* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
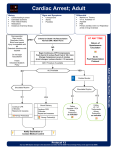
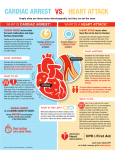
LAY RESCUER TRAINING IN CARDOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION. It is not uncommon to hear in daily news of anecdotal reports of people dying due to cardiac arrest. Sudden Cardiac Death or correctly termed Cardiac arrest is an important public health problem worldwide.In a situation of In- Hospital Cardiac Arrest,because of the presence of trained doctors,paramedical personnel , nursing staff and the presence of life-saving equipment ,the survival rate is naturally above 60-70 %. Whereas in a situation of Out-Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest(eg., Home,bus stand,railway station,airport,library,malls or any public place),the chance of saving a person as per statistics is only 6 %.Despite major advances in medical science,Sudden cardiac death remains an important public health problem. Though it is more than 50 years since modern CPR has come into practice,the survival rate of Out-Of –Hospital Cardiac Arrest remains 6 % only. The chance of saving a victim of cardiac arrest depends on the presence of a trained rescuer in the scene of cardiac arrest. In a situation of Out-Of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest ,as it takes more than 7—8 minutes for an ambulance or paramedics to arrive on scene, the chance of saving a cardiac arrest victim remains in the hands of bystanders in that scene.By training lay public n CPR and providing life-saving equipment the survival rate of a cardiac arrest victim can be improved. In countries like the USA,European countries and various other foreign countries,lay public above the age of 13 years,starting from High school students,college students,family members,office staff,staff in railway stations,bus stands,airports ,hotels and various public places are trained in CPR. In a report by the World Heart Federation,the awareness of Cardiac arrest and CPR among Indian public is not even 1 %.Though a few organisations have been imparting training in CPR to lay public in India,these have not been targeting the entire multilinguistic Indian population systematically. With this background,Srinivasa Heart Foundation has initiated training lay public in CPR as per accepted international guidelines Before actually learning CPR it is important to know a few facts about Sudden cardiac death,its causes and certain important facts Definition of Sudden Cardiac Death.— Death occurring within one hour of onset of symptoms of heart disease—chest pain,palpitations and breathlessness in a person with or without past history of heart disease. However the term Sudden cardiac Death is a misnomer as a few victims may be saved due to CPR.hence the right term would be Cardiac arrest and the survivor is a cardiac arrest survivor. Causes of Cardiac arrest— 1.Coronary artery disease-Heart attack. 2.Cardiomyopathy—disease of the heart muscle-dilated cardiomyopathy,and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 3.hypertension. 4.pulmonary hypertension. 5.heart failure. 6.congenital heart disease-defects in the heart by birth. 7.diseases of the heart valves. 8.artificial heart valve replacement—persons who have undergone artificial heart valve replacement. 9.disorders of heart rhythm—abnormalities in heart rate and rhythm. 10.electric shock. 11.apart from heart disease ,the other causes of cardiac arrest are—diseases of the kidneys and brain. Facts about heart disease1.in children,particularly those less than 6 months,sudden nfant death syndrome is an important cause. 2.cardiac arrest can be due to genetic or familial causes also. 3.cardiac arrests are more common in males. 4.cardiac arrest can also be due to high blood pressure,diabetes, heart failure due to diseases of the heart muscle,or abnormalities in heart rate and rhythm. Why should someone have a cardiac arrest or what are the stages leading to cardiac arrest? Or in other words,Can we avert cardiac arrest?. Stage 1.Symptoms of heart diseaseInitially the person has symptoms of heart disease -Chest pain,breathlessness,palpitations, or undue fatigue. Stage 2.Changes in the working of the heart-after the onset of symptoms,there may be a change in the heart rate and rhythm. Changes in heart rate and rhythm. Drop in blood pressure—low b.p. Stage 3.Cardiac arrest—the adverse changes in heart rate and rhythm ,medically termed as ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation lead to cardiac arrest. The victim collapses,there is a circulatory arrest—the blood circulation stops and the person becomes unconscious. Stage 4.death-the electrical activity of the heart ceases and the heart stops functioning.the blood supply to the brain is reduced and within minutes results in death. If proper care and measures are taken during any of the stages mentioned above,it is possible to save the victim’s life. After knowing about the definition of cardiac arrest,causes of cardiac arrest-sudden cardiac death,facts regarding sudden death and stages leading to cardiac arrest, it is essential for us to know about CPR. CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION The life –saving measures followed to save a victim of cardiac arrest is called CPR. The series of steps followed to save a victim of cardiac arrest is called Chain of survival concept which was released by the American Heart Association in 2010. According to the Chain of survival concept,the following steps should be followed to save when someone collapses and has a cardiac arrest— 1.recognition of cardiac arrest and alerting the emergency medical response system. 2.to start CPR immediately.High- quality chest compressions should be done immediately. 3.Use of an AED to deliver shock. 4.once the ambulance arrives on scene,the victim has to be transferred to the hospital. 5.once the cardiac arrest vicim is shifted to the hospital,delivering post-cardiac arrest care. Now let us learn in detail about each of these steps in CPR. If someone collapses in front you, It is important first to recognize that cardiac arrest has occurred. If the collapsed person does not respond to your commands or if there is no breathing or if there is abnormal breathing ,you should come to an immediate conclusion that the person has a cardiac arrest. Then immediately alert the emergency medical response system in your area. 2.start CPR immediately. 