* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download fghjhj
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
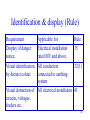
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
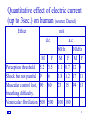
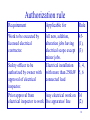
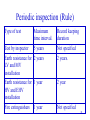
Indian regulations in Electrical Safety P.Lahiri BARC 1 Indian regulations. • Indian Electricity Act-1910. • Indian Electricity (Supply) Act- 1948. • Indian Electricity Regulatory Commission Act-1998. • The Electricity Act –2003. Repealed under section 185 of Electricity act -2003 • Indian Electricity Rules- 1956. 2 Objectives of regulations • Make generation, transmission, distribution and utilization of electricity as safe as possible. • Identification of different categories of agencies. • Remove ambiguities from existing qualitative guidelines and pronounce precise quantitative technical requirement with respect to safety. 3 Categories of agencies • • • • • Supplier of electricity. Consumer of electricity. Electrical inspector. Electrical contractor and supervisors. Authorized persons. 4 Hazards of electricity • Electric shock:- Current flows through body or part of body when two surfaces having electrical potential difference is touched resulting in burn, disability or even death. • Flashover:-Sudden collapse of electric field by having a conducting path between two electrical potential different surfaces resulting in burn, fire. • Blast:-Failure of dielectric medium between two electrical potential different surfaces resulting in projectile, mechanical force, fire or burn. • Heat:-Caused by loose connection in the circuit, overheating of insulation/ conductor due to overload or prolonged short circuit current etc. resulting in fire, burn. 5 Quantitative effect of electric current (up to 3sec.) on human (source Daziel) Effect mA d.c M F Perception threshold 5.2 3.5 Shock but not painful 9 6 Muscular control lost, 90 60 breathing difficulty. Ventricular fibrillation 500 500 a.c 60Hz M F 1.1 0.7 1.8 1.2 23 15 10kHz M F 12 8 17 11 94 63 100 100 6 Flash and flame burn Thermal burns, Current flows typically external, Damage to skin 7 Electric shock and flash burn 8 Occurrence of blast EXPLOSION 9 Classification of rated voltage as per IE rule Above 33kV Extra High Voltage (EHV) 33kV High Voltage (HV) 650V 250V Medium Voltage (MV) Low Voltage (LV) 10 Authorization • Authorization. • • • • • • • • • • Electrical isolation. Identification & display. Restriction of access. Inspection, testing etc. Preparedness for adversity. Other hazard precaution. Protection & interlocks. Clearances. Earthing. Reporting accidents. • Avoid chaos • Fixing up of responsibility • Ensures expertise 11 Authorization rule Requirement Applicable for Rule Work to be executed by licensed electrical contractor. All new, addition, alteration jobs having electrical scope except minor jobs. Electrical installation with more than 250kW connected load 45(1), (3) Safety officer to be authorized by owner with approval of electrical inspector. Prior approval from Any electrical work on electrical inspector to work live apparatus/ line 3, 4, 5, 6 36 (2) 12 Authorization cntd. Qualifications rule Agency Minimum qualification Rule Authorized O & M person for generating station of capacity above 100MW and sub-stations of 132kV and above. Second class diploma in mechanical or electrical engineering & training from CEA approved institute. ITI & training from CEA approved institute 3 (2A) Assistants to above 3 (2A) 13 Electrical isolation. • Authorization. • Electrical isolation. • • • • • • • • • Identification & display. Restriction of access. Inspection, testing etc. Preparedness for adversity. Other hazard precaution. Protection & interlocks. Clearances. Earthing. Reporting accidents. • Quick de-energization • Ensure de-energization while on work 14 Electrical isolation(Rule) Rating of service connection Isolation device CB SFU Rule LV, MV service connection upto 1000kVA at 11kV Above 1000kVA at 11kV 50(b) (i) (ii) upto 2500kVA at 33kV Above 2500kVA at 33kV * Any rating beyond 33kV 15 LV,MV 16 11k,33k or 17 >33k 18 Electrical isolation device for transformers (Rule) Rating of transformer Isolation device Pri: Sec: CB SFU CB SFU * * Upto 630kVA and primary side less than HV upto 630kVA and primary side HV and above. 630kVA to 1000kVA irrespective of primary voltage Above 1000kVA irrespective of primary voltage Rul e 50(b) (i) (ii) 19 Above 1000kVA 20 Primary HV 21 630kVA 22 Identification & display • Authorization. • Electrical isolation. • Electricity is invisible:- – – – • Restriction of access. – • Inspection, testing etc. • Preparedness for adversity. – • Identification & display. • • • • • Other hazard precaution. Protection & interlocks. Clearances. Earthing. Reporting accidents. Various current carrying portions Different circuits/ phases/ a.c/ d.c. etc. Different voltages LV,HV,MV etc Power flow directions. ON/OFF positions and direction of operation of SFUs/CBs/Isolators. – Source locations of PCCs/ MCCs and load locations of each feeders of MCCs – Danger notices. 