Endoparasite- Decomposer- Ectoparasite- Omnivore- Host- Scavenger- Trophic Levels Review ENERGY 0.1% 1% 10% 100% Symbiosis Predators A. Organism who eat other organisms B. Secondary Consumers and higher C. Carnivores & Omnivores D. Tools: – – – – – – – Speed Sharp Teeth or Beak Claws or Talons Strength Camouflage/Stealth Good Senses Group Hunting Prey A. Organism eaten by other organisms B. Primary and 2nd Consumers C. Herbivores (carnivores sometimes) D. Tools: – – – – – – – Speed Size Poison Odor Good Senses Shelter Mimicry (2 types): • Physical (like Octopus) • Chemical (for example…) Mimicry: imitating another organism as a means of defense or stealth What is this? III. Parasitism A. Organisms who infects a host a means of gaining their needs. B. ENDO-parasite C. ECTO-parasite D. Require host – Feeding – Shelter – Maturing III. Parasitism A. Organisms who infects a host a means of gaining their needs. B. ENDO-parasite C. ECTO-parasite D. Require host – – – – – Feeding Shelter Maturing Replicating Transport Think about it… I. Explain the difference between parasitism and predation. On the back of your notes: 1. List differences between parasites and predators. 2. List similarities between parasites and predators. Think about it… I. Explain the difference between parasitism and predation. Create a class list of our comparisons and add any that you didn’t think of to your list. Explain in three or less sentences why parasites are not considered predators beneath your list. IV. Types of Relationships • Commensalism – One organism benefits, the other is not harmed or helped. IV. Types of Relationships •Competition •Two or more organisms trying to gain the same necessities. IV. Types of Relationships •Mutualism •Both organisms benefit. Think about it… II. Describe the major types of interactions between species You will be assigned one of six types of species interactions explored yesterday and today. Working in a group of 3-4 peers you will need to form a presentation that represents your interaction type. Ideas include… Ideas include but are not limited to: • Skit • • act it out Story-board • • step by step narrative that is drawn out in stages Song • sing or rap it - just make sure you don’t chicken out! Objectives: Day 7 I. Explain the difference between parasitism and predation. II. Describe the major types of interactions between species