3.while chest compressions are performed,once the AED is brought to the scene,AED has to be used to deliver shock. Important points to be remembered in delivering high quality chest compressions- 1.chest compressions have to be started within 10 seconds. 2.Push hard and push fast is the rule when performing chest compressions. 3.in conventional CPR,after performing 30 chest compressions,2 times mouth –to-mouth breathing has to be given.performing 30 chest compressions followed by 2 times mouth to mouth breathing becomes one cycle. 4.100 chest compressions have to be given in 1 minute. 5.deliver chest compressions in such a way that the chest goes 2 inches or 5 cms. Deep. 6.deliver chest compressions in such a way that the chest recoils back to its original position after each chest compression. 7.there should be no interruption during chest compressions. 8.5 cycles have to be completed in 2 minutes. How to perform effective chest compressions? 1.Kneel beside the victim and place the heel of one hand at thecentre of the lower end of the chest on an imaginary line across both the nipples. And lock this with the heel of the other hand. Deliver chest compressions without bending at the elbows and deliver the force perpendicular to the body. 2.effective chest compressions increase the pressure in the chest and activates the heart and thereby improve circulation. 3.effective chest compressions increase blood pressure by 60—80 mm. Hg. 4.effective chest compressions improve circulation to the brain and also heart. 5.If chest compressions are given,“shock” by an AED works better. 6.chest compressions have to be given faster and with force. 7.chest compressions have to be given 100 times in a minute and 5 cm. Or 2 inches deeper. 8.after each chest compression ,the chest has to recoil to its original position. 9.there should be no interruption in between chest compressions.if one gets tired,it has to be taken over by the other bystander on scene. While chest compressions are performed,once an AED-automatic defibrillator is brought to the scene,it has to be utilised to deliver shock. What is an AED? An automatic defibrillator is a computer like instrument. Once an AED is brought to the scene,the AED is turned “On” and the pads placed over the chest as per the ‘Voice prompts” given by the AED and if it prompts to deliver a “shock”,shock has to be delivered. Unlike a defibrillator-monitor available in hospitals,an AED does not have a monitor.It is a battery operated instrument which recognises the heart rate and rhythm and through Voice Prompts instructs the lay public about the need to deliver a shock if required. In foreign countries,such AEDs are installed in public places like railway stations,airports,bus stands,office buildings-both government and private,business establishments,meeting places,school and college buildings,court buildings,libraries,hotels,entertainment places and sports arenas and the staff in these areas are also trained in CPR and use of AEDs. As per the guidelines of American Heart Association prior to 2010,the sequential steps to be followed in saving a victim of cardiac arrest were-ABC-ie.A-Airway--To check the airway,B— Breathing .ie .to give mouth to mouth breaths, and C—Circulation—To improve circulation,giving chest compressions. In 2010,The American Heart Association,gave new guidelines of CPR and the sequence of doing CPR was changed from ABC to CAB—ie.C-To improve circulation,chest compressions have to be given first. The prime reasons for cardiac arrest are heart related causes-primarily changes in heart rate and rhythm,medically termed as ventricular tachycardia and Ventricular fibrillation.Hence,in a situation of cardiac arrest,chest compressions along with delivering shock by a AED will increase the chances of survival of the cardiac arrest victim. By trying to check the airway and providing mouth to mouth breaths,precious time will be lost and hence a lay rescuer should attempt to provide chest compressions first rather than trying to give mouth to mouth breaths. *In conventional CPR ,along with chest compressions mouth to mouth breathing also has to be given.In some instances ,respiratory arrest is a cause of cardiac arrest.eg. In infants,in situations of drowning,drug overdose,the vitim has difficulty in breathing or abnormal breathing leading to cardiac arrest and hence in such situations it is important to give mouth to mouth breaths first. The chances of saving a cardiac arrest victim are improved— 1.in the presence of bystanders. 2.when the bystander does CPR effectively. 3.when the victim is under the supervision of trained medical personnel. Bystander CPR or Hands only CPR—In a situation of cardiac arrest,the bystanders in that place should immediately recognise cardiac arrest,alert the emergency medical response system in the area,start CPR immediately ,perform chest compressions –in the centre of the chest-pushing the chest faster and with force.This has to be continued until the ambulance arrives on scene and taken over by paramedics .If the cardiac arrest victim responds and if he continues to take normal breathing ,then chest compressions can be stopped.This is called as Bystander CPR or Hands only CPR. It has been proved scientifically that the chance of saving a cardiac arrest victim is 49—75 % if CPR+defibrillation shock are given within 3---5 minutes of cardiac arrest. Each minute of delay in doing CPR reduces the chances of survival of a cardiac arrest victim by 7%-10 %. CPR should not be done in the following instances1.I f there is a specific legal order –DNAR order –Do not attempt to resuscitate order issued already. 2.if there are signs of death—rigor mortis,decapitated body or mutilated body. 3.Despite the best medical efforts ,if there is no hope of saving the victim if there is multiorgan failure and there are signs of brain death. *92 % of victim of cardiac arrest die before they reach the hospital..If CPR is done immediately,the chances of saving the cardiac arrest victim is improved 2—3 times. If CPR is done within 4—6 minutes after cardiac arrest,the chances of survival are high. Only 32 % of cardiac arrest victims are receiving CPR from bystanders. As it takes more than 7—8 minutes for emergency medical personnel to reach the scene of cardiac arrest,the chances of saving a cardiac arrest victim lie in the hands of a trained lay rescuer.Hence,by training lay persons in CPR and installing AEDs in public places,this important public health problem can be tackled effectively.