23 Identification & display (Rule) Requirement Applicable for Rule Display of danger notice. Electrical installation rated MV and above. 35 Visual identification All conductors 32(1) by distinct colour. connected to earthing system Visual distinction of All electrical installation 41 circuits, voltages, feeders etc. 24 Restriction of access • Authorization. • Electrical isolation. • Identification & display. • Restriction of access. • Thwart accidental or unauthorized access:- • Inspection, testing etc. • Preparedness for adversity. • Other hazard precaution. • Protection & interlocks. • Clearances. • Earthing. • Reporting accidents. 25 Restriction of access (Rule) Requirement Applicable for Metallic covering All live conductors for which is electrically indoor installations. and mechanically continuous Metallic fencing of Out door sub-station. height not less than 1.8M. Rule 51(1) (a) 68(b) 26 Inspection testing & maintenance • • • • Authorization. Electrical isolation. Identification & display. Restriction of access. • Inspection, testing etc. • • • • • • Preparedness for adversity. Other hazard precaution. Protection & interlocks. Clearances. Earthing. Reporting accidents. • Ensure adequacy of safety related parameter: • Maintaining safety related parameter within limit. 27 Commissioning inspection (Rule) Type of Installation Any installation upto MV (not generating plant) Generating plant of capacity less than 10kW Type of test (Rule do not specify) interpreted. Visual inspection. Insulation resistance. High voltage. Earth resistance. Any functional requirement. Same as above Inspecting authority Supplier. Owner 28 Commissioning inspection (Rule) cntd. Type of Installation Generating plant of capacity more than 10kW HV or EHV installation Type of test (Rule do not specify) interpreted. Depending upon voltage level as desired by Electrical Inspector Inspecting authority Electrical Inspector. Visual inspection, insulation Electrical resistance, high voltage, Inspector. earth resistance, functional tests and test as desired by 29 Electrical Inspector. Periodic inspection (Rule) Type of test Maximum time interval. Record keeping duration Test by inspector 5 years Not specified Earth resistance for 2 years LV and MV installation 2 years. Earth resistance for 1 year HV and EHV installation 2 year Fire extinguishers Not specified 1 year 30 Preparedness. • • • • • Authorization. Electrical isolation. Identification & display. Restriction of access. Inspection, testing etc. • Preparedness for adversity. • • • • • • Mitigate the effect of fast acting electrical disaster • Ensure correct course of action Other hazard precaution. Protection & interlocks. Clearances. Earthing. Reporting accidents. 31 Preparedness (Rule) Essential Applicable for Rule First-aid box, Restoration chart, Fire buckets Two or more gas masks Every generating station, enclosed sub-station and enclosed switch station 43(2), 44(1), 43(1) 1.Generating station with capacity of 5MW and above 2.Enclosed sub-station with transformation capacity of 5 MVA and above 43(3) 32 Preparedness (Rule) cntd. Essential Applicable for Rule Artificial respirator Every manned high voltage or 44(4) extra-high voltage generating station, sub-station or switch station Trained All attended generating 44(3) personnel for station and sub-station. providing artificial respiration. 33 Possibility of success of artificial respiration source Edition Electric Institute resuscitation manual 34 Other hazard precaution. • • • • • • Authorization. Electrical isolation. Identification & display. Restriction of access. Inspection, testing etc. Preparedness for adversity. • Other hazard precaution. • • • • • Reduce potential initiating events of accident Protection & interlocks. Clearances. Earthing. Reporting accidents. 35 Other hazard precaution.(Rule) Situation Safety measure Rule Electrical installation in explosive atmosphere Multistoried building with height more than 15M. Explosion proof/ dust tight depending upon the hazardous zone as per IS5571 1. Power cable ducts shall not be used for other services 2. Power cable ducts shall have fire barrier at each floor crossing 51(d) 50A(4) 36 Other hazard precaution.(Rule) cntd.. Situation Safety measure Electrical 1.Baffle wall of 4hr fire rating installation with between single phase banks more than and on consumer premise. 2000litres of oil 2.Oil soak pit for full quantity of oil Electrical 1.Measures mentioned above. installation with 2.Fire extinguisher. more than 3.Oil draining arrangement. 