* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human (mammalian) Body Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
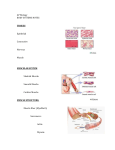
Human (mammalian) Body Systems Remember that all of your body systems are integrated and regulated by the neuroendocrine system (the coordination of the nervous and endocrine (hormones) systems. As time is limited, focus on the figures indicated. Digestive System 2.10, 2.11 Figures 2.24, 2.25 * components (primary organs, accessory organs/glands) * absorptive structures of the intestines (capillary interface) ... villi * peristalsis, sphincters Endocrine system - since hormones are the signal molecules and they control pretty much everything, they are interspersed throughout the text. A table of the major endocrine glands and their function can be found at my website. I made it just for you. * definition of hormone ** types of hormones (chemical classes) * the connection to the brain/nervous system ... the hypothalamus * homeostasis ... ooh, this is big! ** major glands and their functions/major hormones Integumentary system p 548 * structure of skin ... layers * features ... nerves, sweat glands, hair follicles, pigments Lymphatic system 23.4, p 206 * major functions * structure * lymph nodes ... where are they concentrated? .... how do they work? * interface with circulatory system * role in immunity * role in the spread of cancer Immune system chapter 23 * non-specific immunity * inflammatory response * WBC’s (leucocytes) * phagocytes ... phagocytosis ... macrophages * antigens and antibodies * specific immunity, immune response * B cells * T cells ... helper T’s, killer T’s, suppressor T’s * Memory cells * Blood cell markers (antigens) * role of immune system in allergic reactions * Auto immune diseases ... rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, type 1 diabetes * How does HIV attack the immune system? Circulatory System (cardiovascular) 7.5 – 7.10 ** three main functions (transport, thermoregulation, immunity) ** components of blood and their functions (RBC’s, WBC’c, platelets, plasma) * vessel types ... veins, arteries, capillaries * blood types ... inheritance; antigen/antibodies; transfusion compatibility ** blood flow ... through the heart/lungs; major veins and arteries * hemoglobin ... anemia ... iron * cardiovascular disease * blood pressure Respiratory System 3.6 ** components (airways; pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveoli) * inhalation/exhalation ... muscles involved (diaphragm, rib muscles) * gas exchange ... alveoli / capillary interface * respiratory conditions/diseases ... asthma, emphysema, lung cancer Urinary (Excretory) System 3.7, 3.8 * role of the kidneys in homeostasis * components (kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra) * three major functions * kidney structure and functions ... capillary interface * process of urine production * nephrons Nervous System chapter 21 through 21.9 * neurons ... the nerve cell ... read all about it * synapse ... neurotransmitters * Central nervous system ... brain and spinal chord * Peripheral nervous system ... sensory, motor, autonomic ... sympathetic * Brain (CPU) .... brain stem, hypothalamus, cerebellum, cerebrum * Sensory receptors Chapter 35-4 * Nerve transmission ... action potentials, resting potentials, Na+/K+ pump Reproductive System 12.6 – 12.9 * male and female anatomy * ovarian and menstrual cycles * fertilization ... implantation * role of hormones * development of embryo and fetus Skeletal System - use Kimball’s biology pages website * structure of bone ... osteocytes * function of bone (support, joint types, marrow, etc...) * major bones of the human body - look online, but you probably know them already Muscular System - use Kimbal as needed * three types of muscle (skeletal, cardiac, smooth) * how skeletal muscle contracts (sarcomeres, role of Ca++, nerve/muscle connection) p 197 * paired muscle concept