* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acoustic Neuroma
Survey
Document related concepts
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
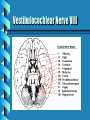
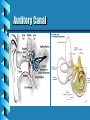
Cranial Nerve Lesion Acoustic Neuroma Presented By: Emma Morales Gigi Sanchez Christine Achenbach Josefina Delgado Introduction of Cranial Nerve Eight: Vestibulocochlear Nerve Arises in the inner ear and goes to the pons Two anatomically and functional parts: Cochlear Nerve Vestibular Nerve Cranial Nerve XIII functions in hearing and balance Vestibulocochlear Nerve VIII Clinical Case of Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Shwannoma) Robin • European-American woman • 51 years old • Professional Executive • Maintained reasonable diet • Overall in perfectly good health Robin’s Symptoms • Symptoms started 2 years ago –telephone communication distorted -right ear –tinnitus-right ear –dizzy spells at work –bumping into things everywhere Robin’s visit to General Physician • First General Physician • diagnosed her with inner ear imbalance from her last plane trip • Antivert medication was prescribed • no change in symptoms • Second Physician • MRI scan • found small 0.9cm Acoustic Neuroma Background: What is Acoustic Neuroma? Non-cancerous tumor of the eighth cranial Nerve leading from brain to inner ear Usually grow slowly over a period of years Not Hereditary: Occur spontaneously without any evidence of inheritable patterns Common Symptoms Major symptom: Hearing Loss 95% of those with tumor Tinnitus Vertigo Headaches Unsteadiness-poor coordination Facial numbness, tingling, twitching Signs of Acoustic Neuroma Decreased speech discrimination Nystagmus Abnormal facial electromyogram Statistical Information Found in autopsy in less than one in one-hundred of the general population Hearing loss and symptoms occur in about one person in 100, 000 Diagnosed in patients between the ages of 30-60 Cause unknown Clinical Findings: Test ENG (Electronystagmography test) Caloric Test MRI scan MRI Classification for AN Entirely Intracanicular Intercranial extension without brainstem distortion Intracranial extension with brainstem distortion Diagnosis: Findings on Clinical Case Detected small .9cm Acoustic Neuroma affected hearing loss and balance Treatment Options Observation Surgery- Microsurgical tumor removal • Partial tumor removal • Total tumor removal Radiation • Gamma Knife • FSR Clinical Case Plan Patient Robin decided on RADIATION FSR treatment • 5 treatments a week • for 5 weeks Robin’s Follow-up • 1 year - improved hearing • 2 years – tumor reduced and 92% hearing back • no significant side effects Neurobiology of Acoustic Neuroma: Structures Involved Eighth Cranial nerve • Vestibular & Cochlear Divisions Auditory Canal Internal Auditory Canal Growth patterns Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3