9000litres of oil Rule 64(2) -(e) 64(2)(e) 37 Other hazard precaution.(Rule) cntd.. Situation Safety measure Substation 1.Entrance shall have 2hr fire rating and switch fire resistance door station in 2.A curb at entrance to trap oil flow. the 3.Direct access to transformer from basement outside 4.Transformer protection by automatic HVWSp/ CO2/ BCF/ BTM/ N2 injection and drain. Rule 64(2) (f)(ii) 38 Other hazard precaution.(Rule) cntd.. Location based on oil inventory Total oil quantity in litre (includes Location Rule Indoor Outdoor Indl: building Res:/ com: transformer and other apparatus) 1st Gr. Other bldg. Any Bs. Fl. floors floor of No oil. 2000 or less 2000 to 9000 9000 or more 64 (2) 39 Protection & interlocks. • • • • • • • Authorization. Electrical isolation. Identification & display. Restriction of access. Inspection, testing etc. Preparedness for adversity. Other hazard precaution. • Avoid human errors • Protection & interlocks. • Clearances. • Earthing. • Reporting accidents. 40 Transformer protection Rating Less than 630kVA and primary side less than HV Less than 630kVA and primary side more than HV 630kVA to 1000kVA Mandatory relay protection No relay based protection is mandatory Over current/ short circuit relay etc for secondary CB. Over current/ short circuit relay etc for secondary CB. Remark Not specified Not specified but implied by R50(b)(ii) Not specified but implied by R50(b)(ii) 41 Transformer protection cntd.. Rating Mandatory relay Remark protection 1000kVA to 10MVA 1. Bucholz R64(2) 2. Winding temp: 3. Oil temp: More than 10MVA 1. Bucholz R64(2) 2. Winding temp: 3. Oil temp: 4. Differential 42 HV & EHV installations interlocks Situation Preventive interlock Isolator and CB in series Isolator operation not allowed when CB is closed. Earthing switch and isolator Earthing switch can not be closed when isolator is closed Two or more incomer Only one feeder can be feeders to a bus bar but switched on at a time not intended for parallel operation Rule 64 (A) (1) 43 HV & EHV installations interlocks cntd.. Situation Two or more transformers in parallel Preventive interlock Rule Secondary CB trips if primary of that transformer trips. Doors or gates give Doors can not be 64 access to live parts opened when any part is (A) live. (1) Neutral switching device GCB can not be closed between neutral and when neutral breaker is earthing is used for open. 44 generator HV & EHV installations protection Protection against. Type of relay Over current. Over current/ short Any Equip., cable circuit relay. supply line etc. Rising touch potential. Earth leakage/ earth fault. Generator rated over 100kVA Internal fault. Differential relay Generator rated over 1MVA Bus bars rated over 200kV Switching over Lightning arrestor voltage/ lightning Mandatory for Overhead line terminations Rule 64A (2) 92(1) 45 Other protections Protection for. Human safety. Type of relay Mandatory for Rule ELCB/ RCCB/ etc. Any installation having connected load more than 5kW at MV or above DC three wire system 61A DC earthing. Over current relay between earthed middle conductor and earth. 61 (1) (d) (i) 46 Time/ Current for a.c 50Hz mSec 50H a.c current (rms mA) Zone 1- Usually no reaction, Zone 2 – Reaction may occur but usually no patho- psychological dangerous effect, Zone 3- No risk of fibrillation, Zone 4- Fibrillation possible (50% probability), Zone 5Unsafe or fibrillation 47 Clearances (physical spacing) • • • • • • • • Authorization. Electrical isolation. Identification & display. Restriction of access. Inspection, testing etc. Preparedness for adversity. Other hazard precaution. Protection & interlocks. • Clearances. • Minimum air insulation clearance. • Minimum space to work. • Minimum space for escape. • Earthing. • Reporting accidents. 48 Clearances for bare conductor other than overhead lines(Rule) Voltage Section clearance (outdoor) in m.m. Upto 11kV 2600 Ground Rule clearance (outdoor) in m.m 2750 33kV 2800 3700 66kV 3000 4000 220kV 4300 5500 400kV 6500 8000 64 49 Clearance above ground of overhead lines across/ along a street (Rule) Condition Across Along Any where else Every where System voltage Clearance in mm LV, MV 5800 HV 6100 LV, MV 5500 HV 5800 LV, MV, HV (upto11kV) 4600 HV(above 11kV) 5200 EHV 5200 + 300 for every 33kV but not less than 6100 Rule 77 50 Clearance of overhead lines from building(Rule) Condition Vertical (IE R 79) System voltage Minimum clearance in mm LV, MV 2500 HV 3700 EHV 3700 + 300 for every 33kV LV, MV 1200 HV upto 11kV 1200 Horizontal (IE R 80) HV above 11kV EHV 2000 2000 + 300 for every 33kV 51 Section clearance SC SC SECTION CLEARANCE 52 Ground clearance GC Height of tall man’s raised finger tip with raised hand2.5m GROUND LEVEL GROUND CLEARANCE 53 Earthing system. • • • • • • • • • Authorization. Electrical isolation. Identification & display. Restriction of access. Inspection, testing etc. Preparedness for adversity. Other hazard precaution. Protection & interlocks. Clearances. • Earthing. • Reporting accidents. • Limit touch potential • Limit step potential • Safe predefined passage for fault current • Facilitate detection of incipient fault • Reduce neutral shifting 54 Step & Touch potential Et F E/X CURVE Es E Earth Mat 1M 0.5M X Earthing (Rule) Requirement Applicable for Rule Earthing terminal by Supplier. LV consumer 33 Separate earthing terminal by supplier and consumer. Minimum two independent and redundant path with two earth electrode. All metallic part not intended to serve as conductor shall be earthed. Grounding of neutral. MV and above 33 Earthing network for equipment, system. R61(2), R61(3), R51(1)(b), All electrical R67(1) apparatus a.c electrical power supply system more than 125V 61(1)(a), 64(3) 56 Reporting of accidents • • • • • • • • • • Authorization. Electrical isolation. Identification & display. Restriction of access. Inspection, testing etc. Preparedness for adversity. Other hazard precaution. Protection & interlocks. Clearances. Earthing. • Reporting for analysis. • Fast reporting prevents suppression of facts. • Reporting accidents. 57 Reporting of accidents (Rule) Type of accident Fatal involving loss or injury Failure of transformer or reactor above 20MVA Report format Maximum Rule period for reporting Telegraphic 24hours 44A and Written 48hours Written 48hours 65(8) 58 Conclusion • Regulations can induce more concern. • Regulations can not rule out accidents by themselves • Every concerned individuals should handle electricity in safe manner • Do not try to find out loopholes of regulation to limit our responsibility. • Try to adopt a proactive approach by understanding the intentions of the regulation authors. • In case of doubt ask electrical inspector or Central Electricity Authority. 59 60 Clearance across the road 61 Clearance along the road 62 Clearance anywhere else 63 Clearance from building Vertical clearance Horizontal clearance 64 Fire barrier in cable duct Fl-4 Cables Fl-2 Fire barrier Fl-1 Electrical service shaft 65 Ground clearance for bare conductor other than overhead lines(Rule) Voltage Clearance in mm Outdoor Upto 11kV 33kV 2750 66kV 4000 220kV 5500 400kV 8000 Height of tall man’s raised finger tip with raised hand2.5m 3700 66 Phase to Phase(Rule) Voltage Clearance in mm Outdoor Ph~Ph Ph~E Sec: Ground 11kV 33kV 66kV 220kV 400kV 460 915 1220 3350 4000 67 Phase to earth(Rule) Voltage 11kV 33kV 66kV 220kV 400kV Clearance in mm Outdoor 305 610 750 1675 3500 68 Clearances It denotes the minimum distance in air between two potentially different points (this includes earthed/ ground surfaces) to avoid flashover during normal and transient over voltage. Phase to earth Phase to earth Minimum distance between live conducting parts and neighboring earthed parts. 69 Clearances It denotes the minimum distance in air between two potentially different points (this includes earthed/ ground surfaces) to avoid flashover during normal and transient over voltage. Phase to earth Phase to phase Phase to Phase Minimum distance between live parts of different phases. 70 Clearances It denotes the minimum distance in air between two potentially different points (this includes earthed/ ground surfaces) to avoid flashover during normal and transient over voltage. Phase to earth Phase to Phase Isolating clearance Isolating clearance Minimum distance between two sides of an open isolator 71 Clearances It denotes the minimum distance in air between two potentially different points (this includes earthed/ ground surfaces) to avoid flashover during normal and transient over voltage. Section clearance Minimum distance Phase to Phase between maintenance zone Isolating clearance and nearest live part plus Section clearance one stretched arm length of a person Phase to earth 72 Clearances It denotes the minimum distance in air between two potentially different points (this includes earthed/ ground surfaces) to avoid flashover during normal and transient over voltage. Phase to earth Phase to Phase Isolating clearance Section clearance Ground clearance Minimum distance between lowest point of support insulator and ground Ground clearance 73 Phase to earth & phase to phase clearance TOWER GANTRY PH-TO PH PHASE TO EARTH CLEARANCES IN OUTDOOR STRUCTURE P-E rule P-P rule 74 Isolating clearance Isolating clearance 75 76 Safety provisions in IE Rules • Authorization. • Electrical isolation. • Identification & display. • Restriction of access. • Inspection, testing etc. • Preparedness for adversity. • Other hazard precaution. • Protection & interlocks. • Clearances. • Earthing. • Reporting accidents. 77 78